Abstract
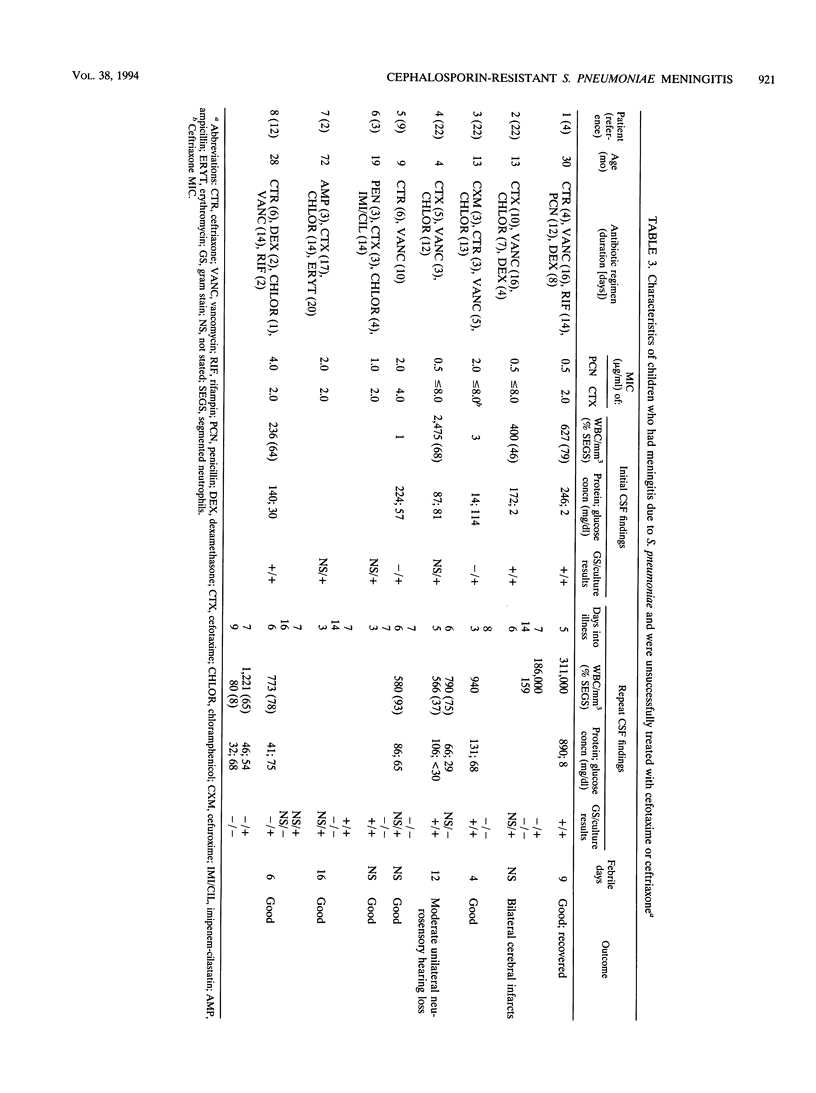
Children with meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates that are relatively or fully resistant to penicillin and have decreased susceptibility to broad-spectrum cephalosporins (MIC, > or = 2.0 micrograms/ml) who have failed treatment with broad-spectrum cephalosporins have been reported. The National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards has newly revised guidelines indicating that S. pneumoniae isolates associated with meningitis for which the MICs are > or = 0.5 micrograms/ml should be considered resistant to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. This recommendation is not clearly based on data related to clinical outcome and may be too conservative. We present data on five children who had S. pneumoniae meningitis due to isolates that were relatively or fully resistant to penicillin (MIC range, 0.125 to 4.0 micrograms/ml) and had cefotaxime or ceftriaxone MICs of 0.50 to 2.0 micrograms/ml. Their clinical courses and outcomes were comparable to those of five children with S. pneumoniae meningitis due to strains that were relatively or fully resistant to penicillin and were inhibited by cefotaxime at concentrations of < or = 0.25 micrograms/ml, as well as to those of 25 patients with S. pneumoniae meningitis due to penicillin-susceptible isolates identified during the same period. Children with meningitis due to S. pneumoniae with cefotaxime or ceftriaxone MICs of < or = 1.0 micrograms/ml may be adequately treated with these antibiotics. Further clinical data are required before solid recommendations can be made regarding cephalosporin breakpoints for S. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahronheim G. A., Reich B., Marks M. I. Penicillin-insensitive pneumococci. Case report and review. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Feb;133(2):187–191. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130020079017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asensi F., Pérez-Tamarit D., Otero M. C., Gallego M., Llanes S., Abadia C., Cantó E. Imipenem-cilastatin therapy in a child with meningitis caused by a multiply resistant pneumococcus. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Dec;8(12):895–895. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198912000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J. S., Connor J. D. Ceftriaxone failure in meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Nov;10(11):871–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cates K. L., Gerrard J. M., Giebink G. S., Lund M. E., Bleeker E. Z., Lau S., O'Leary M. C., Krivit W., Quie P. G. A penicillin-resistant pneumococcus. J Pediatr. 1978 Oct;93(4):624–626. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80901-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H. Meningitis caused by nontypable Haemophilus influenzae in a four-month-old infant. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Mar;10(3):254–255. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199103000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland I. R., Paris M., Ehrett S., Hickey S., Olsen K., McCracken G. H., Jr Evaluation of antimicrobial regimens for treatment of experimental penicillin- and cephalosporin-resistant pneumococcal meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Aug;37(8):1630–1636. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.8.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland I. R., Shelton S., McCracken G. H., Jr Screening for cephalosporin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae with the Kirby-Bauer disk susceptibility test. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1619–1621. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1619-1621.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland I. R., Shelton S., Paris M., Rinderknecht S., Ehrett S., Krisher K., McCracken G. H., Jr Dilemmas in diagnosis and management of cephalosporin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993 Mar;12(3):196–200. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199303000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner J. C., Michaels R. H. Meningitis from a pneumococcus moderately resistant to penicillin. JAMA. 1979 Apr 20;241(16):1707–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. A., Shelton S., Nelson J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Relatively penicillin-resistant pneumococcal infections in pediatric patients. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):129–132. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198403000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman M. D., Weinberg G. A., Reynolds J. K., Allen S. D. Meningitis with beta-lactam-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: the need for early repeat lumbar puncture. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993 Sep;12(9):782–784. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199309000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P., Koornhof H. J. Drug resistance patterns and serogroups or serotypes of pneumococcal isolates from cerebrospinal fluid or blood, 1979-1986. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):956–964. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J. R., Joncas J. H. Meningitis in a Canadian infant due to pneumococcus resistant to penicillin and chloramphenicol. J Pediatr. 1983 Oct;103(4):580–582. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D., Kaplan S. L., Overturf G. D., Rodriguez W. J., Steele R. W. Consensus report: antimicrobial therapy for bacterial meningitis in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Jun;6(6):501–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sakata Y. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae strains with different susceptibilities to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):141–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naraqi S., Kirkpatrick G. P., Kabins S. Relapsing pneumococcal meningitis: isolation of an organism with decreased susceptibility to penicillin G. J Pediatr. 1974 Nov;85(5):671–673. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paredes A., Taber L. H., Yow M. D., Clark D., Nathan W. Prolonged pneumococcal meningitis due to an organism with increased resistance to penicillin. Pediatrics. 1976 Sep;58(3):378–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radetsky M. S., Istre G. R., Johansen T. L., Parmelee S. W., Lauer B. A., Wiesenthal A. M., Glode M. P. Multiply resistant pneumococcus causing meningitis: its epidemiology within a day-care centre. Lancet. 1981 Oct 10;2(8250):771–773. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloas M. M., Barrett F. F., Chesney P. J., English B. K., Hill B. C., Tenover F. C., Leggiadro R. J. Cephalosporin treatment failure in penicillin- and cephalosporin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992 Aug;11(8):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. Q., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L. Systemic infections due to Streptococcus pneumoniae relatively resistant to penicillin in a children's hospital: clinical management and outcome. Pediatrics. 1992 Dec;90(6):928–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Swenson J. M., McDougal L. K. Screening for extended-spectrum cephalosporin resistance in pneumococci. Lancet. 1992 Dec 5;340(8832):1420–1420. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92617-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Doroshow C. A., Hackbarth C. J., Rusnak M. G., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Antibacterial activity of beta-lactam antibiotics in experimental meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):568–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viladrich P. F., Gudiol F., Liñares J., Pallarés R., Sabaté I., Rufí G., Ariza J. Evaluation of vancomycin for therapy of adult pneumococcal meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2467–2472. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten R. D., Markiewicz Z., Gilbert D. N. Meningitis due to penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in adults. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):118–124. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


