Abstract
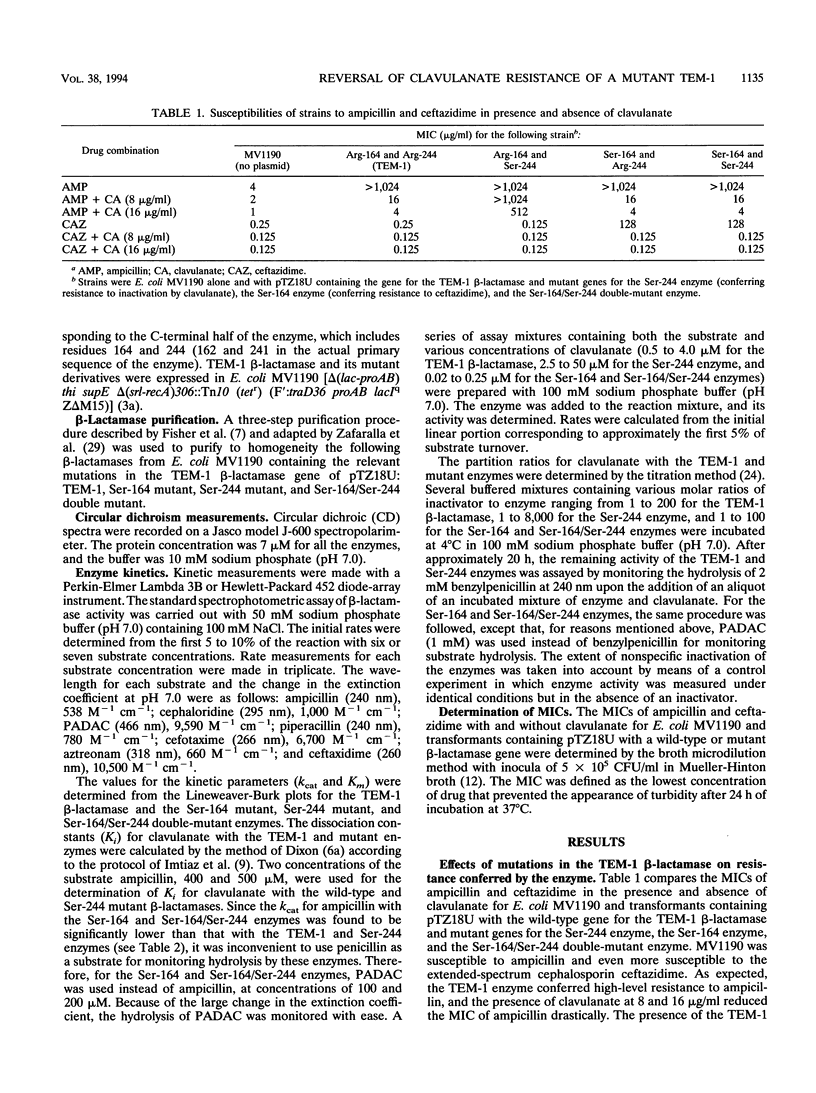
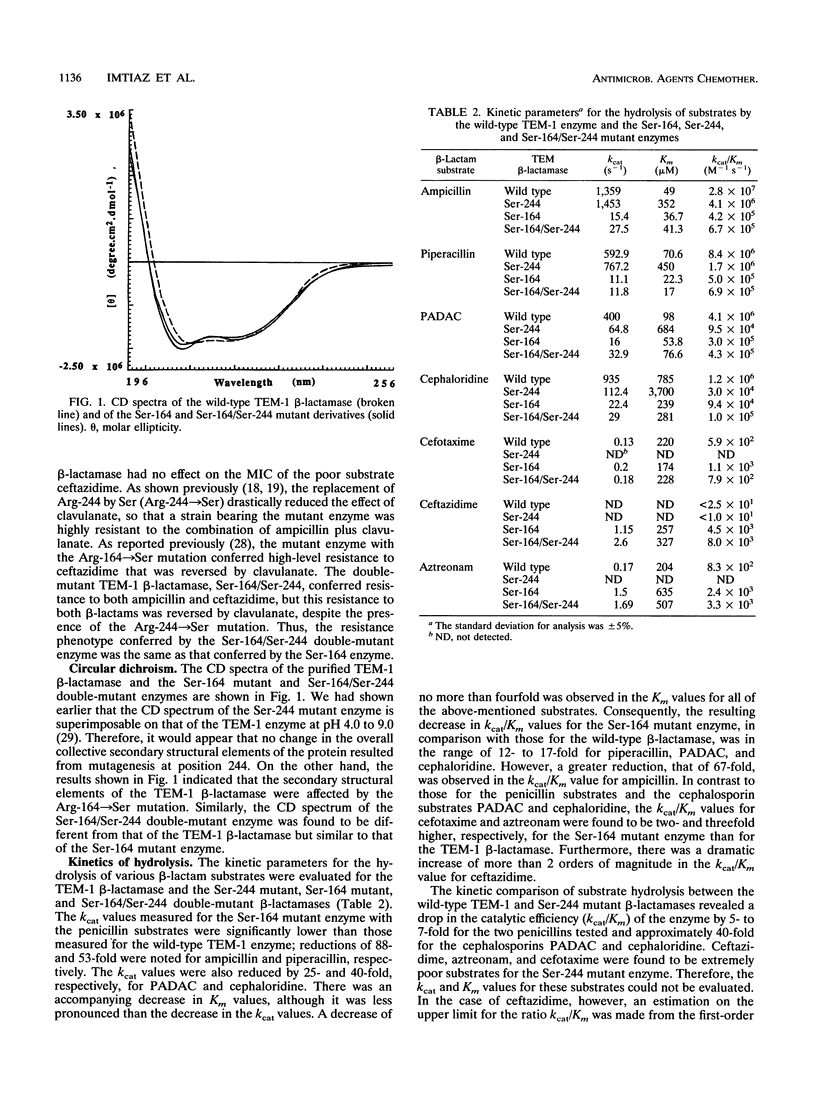
The mutation of Arg-244 to Ser (Arg-244-->Ser mutation) in the TEM-1 beta-lactamase has been shown to produce resistance to inactivation by clavulanate in the mutant enzyme and resistance to ampicillin plus clavulanate in a strain of Escherichia coli producing this enzyme. The Arg-164-->Ser mutation in the TEM-1 beta-lactamase (TEM-12 enzyme) is known to enhance the activity of the enzyme against ceftazidime, resulting in resistance to the drug in a strain producing the mutant enzyme (D. A. Weber, C. C. Sanders, J. S. Bakken, and J. P. Quinn, J. Infect. Dis. 162:460-465, 1990). The doubly mutated derivative of the TEM-1 enzyme (Ser-164/Ser-244) retains the characteristics of the Ser-164 mutant enzyme, i.e., enhanced activity against ceftazidime and sensitivity to inactivation by clavulanate. It also confers the same phenotype as the Ser-164 mutant enzyme, i.e., resistance to ceftazidime and ampicillin, with reversal of this resistance in the presence of clavulanate. Thus, the Arg-164-->Ser mutation in the TEM-1 beta-lactamase suppresses the effect of the Arg-244-->Ser mutation which, by itself, reduces the sensitivity of the enzyme to inactivation by clavulanate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Coulson A. F., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Joris B., Forsman M., Levesque R. C., Tiraby G., Waley S. G. A standard numbering scheme for the class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):269–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2760269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):259–263. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 1, 2a, 2b, and 2b'. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaire M., Labia R., Samama J. P., Masson J. M. Site-directed mutagenesis at the active site of Escherichia coli TEM-1 beta-lactamase. Suicide inhibitor-resistant mutants reveal the role of arginine 244 and methionine 69 in catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20600–20606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Belasco J. G., Khosla S., Knowles J. R. beta-Lactamase proceeds via an acyl-enzyme intermediate. Interaction of the Escherichia coli RTEM enzyme with cefoxitin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2895–2901. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O. Refined crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1 at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 20;217(4):701–719. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90527-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imtiaz U., Manavathu E. K., Lerner S. A., Mobashery S. Critical hydrogen bonding by serine 235 for cephalosporinase activity of TEM-1 beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2438–2442. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Medeiros A. A. More extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. R., Moews P. C. Beta-lactamase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C. Refinement at 2 A resolution and analysis of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):435–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90023-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte-Brasseur J., Dive G., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M. Mechanism of acyl transfer by the class A serine beta-lactamase of Streptomyces albus G. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):213–221. doi: 10.1042/bj2790213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Courvalin P. Development of "oligotyping" for characterization and molecular epidemiology of TEM beta-lactamases in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2210–2216. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Knox J. R., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M. Beta-lactamase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C at 2 A resolution. Proteins. 1990;7(2):156–171. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr beta-Lactam resistance in gram-negative bacteria: global trends and clinical impact. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;15(5):824–839. doi: 10.1093/clind/15.5.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowek J. A., Singer S. B., Ohringer S., Malley M. F., Dougherty T. J., Gougoutas J. Z., Bush K. Substitution of lysine at position 104 or 240 of TEM-1pTZ18R beta-lactamase enhances the effect of serine-164 substitution on hydrolysis or affinity for cephalosporins and the monobactam aztreonam. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3179–3188. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., Adachi H., Jensen S. E., Johns K., Sielecki A., Betzel C., Sutoh K., James M. N. Molecular structure of the acyl-enzyme intermediate in beta-lactam hydrolysis at 1.7 A resolution. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):700–705. doi: 10.1038/359700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedel G., Belaaouaj A., Gilly L., Labia R., Philippon A., Névot P., Paul G. Clinical isolates of Escherichia coli producing TRI beta-lactamases: novel TEM-enzymes conferring resistance to beta-lactamase inhibitors. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Oct;30(4):449–462. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber D. A., Sanders C. C., Bakken J. S., Quinn J. P. A novel chromosomal TEM derivative and alterations in outer membrane proteins together mediate selective ceftazidime resistance in Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):460–465. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafaralla G., Manavathu E. K., Lerner S. A., Mobashery S. Elucidation of the role of arginine-244 in the turnover processes of class A beta-lactamases. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 21;31(15):3847–3852. doi: 10.1021/bi00130a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


