Abstract
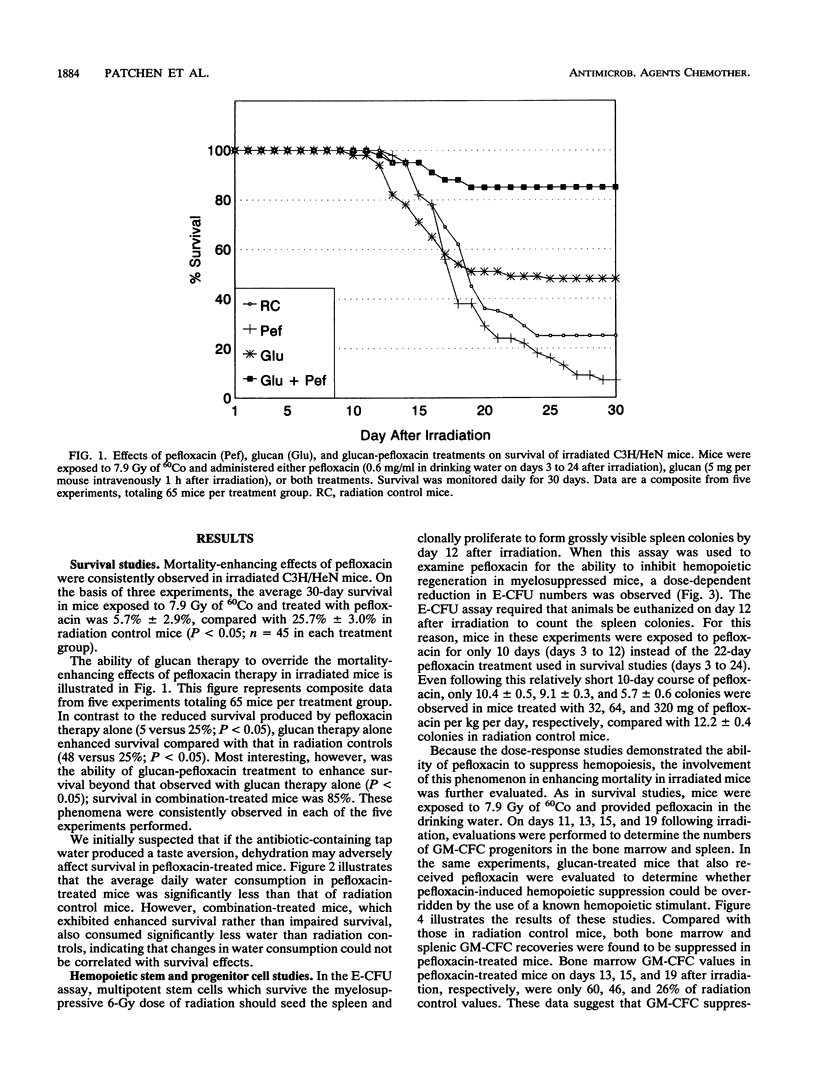
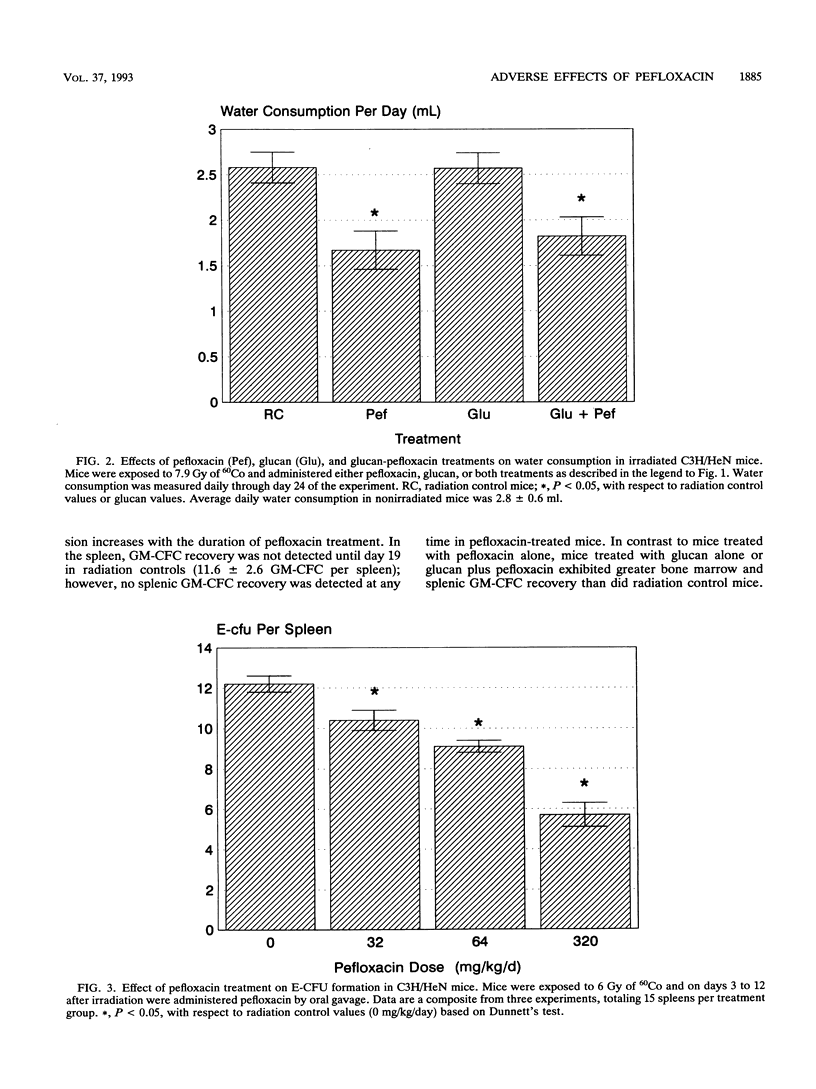
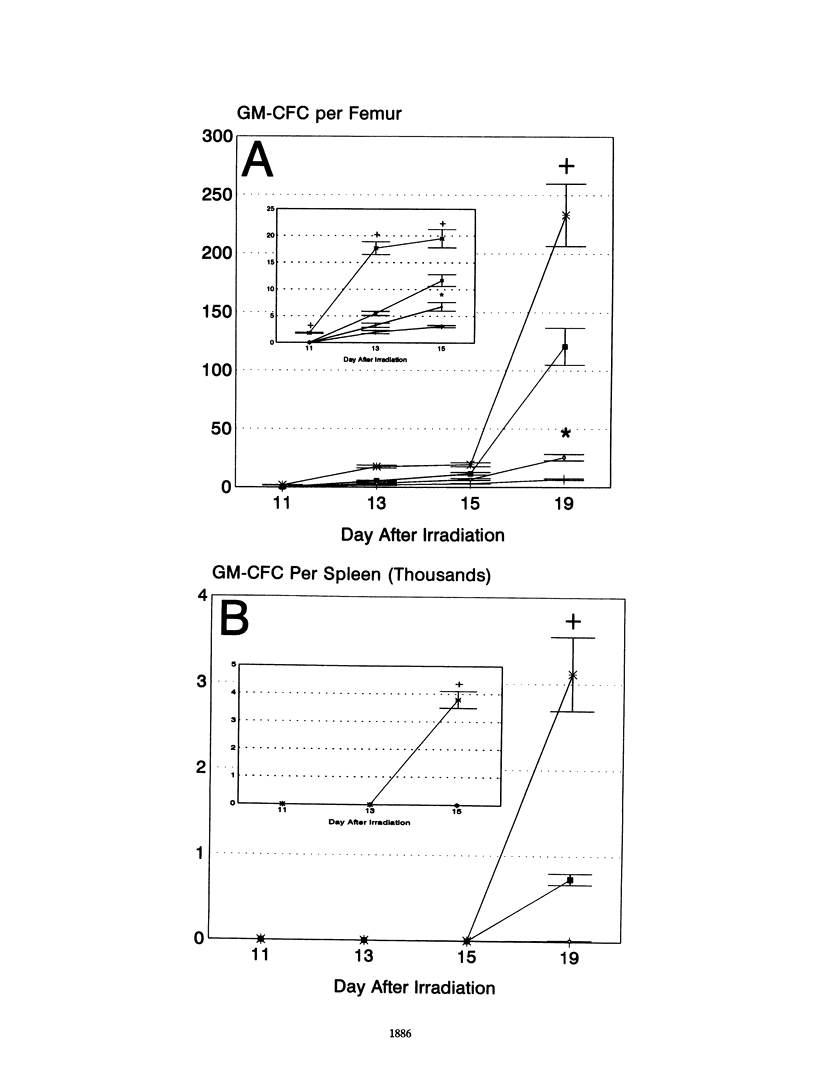
Opportunistic bacterial infections are the predominant cause of death following myelosuppressive radiation exposure. When used alone, a variety of immunomodulators and antibiotics have been reported to reduce radiation-induced death. In these studies, the combined therapeutic effects of the immunomodulator glucan and the quinolone antibiotic pefloxacin were evaluated for survival-enhancing effects in myelosuppressed C3H/HeN mice. Mice were exposed to 7.9 Gy of whole-body 60Co radiation and treated with saline, glucan (250 mg/kg of body weight intravenously, 1 h after irradiation), pefloxacin (64 mg/kg/day orally, days 3 to 24 after irradiation), or glucan plus pefloxacin. Survival 30 days after irradiation in mice receiving these respective treatments was 25, 48, 7, and 85%. Evaluation of granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cell (GM-CFC) recovery in mice receiving these treatments revealed that, compared with recovery in saline-treated mice, glucan stimulated GM-CFC recovery, pefloxacin suppressed GM-CFC recovery, and glucan administered in combination with pefloxacin could override pefloxacin's hemopoietic suppressive effect.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A protocol for the determination of absorbed dose from high-energy photon and electron beams. Med Phys. 1983 Nov-Dec;10(6):741–771. doi: 10.1118/1.595446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B. Influence of irradiation on resistance to infection. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Mar;24(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/br.24.1.35-40.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I., Elliott T. B., Ledney G. D. Quinolone therapy of Klebsiella pneumoniae sepsis following irradiation: comparison of pefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and ofloxacin. Radiat Res. 1990 May;122(2):215–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I., Elliott T. B. Quinolone therapy in the prevention of mortality after irradiation. Radiat Res. 1991 Oct;128(1):100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luzio N. R., Williams D. L., McNamee R. B., Edwards B. F., Kitahama A. Comparative tumor-inhibitory and anti-bacterial activity of soluble and particulate glucan. Int J Cancer. 1979 Dec 15;24(6):773–779. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P. Uptake of ciprofloxacin by macrophages. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Apr;38(4):442–444. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.4.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni M., Tamburrini E., Pallavicini F., Antinori A., Nervo P. Influence of ofloxacin and pefloxacin on human lymphocyte immunoglobulin secretion and on polymorphonuclear leucocyte superoxide anion production. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Aug;22(2):193–196. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Bredberg A., Riesbeck K. New quinolones: in vitro effects as a potential source of clinical toxicity. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11 (Suppl 5):S1382–S1389. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_5.s1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Schlossman S. F., Tedder T. F. 4-Quinolone drugs affect cell cycle progression and function of human lymphocytes in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):768–773. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez J. P., Henwood J. M. Pefloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1989 May;37(5):628–668. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198937050-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootz T. D., Barrett J. F., Sutcliffe J. A. Inhibitory effects of quinolone antibacterial agents on eucaryotic topoisomerases and related test systems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):8–12. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkin H. Adverse effects of the fluoroquinolones. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10 (Suppl 1):S258–S261. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_1.s258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathorn J. W., Rubin M., Pizzo P. A. Empirical antibiotic therapy in the febrile neutropenic cancer patient: clinical efficacy and impact of monotherapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):971–977. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussy P., Maass G., Tümmler B., Grosse F., Schomburg U. Effect of 4-quinolones and novobiocin on calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha primase complex, topoisomerases I and II, and growth of mammalian lymphoblasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Phillips I. The comparative in-vitro activity of pefloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):1–10. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijne E. I., van der Winden-van Groenewegen R. J., Ploemacher R. E., Vos O., David J. A., Huiskamp R. The effects of x-irradiation on hematopoietic stem cell compartments in the mouse. Exp Hematol. 1991 Aug;19(7):617–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montay G., Goueffon Y., Roquet F. Absorption, distribution, metabolic fate, and elimination of pefloxacin mesylate in mice, rats, dogs, monkeys, and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):463–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., D'Alesandro M. M., Brook I., Blakely W. F., MacVittie T. J. Glucan: mechanisms involved in its "radioprotective" effect. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Aug;42(2):95–105. doi: 10.1002/jlb.42.2.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., D'Alesandro M. M., Chirigos M. A., Weiss J. F. Radioprotection by biological response modifiers alone and in combination with WR-2721. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;39(1-3):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., Fischer R., MacVittie T. J. Effects of combined administration of interleukin-6 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on recovery from radiation-induced hemopoietic aplasia. Exp Hematol. 1993 Feb;21(2):338–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., Lotzová E. The role of macrophages and T-lymphocytes in glucan-mediated alteration of murine hemopoiesis. Biomedicine. 1981 Sep;34(2):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., MacVittie T. J. Hemopoietic effects of intravenous soluble glucan administration. J Immunopharmacol. 1986;8(3):407–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., MacVittie T. J., Jackson W. E. Postirradiation glucan administration enhances the radioprotective effects of WR-2721. Radiat Res. 1989 Jan;117(1):59–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., MacVittie T. J., Solberg B. D., D'Alesandro M. M., Brook I. Radioprotection by polysaccharides alone and in combination with aminothiols. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(2-3):233–248. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90113-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., MacVittie T. J. Stimulated hemopoiesis and enhanced survival following glucan treatment in sublethally and lethally irradiated mice. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(6):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., MacVittie T. J., Wathen L. M. Effects of pre- and post-irradiation glucan treatment on pluripotent stem cells, granulocyte, macrophage and erythroid progenitor cells, and hemopoietic stromal cells. Experientia. 1984 Nov 15;40(11):1240–1244. doi: 10.1007/BF01946654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchen M. L., MacVittie T. J., Williams J. L., Schwartz G. N., Souza L. M. Administration of interleukin-6 stimulates multilineage hematopoiesis and accelerates recovery from radiation-induced hematopoietic depression. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):472–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Fay M., Etienne D., Forest N., Pocidalo J. J. Comparative effects of quinolones on human mononuclear leucocyte functions. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jun;19(6):781–790. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Dixon F. J. The functional capacity of x-irradiated macrophages. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1624–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TILL J. E., McCULLOCH E. A. Early repair processes in marrow cells irradiated and proliferating in vivo. Radiat Res. 1963 Jan;18:96–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


