Abstract
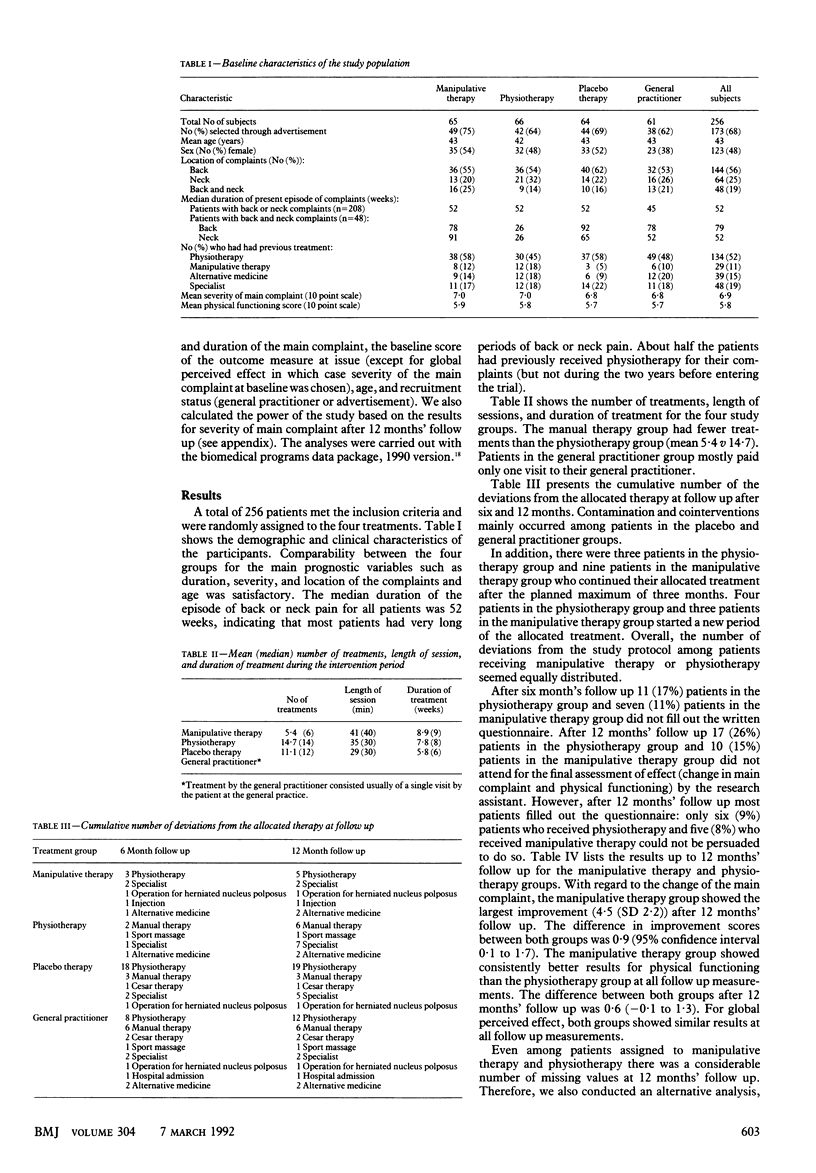
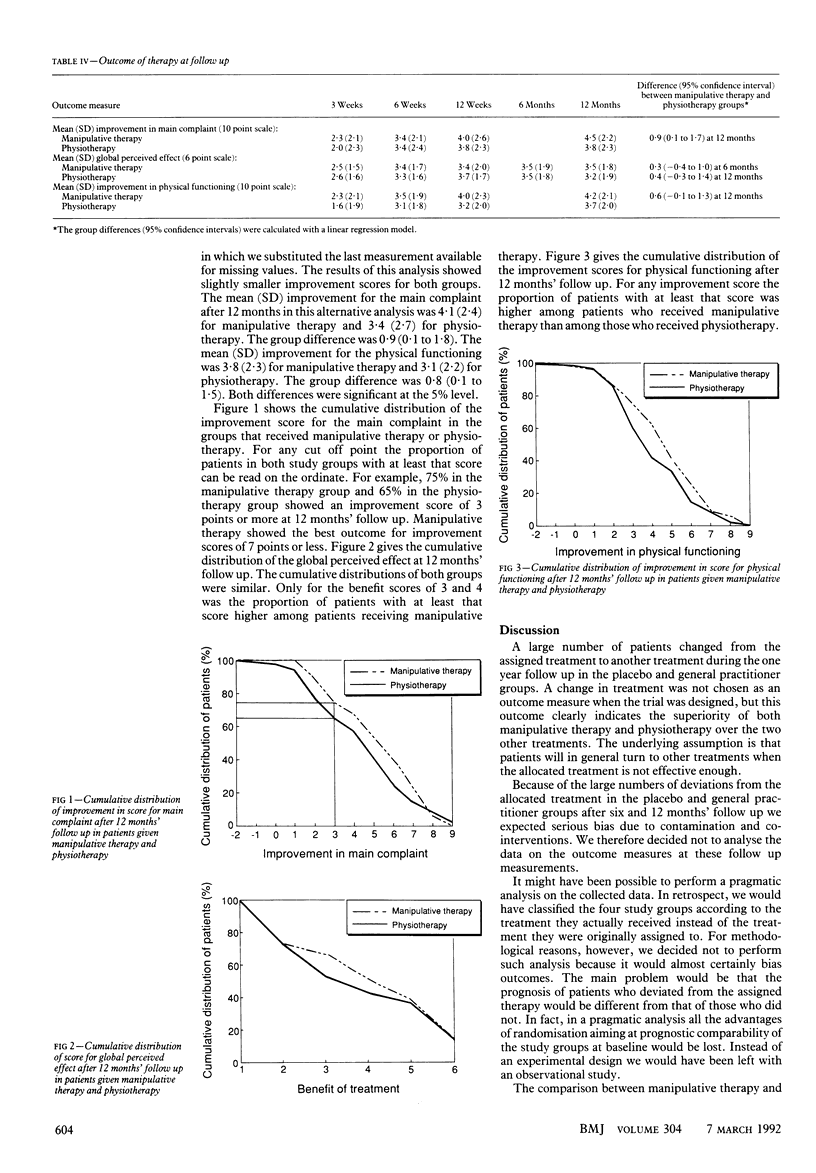
OBJECTIVE--To compare the effectiveness of manipulative therapy, physiotherapy, treatment by the general practitioner, and placebo therapy in patients with persistent non-specific back and neck complaints. DESIGN--Randomised clinical trial. SETTING--Primary health care in the Netherlands. PATIENTS--256 patients with non-specific back and neck complaints of at least six weeks' duration who had not received physiotherapy or manipulative therapy in the past two years. INTERVENTIONS--At the discretion of the manipulative therapists, physiotherapists, and general practitioners. Physiotherapy consisted of exercises, massage, and physical therapy (heat, electrotherapy, ultrasound, shortwave diathermy). Manipulative therapy consisted of manipulation and mobilisation of the spine. Treatment by general practitioners consisted of drugs (for example, analgesics), advice about posture, home exercises, and (bed)rest. Placebo treatment consisted of detuned shortwave diathermy (10 minutes) and detuned ultrasound (10 minutes). MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Changes in severity of the main complaint and limitation of physical functioning measured on 10 point scales by a blinded research assistant and global perceived effect measured on a 6 point scale by the patients. RESULTS--Many patients in the general practitioner and placebo groups received other treatment during follow up. Improvement in the main complaint was larger with manipulative therapy (4.5) than with physiotherapy (3.8) after 12 months' follow up (difference 0.9; 95% confidence interval 0.1 to 1.7). Manipulative therapy also gave larger improvements in physical functioning (difference 0.6; -0.1 to 1.3). The global perceived effect after six and 12 months' follow up was similar for both treatments. CONCLUSIONS--Manipulative therapy and physiotherapy are better than general practitioner and placebo treatment. Furthermore, manipulative therapy is slightly better than physiotherapy after 12 months.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergquist-Ullman M., Larsson U. Acute low back pain in industry. A controlled prospective study with special reference to therapy and confounding factors. Acta Orthop Scand. 1977;(170):1–117. doi: 10.3109/ort.1977.48.suppl-170.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deyo R. A. Conservative therapy for low back pain. Distinguishing useful from useless therapy. JAMA. 1983 Aug 26;250(8):1057–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran D. M., Newell D. J. Manipulation in treatment of low back pain: a multicentre study. Br Med J. 1975 Apr 26;2(5964):161–164. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5964.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frymoyer J. W. Back pain and sciatica. N Engl J Med. 1988 Feb 4;318(5):291–300. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802043180506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koes B. W., Assendelft W. J., van der Heijden G. J., Bouter L. M., Knipschild P. G. Spinal manipulation and mobilisation for back and neck pain: a blinded review. BMJ. 1991 Nov 23;303(6813):1298–1303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6813.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koes B. W., Bouter L. M., Beckerman H., van der Heijden G. J., Knipschild P. G. Physiotherapy exercises and back pain: a blinded review. BMJ. 1991 Jun 29;302(6792):1572–1576. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6792.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Dyer S., Browne W., Townsend J., Frank A. O. Low back pain of mechanical origin: randomised comparison of chiropractic and hospital outpatient treatment. BMJ. 1990 Jun 2;300(6737):1431–1437. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6737.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachemson A. A critical look at the treatment for low back pain. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1979;11(4):143–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siehl D., Olson D. R., Ross H. E., Rockwood E. E. Manipulation of the lumbar spine with the patient under general anesthesia: evaluation by electromyography and clinical-neurologic examination of its use for lumbar nerve root compression syndrome. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1971 Jan;70(5):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims-Williams H., Jayson M. I., Young S. M., Baddeley H., Collins E. Controlled trial of mobilisation and manipulation for low back pain: hospital patients. Br Med J. 1979 Nov 24;2(6201):1318–1320. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6201.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims-Williams H., Jayson M. I., Young S. M., Baddeley H., Collins E. Controlled trial of mobilisation and manipulation for patients with low back pain in general practice. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 11;2(6148):1338–1340. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6148.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell G. 1987 Volvo award in clinical sciences. A new clinical model for the treatment of low-back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1987 Sep;12(7):632–644. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


