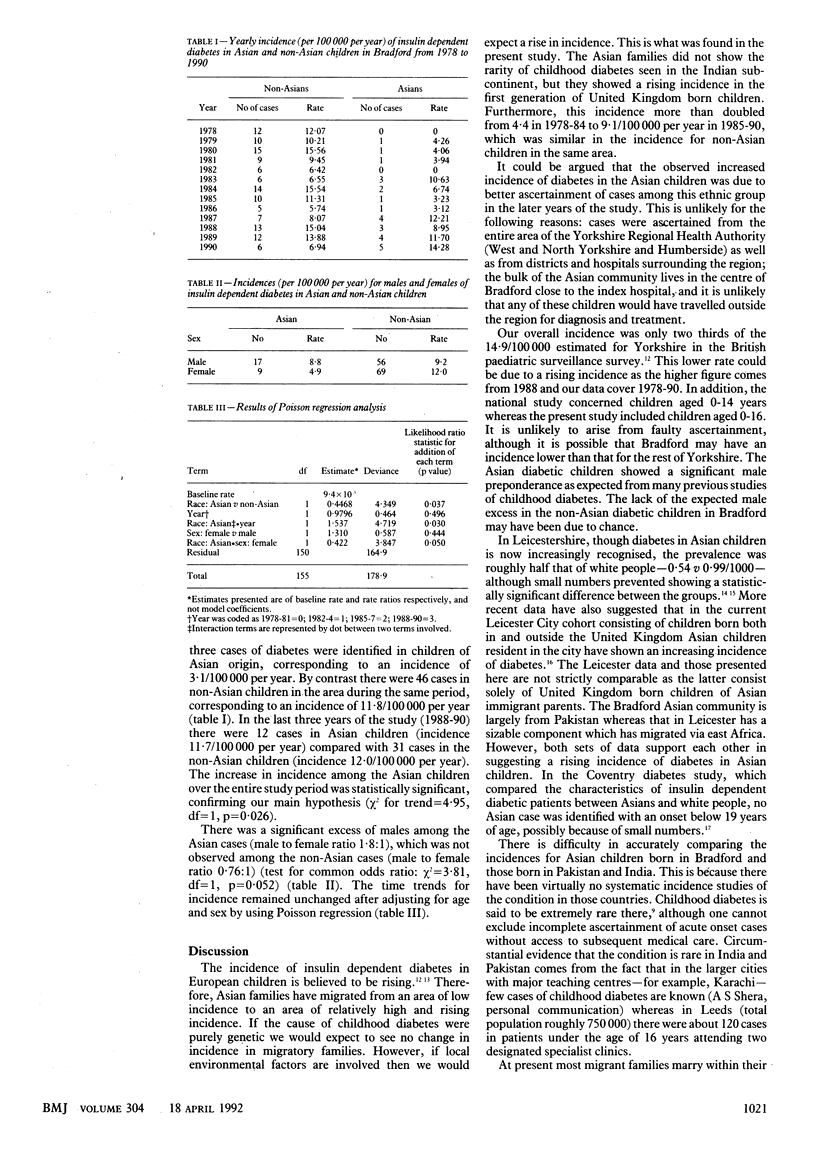
Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To examine whether children of families moving from an area of low incidence of childhood diabetes to one which is higher show a corresponding rise in disease incidence. DESIGN--Disease incidence study over 12 years. SETTING--Bradford District Metropolitan Council area. SUBJECTS--All subjects aged 0-16 years resident within the study area. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--The incidences of childhood diabetes in Asian and non-Asian families. RESULTS--The incidence of diabetes in Asian children increased from 3.1/100,000 per year in 1978-81 to 11.7/100,000 per year in 1988-90 (chi 2 for trend = 4.95, df = 1, p = 0.026) whereas that for other children remained constant at 10.5/100,000 per year. Over the entire study period rates were lower in Asian females (4.9/100,000 per year) than in Asian males (8.8/100,000 per year) whereas the reverse was true for other children (males 9.2/100,000 per year; females 12.0/100,000 per year) (test for common odds ratio: chi 2 = 3.81, df = 1, p = 0.052). CONCLUSIONS--Offspring of this transmigratory population had a rising incidence of childhood diabetes which was approaching that of the indigenous population. The data provide strong evidence for an environmental effect in the aetiology of insulin dependent diabetes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett A. H., Eff C., Leslie R. D., Pyke D. A. Diabetes in identical twins. A study of 200 pairs. Diabetologia. 1981 Feb;20(2):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00262007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingley P. J., Gale E. A. Rising incidence of IDDM in Europe. Diabetes Care. 1989 Apr;12(4):289–295. doi: 10.2337/diacare.12.4.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky H. J., Beverley D. W., Gelsthorpe K., Saunders A., Bottazzo G. F., Haigh D. Insulin dependent diabetes in Asians. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Mar;62(3):227–230. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky H. J., Staines A., Stephenson C., Haigh D., Cartwright R. Evidence for an environmental effect in the aetiology of insulin dependent diabetes in a transmigratory population. BMJ. 1992 Apr 18;304(6833):1020–1022. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6833.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgason T., Jonasson M. R. Evidence for a food additive as a cause of ketosis-prone diabetes. Lancet. 1981 Oct 3;2(8249):716–720. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe M. A., Baum J. D. Incidence of insulin dependent diabetes in children aged under 15 years in the British Isles during 1988. BMJ. 1991 Feb 23;302(6774):443–447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6774.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijonen H., Ilonen J., Knip M., Michelsen B., Akerblom H. K. HLA-DQ beta-chain restriction fragment length polymorphism as a risk marker in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: a Finnish family study. Diabetologia. 1990 Jun;33(6):357–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00404640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A., Burden A. C., Hearnshaw J. R., Swift P. G. Diabetes in Asian children. Lancet. 1990 Jun 2;335(8701):1341–1341. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91219-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A., Burden A. C., Jones G. R., Woollands I. G., Clarke M., Swift P. G., Hearnshaw J. R. Prevalence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Asian children. Diabet Med. 1987 Jan-Feb;4(1):65–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1987.tb00832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. Prevalence and age of onset of type 1 diabetes in adult Asians in the Coventry Diabetes Study. Diabet Med. 1990 Mar-Apr;7(3):238–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A., Cudworth A. G. Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetic multiplex families: mode of genetic transmission. Diabetes. 1980 Dec;29(12):1036–1039. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.12.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


