Abstract
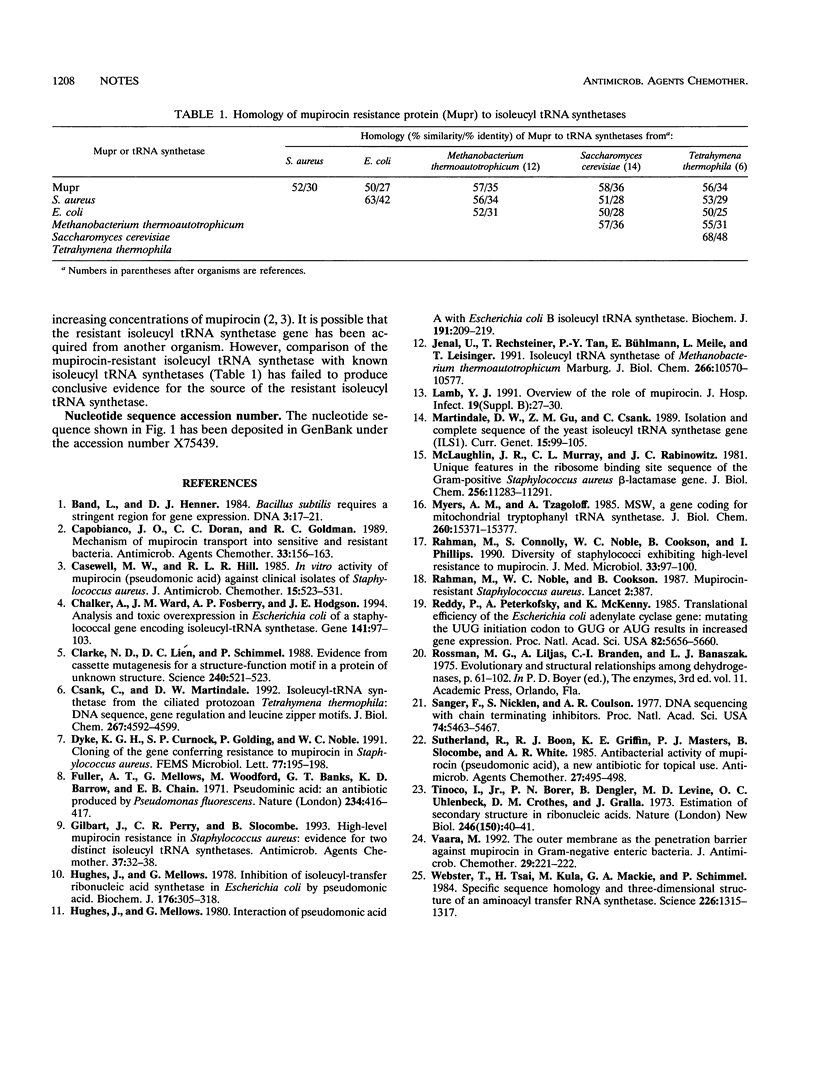
The nucleotide sequence of the ileS gene conferring high-level resistance to mupirocin in Staphylococcus aureus J2870 has been determined. The gene sequence is substantially different from that of the native ileS gene of S. aureus, indicating that high-level resistance to mupirocin results from the acquisition of a novel ileS gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band L., Henner D. J. Bacillus subtilis requires a "stringent" Shine-Dalgarno region for gene expression. DNA. 1984;3(1):17–21. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco J. O., Doran C. C., Goldman R. C. Mechanism of mupirocin transport into sensitive and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):156–163. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casewell M. W., Hill R. L. In-vitro activity of mupirocin ('pseudomonic acid') against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 May;15(5):523–531. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker A. F., Ward J. M., Fosberry A. P., Hodgson J. E. Analysis and toxic overexpression in Escherichia coli of a staphylococcal gene encoding isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Gene. 1994 Apr 8;141(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. D., Lien D. C., Schimmel P. Evidence from cassette mutagenesis for a structure-function motif in a protein of unknown structure. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):521–523. doi: 10.1126/science.3282306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csank C., Martindale D. W. Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase from the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila. DNA sequence, gene regulation, and leucine zipper motifs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4592–4599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke K. G., Curnock S. P., Golding M., Noble W. C. Cloning of the gene conferring resistance to mupirocin in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90550-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. T., Mellows G., Woolford M., Banks G. T., Barrow K. D., Chain E. B. Pseudomonic acid: an antibiotic produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Nature. 1971 Dec 17;234(5329):416–417. doi: 10.1038/234416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbart J., Perry C. R., Slocombe B. High-level mupirocin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for two distinct isoleucyl-tRNA synthetases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jan;37(1):32–38. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Mellows G. Inhibition of isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase in Escherichia coli by pseudomonic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):305–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1760305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Mellows G. Interaction of pseudomonic acid A with Escherichia coli B isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):209–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1910209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenal U., Rechsteiner T., Tan P. Y., Bühlmann E., Meile L., Leisinger T. Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg. Cloning of the gene, nucleotide sequence, and localization of a base change conferring resistance to pseudomonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10570–10577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb Y. J. Overview of the role of mupirocin. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Sep;19 (Suppl B):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90199-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martindale D. W., Gu Z. M., Csank C. Isolation and complete sequence of the yeast isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase gene (ILS1). Curr Genet. 1989 Feb;15(2):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00435455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mupirocin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):387–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. MSW, a yeast gene coding for mitochondrial tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15371–15377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M., Connolly S., Noble W. C., Cookson B., Phillips I. Diversity of staphylococci exhibiting high-level resistance to mupirocin. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Oct;33(2):97–100. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-2-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Peterkofsky A., McKenney K. Translational efficiency of the Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase gene: mutating the UUG initiation codon to GUG or AUG results in increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5656–5660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Boon R. J., Griffin K. E., Masters P. J., Slocombe B., White A. R. Antibacterial activity of mupirocin (pseudomonic acid), a new antibiotic for topical use. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):495–498. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. The outer membrane as the penetration barrier against mupirocin in gram-negative enteric bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Feb;29(2):221–222. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T., Tsai H., Kula M., Mackie G. A., Schimmel P. Specific sequence homology and three-dimensional structure of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



