Abstract
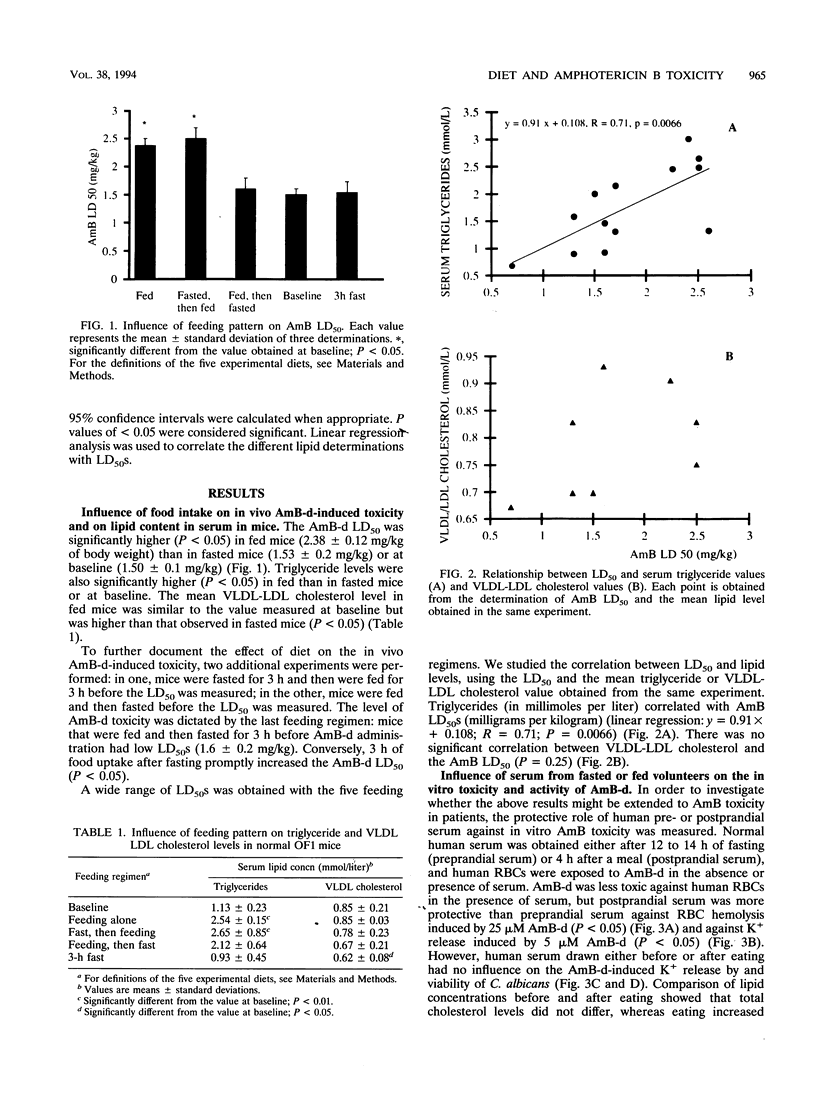
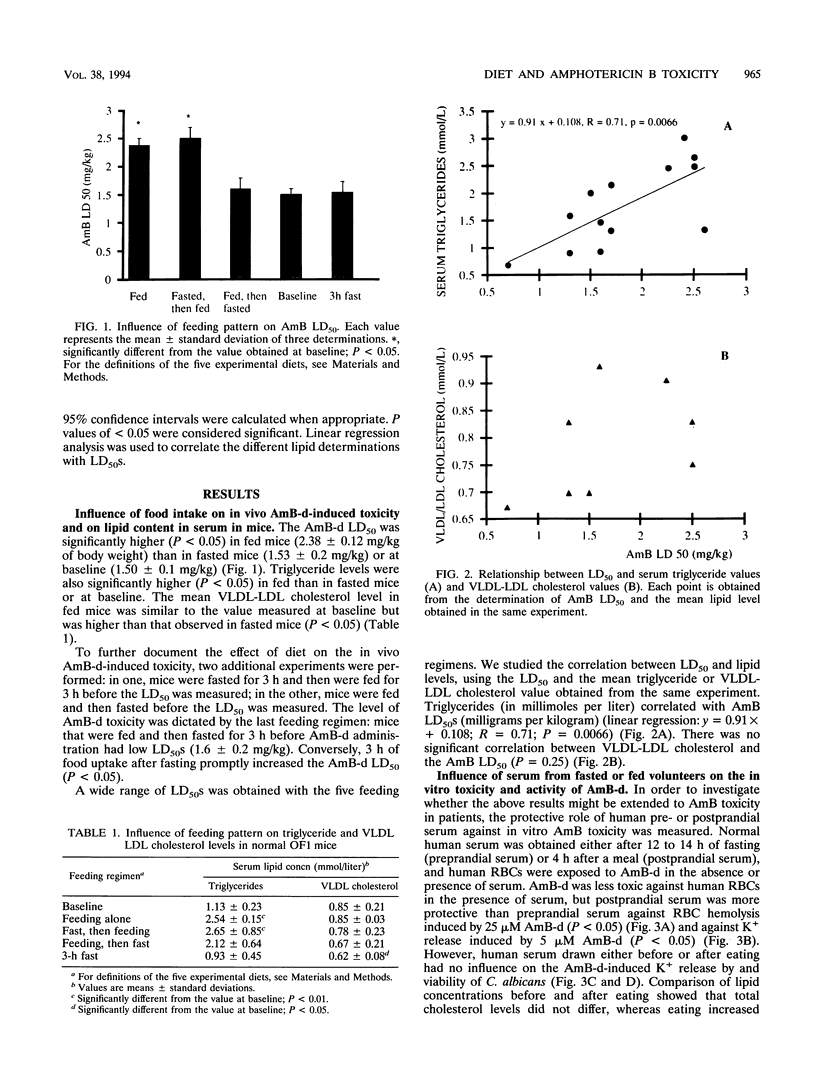
The effects of pre- and postprandial levels of lipids in serum on the experimental in vivo and in vitro toxicities of amphotericin B deoxycholate (AmB-d) were studied. Normal OF1 mice were tested at baseline, after normal feeding, after 3 h of fasting, or after a sequence of feeding and fasting and vice versa. The 50% lethal dose (LD50) of AmB-d was significantly higher in fed mice than in mice which fasted or at baseline (2.38 +/- 0.12 versus 1.53 +/- 0.2 and 1.50 +/- 0.1 mg/kg of body weight, respectively; P < 0.05). When different nutritional regimens were alternated over a short period, the level of in vivo AmB-d toxicity was dictated by the last feeding regimen. Serum triglycerides, but not cholesterol in very-low-density and low-density lipoproteins, correlated significantly (P < 0.01) with the LD50 of AmB. In vitro experiments showed that the addition of human serum reduced AmB-d-induced toxicity against human erythrocytes, but serum drawn after fasting was less protective than postprandial serum. However, neither serum decreased the in vitro activity of AmB-d against Candida albicans. Circular dichroism, a method that enables the amount of free AmB to be measured, showed that both mouse and human total serum lipoproteins bound more AmB-d when serum was isolated postprandially than when it was obtained after fasting. Our results show that AmB-d toxicity is reduced by feeding-induced modifications in serum lipids. The influence of food intake on the clinical toxicity of the drug merits being investigated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson A. J., Jr, Bennett J. E. Amphotericin B pharmacokinetics in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barwicz J., Christian S., Gruda I. Effects of the aggregation state of amphotericin B on its toxicity to mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2310–2315. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolard J., Legrand P., Heitz F., Cybulska B. One-sided action of amphotericin B on cholesterol-containing membranes is determined by its self-association in the medium. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 11;30(23):5707–5715. doi: 10.1021/bi00237a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Bolard J., Kobayashi G. S., Levy R. A., Ostlund R. E., Jr, Schlessinger D., Medoff G. Interaction of plasma proteins and lipoproteins with amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):986–997. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Effects of serum lipoproteins on damage to erythrocytes and Candida albicans cells by polyene antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):623–626. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Powderly W. G., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Amphotericin B: delivery systems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):381–384. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R., Morfin R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus M. C., Aubert R., Bourgeois F., Herzog J., Alexiu A., Lemonnier D. Serum lipoprotein and apolipoprotein profiles of the genetically obese ob/ob mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 1;961(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus M. C., Chapman M. J., Forgez P., Laplaud P. M. Distribution and characterization of the serum lipoproteins and apoproteins in the mouse, Mus musculus. J Lipid Res. 1983 Sep;24(9):1210–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. R., Myers G. L., Smith S. J., Schlant R. C. Blood lipid measurements. Variations and practical utility. JAMA. 1992 Mar 25;267(12):1652–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. A., Talbot G. H., Maislin G., McKeon B. P., Tynan K. P., Strom B. L. Risk factors for Amphotericin B-associated nephrotoxicity. Am J Med. 1989 Nov;87(5):547–552. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80612-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruda I., Gauthier E., Elberg S., Brajtburg J., Medoff G. Effects of the detergent sucrose monolaurate on binding of amphotericin B to sterols and its toxicity for cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):954–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha Y. C., Barter P. J. Differences in plasma cholesteryl ester transfer activity in sixteen vertebrate species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;71(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Grant C. W., Barber K. R., Kalp M. A. Mechanism of the selective toxicity of amphotericin B incorporated into liposomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;31(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien S., Vertut-Croquin A., Brajtburg J., Bolard J. Circular dichroism for the determination of amphotericin B binding to liposomes. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90432-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan V. L., Bennett J. E., Amantea M. A., Smolskis M. C., McManus E., Grasela D. M., Sherman J. W. Comparative safety, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics of amphotericin B lipid complex and amphotericin B desoxycholate in healthy male volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):418–421. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koldin M. H., Kobayashi G. S., Brajtburg J., Medoff G. Effects of elevation of serum cholesterol and administration of amphotericin B complexed to lipoproteins on amphotericin B-induced toxicity in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):144–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand P., Romero E. A., Cohen B. E., Bolard J. Effects of aggregation and solvent on the toxicity of amphotericin B to human erythrocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2518–2522. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A., Ostlund R. E., Jr, Brajtburg J. The effects of amphotericin B on lipid metabolism in cultured human skin fibroblasts. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;21(1):26–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02620910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. C., Maranhão R. C., Schreier S., Campa A. In-vitro and in-vivo studies of the decrease of amphotericin B toxicity upon association with a triglyceride-rich emulsion. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Jul;32(1):123–132. doi: 10.1093/jac/32.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm A. M., Diasio R. B., Dismukes W. E., Shadomy S., Cloud G. A., Bowles C. A., Karam G. H., Espinel-Ingroff A. Toxicity of amphotericin B plus flucytosine in 194 patients with cryptococcal meningitis. Am J Med. 1987 Aug;83(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasan K. M., Brazeau G. A., Keyhani A., Hayman A. C., Lopez-Berestein G. Roles of liposome composition and temperature in distribution of amphotericin B in serum lipoproteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Feb;37(2):246–250. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasan K. M., Vadiei K., Lopez-Berestein G., Luke D. R. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and toxicity of free and liposomal amphotericin B in diabetic rats. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):562–566. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]