Abstract
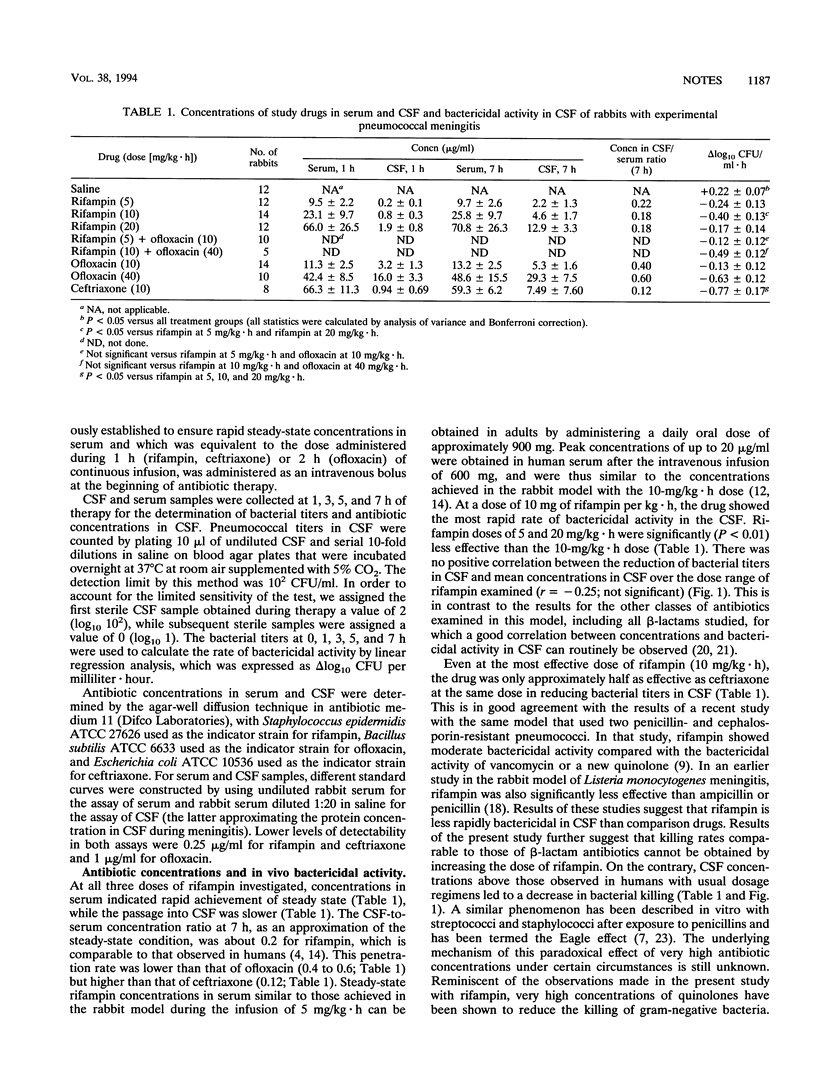
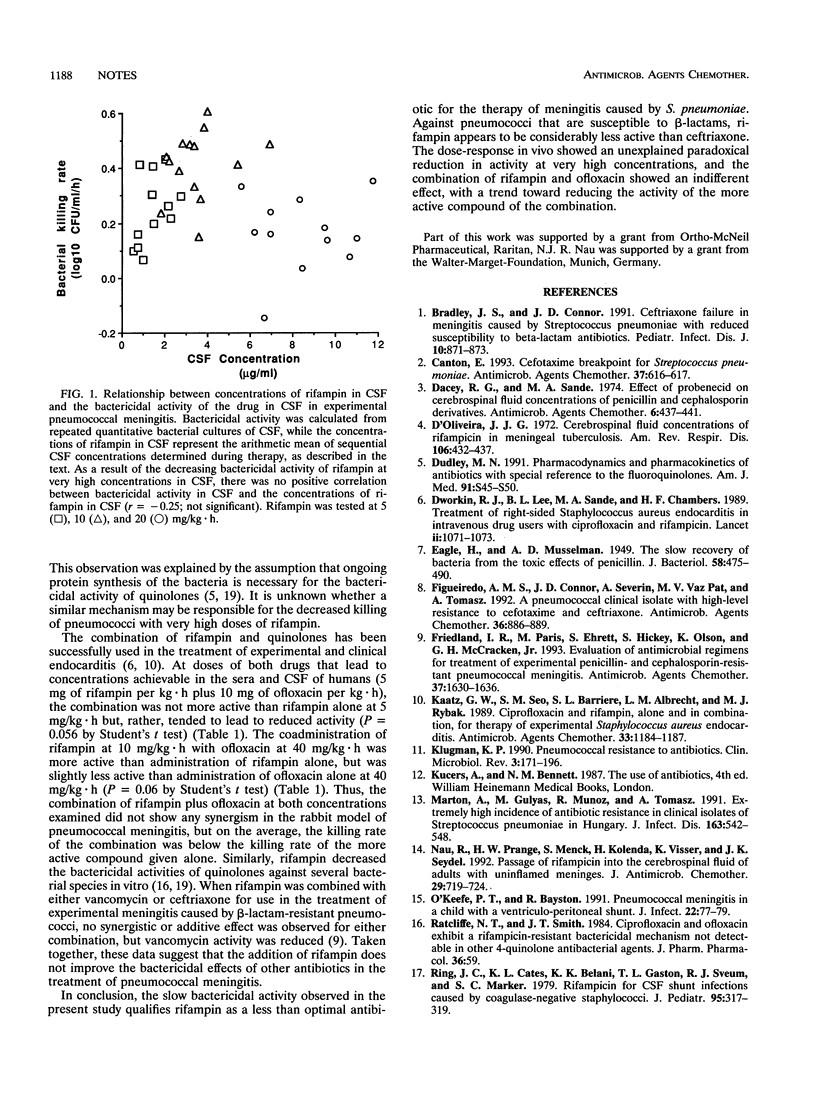
Rifampin at a maximally effective dose was less active than ceftriaxone (both drugs at 10 mg/kg of body weight.h) in a rabbit model of pneumococcal meningitis (delta log10 CFU/ml.h, -0.40 +/- 0.13 versus -0.77 +/- 0.18; P < 0.01). The bactericidal activity of rifampin decreased at concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid greater than those that are clinically achievable, and use of rifampin in combination with ofloxacin had no synergistic or additive effect.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley J. S., Connor J. D. Ceftriaxone failure in meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Nov;10(11):871–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantón E. Cefotaxime breakpoint for Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):616–617. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Oliveira J. J. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of rifampin in meningeal tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Sep;106(3):432–437. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacey R. G., Sande M. A. Effect of probenecid on cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of penicillin and cephalosporin derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R. J., Lee B. L., Sande M. A., Chambers H. F. Treatment of right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in intravenous drug users with ciprofloxacin and rifampicin. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1071–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H., Musselman A. D. THE SLOW RECOVERY OF BACTERIA FROM THE TOXIC EFFECTS OF PENICILLIN. J Bacteriol. 1949 Oct;58(4):475–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.4.475-490.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo A. M., Connor J. D., Severin A., Vaz Pato M. V., Tomasz A. A pneumococcal clinical isolate with high-level resistance to cefotaxime and ceftriaxone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):886–889. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland I. R., Paris M., Ehrett S., Hickey S., Olsen K., McCracken G. H., Jr Evaluation of antimicrobial regimens for treatment of experimental penicillin- and cephalosporin-resistant pneumococcal meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Aug;37(8):1630–1636. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.8.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Ciprofloxacin and rifampin, alone and in combination, for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1184–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P. Pneumococcal resistance to antibiotics. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Apr;3(2):171–196. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A., Hamberger A. Inhibition of cholinergic response by taurine in frog isolated skeletal muscle. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;36(1):59–61. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb02991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton A., Gulyas M., Munoz R., Tomasz A. Extremely high incidence of antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Hungary. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):542–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau R., Prange H. W., Menck S., Kolenda H., Visser K., Seydel J. K. Penetration of rifampicin into the cerebrospinal fluid of adults with uninflamed meninges. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Jun;29(6):719–724. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keeffe P. T., Bayston R. Pneumococcal meningitis in a child with a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. J Infect. 1991 Jan;22(1):77–79. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(91)91066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring J. C., Cates K. L., Belani K. K., Gaston T. L., Sveum R. J., Marker S. C. Rifampin for CSF shunt infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Pediatr. 1979 Aug;95(2):317–319. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80682-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Fletcher D. D., Fink F. N., Sande M. A. Response to therapy in an experimental rabbit model of meningitis due to Listeria monocytogenes. J Infect Dis. 1979 Sep;140(3):287–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T. The mode of action of 4-quinolones and possible mechanisms of resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):21–29. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Doroshow C. A., Hackbarth C. J., Rusnak M. G., Drake T. A., Sande M. A. Antibacterial activity of beta-lactam antibiotics in experimental meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):568–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Hackbarth C. J., Scott K. G., Rusnak M. G., Sande M. A. New cephalosporins cefotaxime, cefpimizole, BMY 28142, and HR 810 in experimental pneumococcal meningitis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):340–342. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viladrich P. F., Gudiol F., Liñares J., Rufi G., Ariza J., Pallares R. Characteristics and antibiotic therapy of adult meningitis due to penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Am J Med. 1988 May;84(5):839–846. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourassowsky E., Van der Linden M. P., Lismont M. J., Crockaert F., Glupczynski Y. Bactericidal effect and regrowth of Streptococcus faecalis exposed to amoxicillin following beta-lactamase. Chemotherapy. 1988;34(6):462–466. doi: 10.1159/000238609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


