Abstract
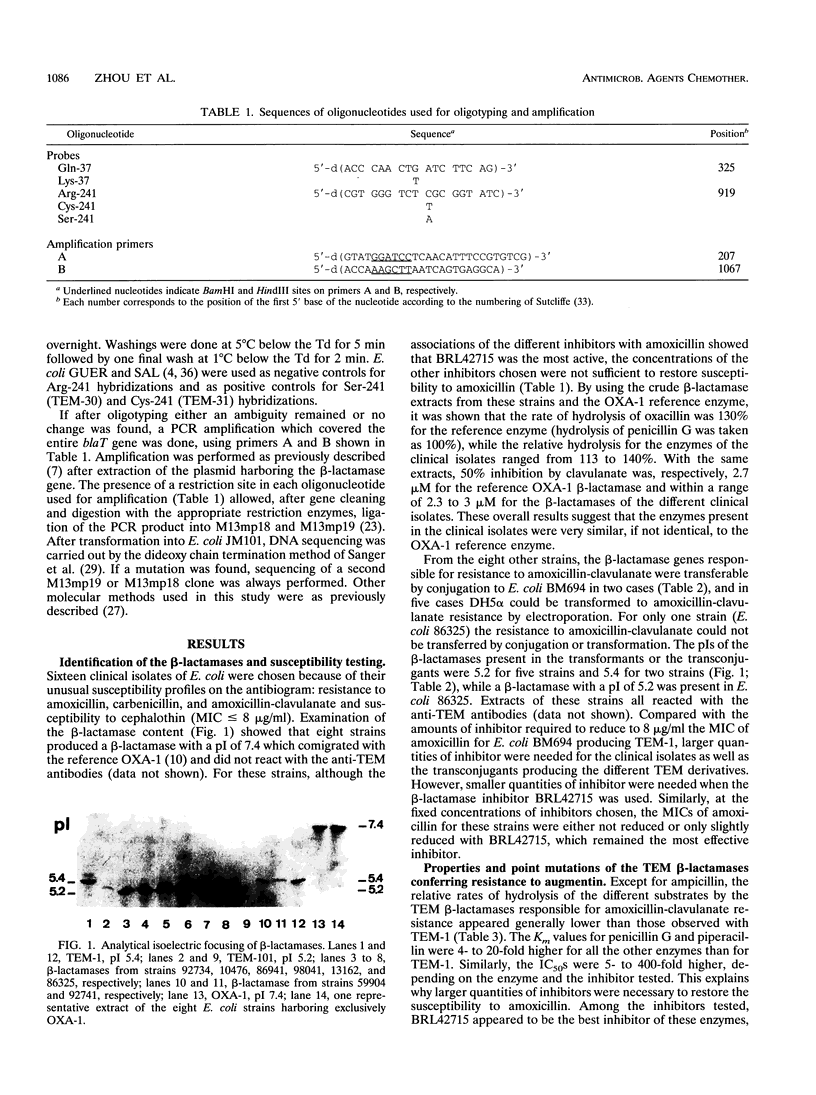
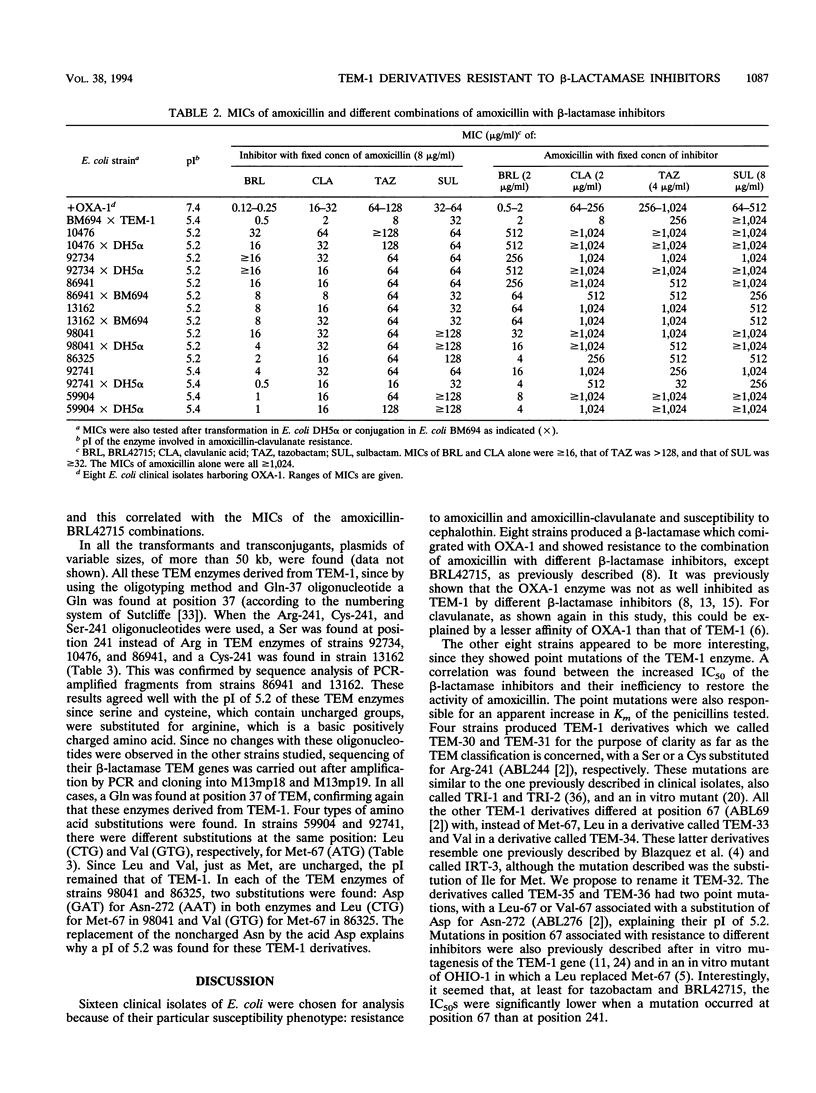
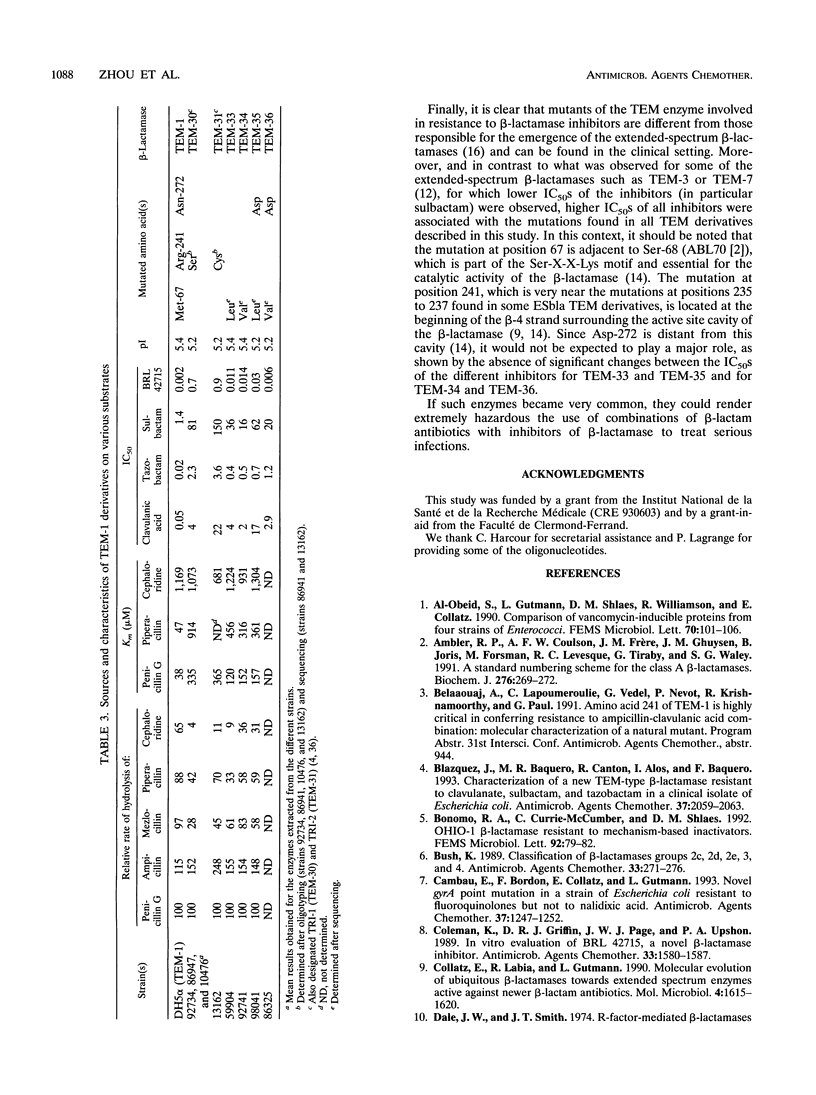
Sixteen Escherichia coli clinical isolates which were resistant to ampicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate but susceptible to cephalothin were studied. Eight strains showed the presence of a beta-lactamase which comigrates with reference OXA-1 enzyme. The eight other strains produced different TEM-1 derivatives which had in common a higher Km for penicillins and a higher 50% inhibitory concentration for the beta-lactamase inhibitors. By oligotyping and sequencing of PCR products, it was shown that Ser (AGC) (TEM-30; also called TRI-1) in three strains and Cys (TGC) (TEM-31; also called TRI-2) in one strain were substituted for Arg-241 (CGC), that Leu (CTG) (TEM-33) and Val (GTG) (TEM-34) in one strain each were substituted for Met-67 (ATG), and that in other mutants the two latter substitutions occurred together with the substitution of Asp (GAT) (TEM-35 and TEM-36) for Asn-272 (AAT). Therefore, different sets of amino acid substitutions of TEM-1 can be found in clinical isolates and lead to resistance to beta-lactamase inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Coulson A. F., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Joris B., Forsman M., Levesque R. C., Tiraby G., Waley S. G. A standard numbering scheme for the class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):269–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2760269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazquez J., Baquero M. R., Canton R., Alos I., Baquero F. Characterization of a new TEM-type beta-lactamase resistant to clavulanate, sulbactam, and tazobactam in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Oct;37(10):2059–2063. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.10.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonomo R. A., Currie-McCumber C., Shlaes D. M. OHIO-1 beta-lactamase resistant to mechanism-based inactivators. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Apr 1;71(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90545-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 2c, 2d, 2e, 3, and 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambau E., Bordon F., Collatz E., Gutmann L. Novel gyrA point mutation in a strain of Escherichia coli resistant to fluoroquinolones but not to nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1247–1252. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K., Griffin D. R., Page J. W., Upshon P. A. In vitro evaluation of BRL 42715, a novel beta-lactamase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1580–1587. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collatz E., Labia R., Gutmann L. Molecular evolution of ubiquitous beta-lactamases towards extended-spectrum enzymes active against newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1615–1620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaire M., Labia R., Samama J. P., Masson J. M. Site-directed mutagenesis at the active site of Escherichia coli TEM-1 beta-lactamase. Suicide inhibitor-resistant mutants reveal the role of arginine 244 and methionine 69 in catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20600–20606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F., Tran Van Nhieu G., Lu T., Carlet J., Collatz E., Williamson R. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-7) involved in resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):860–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Yamabe S., Acar J. F. Comparative evaluation of a new beta-lactamase inhibitor, YTR 830, combined with different beta-lactam antibiotics against bacteria harboring known beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):955–957. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1 at 2.5 A resolution. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):694–701. doi: 10.1126/science.3107125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Aronoff S. C., Johenning S., Shlaes D. M., Yamabe S. Comparative activities of the beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, clavulanate, and sulbactam combined with ampicillin and broad-spectrum penicillins against defined beta-lactamase-producing aerobic gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):980–985. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Medeiros A. A. More extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Translocation of sequences encoding antibiotic resistance from the chromosome to a receptor plasmid in Salmonella ordonez. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):390–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00293927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Moosdeen F., Lindridge M. A., Kho P., Williams J. D. Behaviour of TEM-1 beta-lactamase as a resistance mechanism to ampicillin, mezlocillin and azlocillin in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Feb;17(2):139–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Courvalin P. Development of "oligotyping" for characterization and molecular epidemiology of TEM beta-lactamases in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2210–2216. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A. Beta-lactamases. Br Med Bull. 1984 Jan;40(1):18–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Struhl K. An efficient method for generating proteins with altered enzymatic properties: application to beta-lactamase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Paul G., Nevot P. Mécanisme de résistance enzymatique aux bêta-lactamines. Presse Med. 1986 Dec 20;15(46):2290–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reguera J. A., Baquero F., Pérez-Díaz J. C., Martínez J. L. Factors determining resistance to beta-lactam combined with beta-lactamase inhibitors in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 May;27(5):569–575. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.5.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Iaconis J. P., Bodey G. P., Samonis G. Resistance to ticarcillin-potassium clavulanate among clinical isolates of the family Enterobacteriaceae: role of PSE-1 beta-lactamase and high levels of TEM-1 and SHV-1 and problems with false susceptibility in disk diffusion tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1365–1369. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K., Williams H., King A., Phillips I. Hyperproduction of TEM-1 beta-lactamase in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli serotype O15. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Feb;55(3):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90016-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the ampicillin resistance gene of Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson C. J., Amyes S. G. Molecular epidemiology of the plasmid-encoded TEM-1 beta-lactamase in Scotland. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Feb;110(1):117–125. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson C. J., Amyes S. G. TRC-1: emergence of a clavulanic acid-resistant TEM beta-lactamase in a clinical strain. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Mar 1;70(2):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90669-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedel G., Belaaouaj A., Gilly L., Labia R., Philippon A., Névot P., Paul G. Clinical isolates of Escherichia coli producing TRI beta-lactamases: novel TEM-enzymes conferring resistance to beta-lactamase inhibitors. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Oct;30(4):449–462. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Obeid S., Gutmann L., Shlaes D. M., Williamson R., Collatz E. Comparison of vancomycin-inducible proteins from four strains of Enterococci. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jun 15;58(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




