Abstract
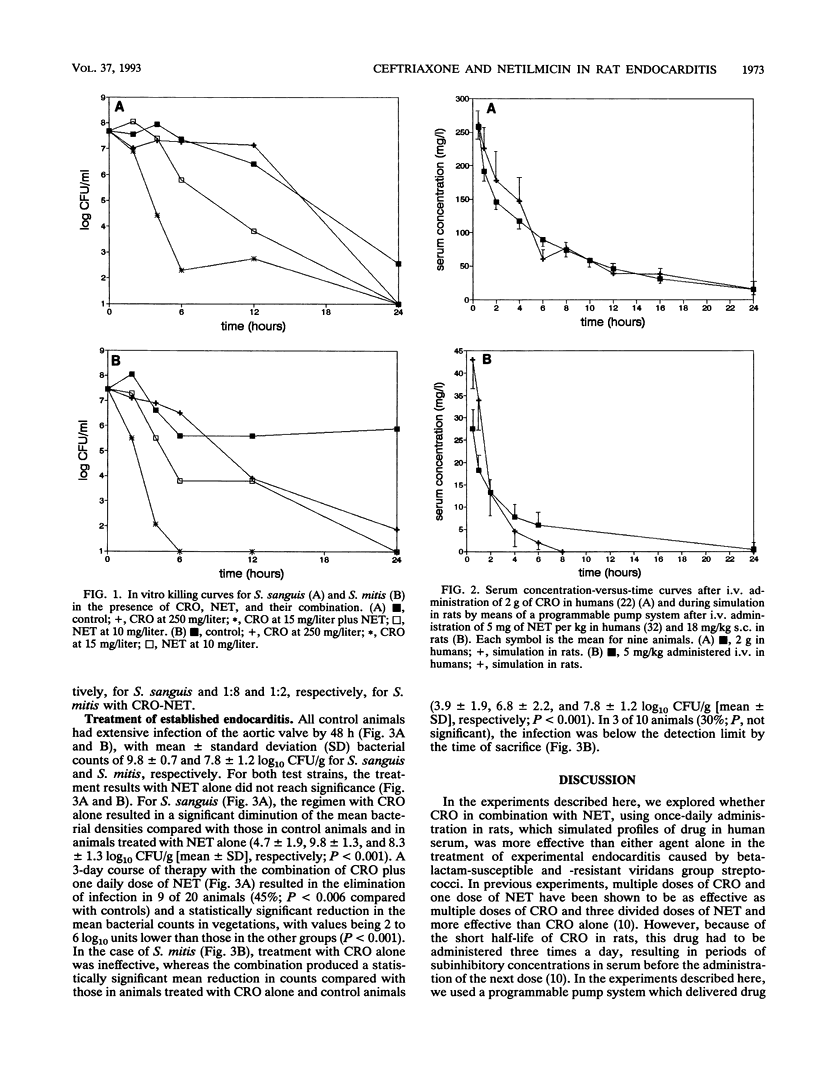
We performed experiments in rats aimed at determining whether a combination of ceftriaxone (CRO) and netilmicin (NET), by using once-daily administration in rats, which simulated profiles of drug in human serum, was more effective than either agent alone in the treatment of endocarditis caused by viridans group streptococci. A programmable infusion pump system enabled the production of profiles of CRO in serum that simulate those found in humans after the intravenous administration of 2 g. The subcutaneous administration of 18 mg of NET per kg of body weight produced levels in the sera of rats comparable to those after the intravenous administration of a dose of 5 mg of NET per kg in humans. Rats with catheter-induced aortic vegetations were infected intravenously with two test strains, a CRO-susceptible Streptococcus sanguis strain (MICs of CRO and NET, 0.064 and 8 mg/liter, respectively) and a relatively CRO-resistant Streptococcus mitis strain (MICs of CRO and NET, 2 and 8 mg/liter, respectively). Against both strains, the combination of CRO and NET was synergistic in vitro as determined by time-kill curves. Treatment of rats was started 48 h postinfection and lasted for 3 days. CRO alone was effective against the susceptible strain (P < 0.001 compared with control animals) but was not effective against the resistant organism. A significantly enhanced antibacterial activity of the CRO-NET combination in reducing the valvular bacterial counts was observed with both test strains (P < 0.001). The synergistic effect was obtained with a single daily injection of NET which provided detectable levels in serum for only 8 h, suggesting that in vivo synergism in the treatment of infections caused by viridans group streptococci can be obtained without 24 h of aminoglycoside coverage. These experimental data might provide a rationale for clinical trials of a once-a-day dosing regimen in the treatment of streptococcal but nonenterococcal endocarditis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Gilbert D. N., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. The influence of dosage regimen on experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: dissociation of peak serum levels from renal failure. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L., Dismukes W. E., Durack D. T., Kaplan E. L., Karchmer A. W., Kaye D., Rahimtoola S. H., Sande M. A., Sanford J. P., Watanakunakorn C. Antimicrobial treatment of infective endocarditis due to viridans streptococci, enterococci, and staphylococci. JAMA. 1989 Mar 10;261(10):1471–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bross J. E., Gordon G. Nocardial meningitis: case reports and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):160–165. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.5.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Maziere B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Azancot A., Raffoul H., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Evaluation of antibiotic diffusion into cardiac vegetations by quantitative autoradiography. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):938–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémieux A. C., Mazière B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Ceftriaxone diffusion into cardiac fibrin vegetation. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation by autoradiography. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1991;5(1):53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1991.tb00701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantin B., Carbon C. Importance of the aminoglycoside dosing regimen in the penicillin-netilmicin combination for treatment of Enterococcus faecalis-induced experimental endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2387–2391. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantin B., Pangon B., Potel G., Vallois J. M., Caron F., Bure A., Carbon C. Ceftriaxone-netilmicin combination in single-daily-dose treatment of experimental Escherichia coli endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):767–770. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francioli P. B., Glauser M. P. Synergistic activity of ceftriaxone combined with netilmicin administered once daily for treatment of experimental streptococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Feb;37(2):207–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francioli P., Etienne J., Hoigné R., Thys J. P., Gerber A. Treatment of streptococcal endocarditis with a single daily dose of ceftriaxone sodium for 4 weeks. Efficacy and outpatient treatment feasibility. JAMA. 1992 Jan 8;267(2):264–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N. Once-daily aminoglycoside therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):399–405. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessen M. T., Pitsakis P. G., Levison M. E. Postantibiotic effect of penicillin plus gentamicin versus Enterococcus faecalis in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):608–611. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Héraïef E., Glauser M. P., Freedman L. R. Natural history of aortic valve endocarditis in rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.127-131.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly V., Pangon B., Vallois J. M., Abel L., Brion N., Bure A., Chau N. P., Contrepois A., Carbon C. Value of antibiotic levels in serum and cardiac vegetations for predicting antibacterial effect of ceftriaxone in experimental Escherichia coli endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1632–1639. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapusnik J. E., Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Carpenter T., Sande M. A. Single, large, daily dosing versus intermittent dosing of tobramycin for treating experimental pseudomonas pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):7–12. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniowski O. M., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr, Sande M. A. Penicillin-netilmicin synergism against Streptococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):430–434. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., el-Sokkary M. A., Feinstein S. A., Lowy F. D. Penicillin-induced effects on streptomycin uptake and early bactericidal activity differ in viridans group and enterococcal streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):763–768. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic syngerism against enterococci. II. Effect of various antibiotics on the uptake of 14 C-labeled streptomycin by enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2580–2584. doi: 10.1172/JCI106758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel I. H., Chen S., Parsonnet M., Hackman M. R., Brooks M. A., Konikoff J., Kaplan S. A. Pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):634–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. H., Thompson W. L., Luthe M. A., Stern R. C., Grossniklaus D. A., Bloxham D. D., Groden D. L., Jacobs M. R., DiScenna A. O., Cash H. A. Once-daily vs. continuous aminoglycoside dosing: efficacy and toxicity in animal and clinical studies of gentamicin, netilmicin, and tobramycin. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):918–932. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saleh-Mghir A., Cremieux A. C., Vallois J. M., Muffat-Joly M., Devine C., Carbon C. Optimal aminoglycoside dosing regimen for penicillin-tobramycin synergism in experimental Streptococcus adjacens endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2403–2407. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Irvin R. G. Penicillin-aminoglycoside synergy in experimental Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):572–576. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Synergy of penicillin-netilmicin combinations against enterococci including strains highly resistant to streptomycin or kanamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):195–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauvin C., Eliopoulos G. M., Willey S., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Continuous-infusion ampicillin therapy of enterococcal endocarditis in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):139–143. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verpooten G. A., Giuliano R. A., Verbist L., Eestermans G., De Broe M. E. Once-daily dosing decreases renal accumulation of gentamicin and netilmicin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Jan;45(1):22–27. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Turnidge J., Leggett J., Craig W. A. In vivo postantibiotic effect in a thigh infection in neutropenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):287–298. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. A., Norton D. R., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Porter G. A., Houghton D. C., Brummett R. E., Bennett W. M., Gilbert D. N. The influence of tobramycin dosage regimens on nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and antibacterial efficacy in a rat model of subcutaneous abscess. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):13–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak E. W., de Vries P. J., Bouter K. P., van der Vegt S. G., Dorrestein G. C., Nortier J. W., van Dijk A., Verkooyen R. P., Verbrugh H. A. Once-daily dosing regimen for aminoglycoside plus beta-lactam combination therapy of serious bacterial infections: comparative trial with netilmicin plus ceftriaxone. Am J Med. 1990 Jul;89(1):58–66. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90099-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]