Abstract
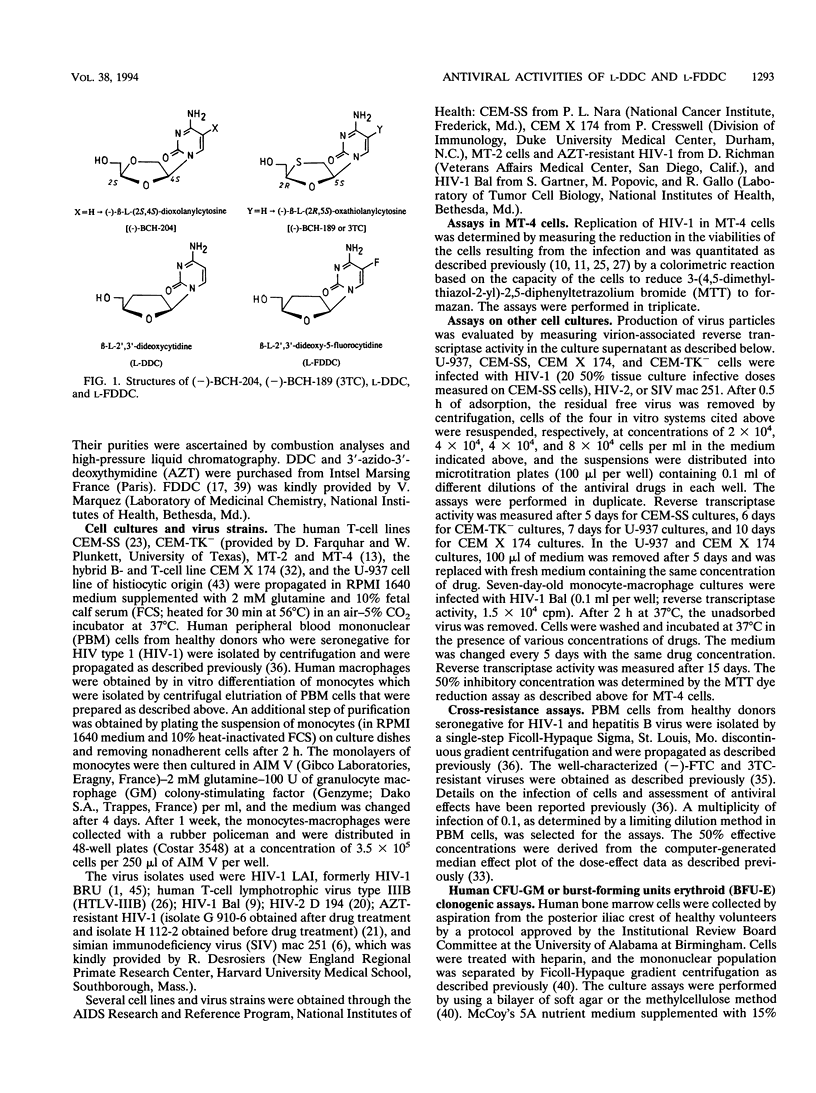
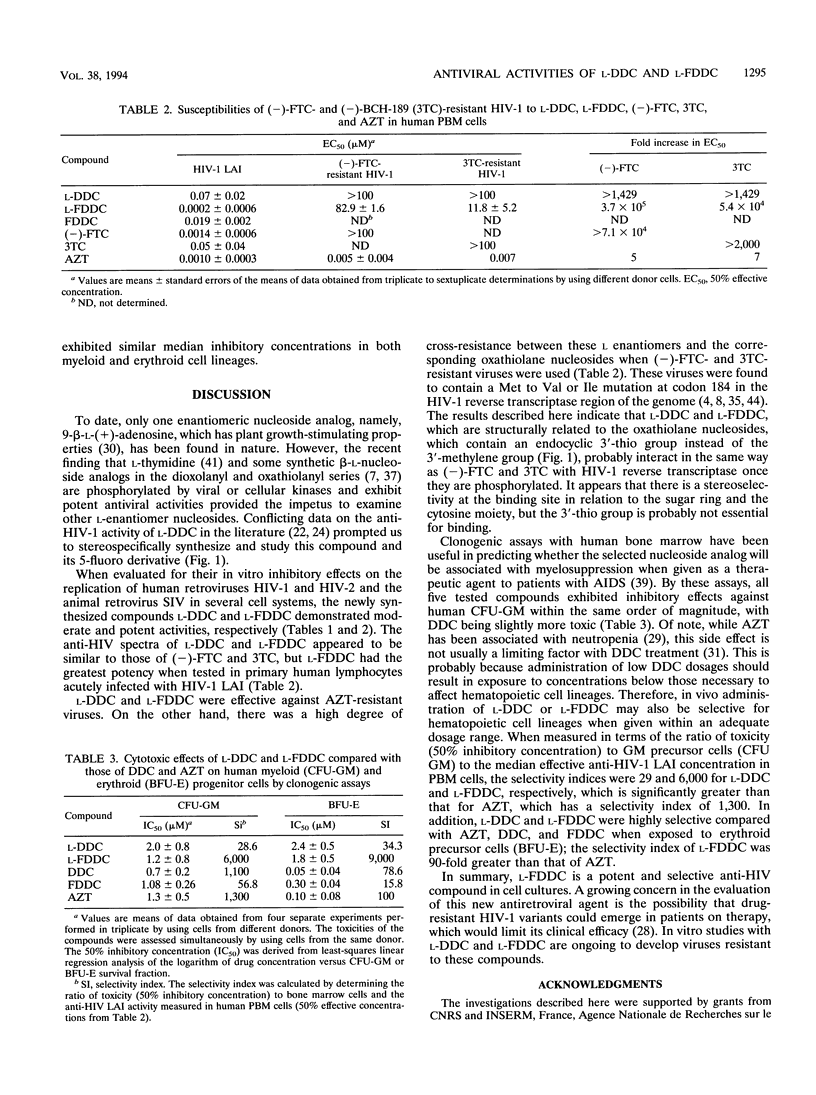
The L enantiomer of 2',3'-dideoxycytidine (DDC) was recently shown to inhibit selectively human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in vitro. In the current study, the potent anti-HIV activity of L-DDC was confirmed and extended to several HIV-1 and HIV-2 strains in various cell culture systems, including primary human lymphocytes and macrophages. Furthermore, its 5-fluoro congener, beta-L-2',3'-dideoxy-5-fluorocytidine (L-FDDC), was found to have more potent anti-HIV activity and a higher therapeutic index in acutely infected human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These compounds had no marked activity against HIV-1 isolates resistant to the oxathiolane pyrimidine nucleosides (-)-beta-L-2',3'-dideoxy-5-fluoro-3'-thiacytidine [(-)-FTC] and (-)-beta-L-2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine, but 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT)-resistant viruses were susceptible to L-DDC and L-FDDC. Cytotoxicity studies with human myeloid progenitor cells indicated that L-DDC and L-FDDC had median inhibitory concentrations comparable to those of AZT, DDC, and FDDC, but L-DDC and L-FDDC were significantly less toxic than AZT, DDC, and FDDC when erythroid progenitor cells were used. L-FDDC had the highest selectivity indices (6,000 and 9,000 for erythroid and myeloid progenitor cells, respectively) of all the compounds evaluated. Further preclinical development of L-FDDC is warranted in order to determine its potential usefulness in the treatment of HIV infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Cammack N., Schipper P., Schuurman R., Rouse P., Wainberg M. A., Cameron J. M. High-level resistance to (-) enantiomeric 2'-deoxy-3'-thiacytidine in vitro is due to one amino acid substitution in the catalytic site of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Oct;37(10):2231–2234. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.10.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates J. A., Cammack N., Jenkinson H. J., Mutton I. M., Pearson B. A., Storer R., Cameron J. M., Penn C. R. The separated enantiomers of 2'-deoxy-3'-thiacytidine (BCH 189) both inhibit human immunodeficiency virus replication in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):202–205. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Davis M., Liotta D. C., Paff M., Frick L. W., Nelson D. J., Dornsife R. E., Wurster J. A., Wilson L. J., Fyfe J. A. The anti-hepatitis B virus activities, cytotoxicities, and anabolic profiles of the (-) and (+) enantiomers of cis-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2686–2692. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Q., Gu Z., Parniak M. A., Cameron J., Cammack N., Boucher C., Wainberg M. A. The same mutation that encodes low-level human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine confers high-level resistance to the (-) enantiomer of 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1390–1392. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin G., Mathé C., Bergogne M. C., Aubertin A. M., Kirn A., Schinazi R. F., Sommadossi J. P., Imbach J. L. Enantiomeric 2',3'-dideoxycytidine derivatives are potent human immunodeficiency virus inhibitors in cell cultures. C R Acad Sci III. 1994 Jan;317(1):85–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2992081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong L. S., Schinazi R. F., Beach J. W., Kim H. O., Nampalli S., Shanmuganathan K., Alves A. J., McMillan A., Chu C. K., Mathis R. Asymmetric synthesis and biological evaluation of beta-L-(2R,5S)- and alpha-L-(2R,5R)-1,3-oxathiolane-pyrimidine and -purine nucleosides as potential anti-HIV agents. J Med Chem. 1993 Jan 22;36(2):181–195. doi: 10.1021/jm00054a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Marquez V. E., Broder S., Mitsuya H., Driscoll J. S. Potential anti-AIDS drugs. 2',3'-Dideoxycytidine analogues. J Med Chem. 1987 May;30(5):862–866. doi: 10.1021/jm00388a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. O., Schinazi R. F., Shanmuganathan K., Jeong L. S., Beach J. W., Nampalli S., Cannon D. L., Chu C. K. L-beta-(2S,4S)- and L-alpha-(2S,4R)-dioxolanyl nucleosides as potential anti-HIV agents: asymmetric synthesis and structure-activity relationships. J Med Chem. 1993 Mar 5;36(5):519–528. doi: 10.1021/jm00057a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel H., von Briesen H., Dietrich U., Adamski M., Mix D., Biesert L., Kreutz R., Immelmann A., Henco K., Meichsner C. Molecular cloning of two west African human immunodeficiency virus type 2 isolates that replicate well in macrophages: a Gambian isolate, from a patient with neurologic acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and a highly divergent Ghanian isolate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2383–2387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Hatch W. C., Dunlop N. M., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Fischinger P. J. Simple, rapid, quantitative, syncytium-forming microassay for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):283–302. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Balzarini J., Baba M., Snoeck R., Schols D., Herdewijn P., Desmyter J., De Clercq E. Rapid and automated tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay for the detection of anti-HIV compounds. J Virol Methods. 1988 Aug;20(4):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puech F., Gosselin G., Lefebvre I., Pompon A., Aubertin A. M., Kirn A., Imbach J. L. Intracellular delivery of nucleoside monophosphates through a reductase-mediated activation process. Antiviral Res. 1993 Oct;22(2-3):155–174. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(93)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Fischl M. A., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Hirsch M. S. The toxicity of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):192–197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D. Resistance of clinical isolates of human immunodeficiency virus to antiretroviral agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ries S. Triacontanol and Its Second Messenger 9-beta-l(+)-Adenosine as Plant Growth Substances. Plant Physiol. 1991 Apr;95(4):986–989. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.4.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S. Treatment of HIV infection: the antiretroviral nucleoside analogues. Nucleoside analogues: adverse effects. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1992 Aug;27 (Suppl 2):26–36. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1992.11705597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Howell D. N., Cresswell P. Genes regulating HLA class I antigen expression in T-B lymphoblast hybrids. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(3):235–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00375376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Chou T. C., Scott R. T., Yao X. J., Nahmias A. J. Delayed treatment with combinations of antiviral drugs in mice infected with herpes simplex virus and application of the median effect method of analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):491–498. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Chu C. K., Peck A., McMillan A., Mathis R., Cannon D., Jeong L. S., Beach J. W., Choi W. B., Yeola S. Activities of the four optical isomers of 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine (BCH-189) against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in human lymphocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Mar;36(3):672–676. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Lloyd R. M., Jr, Nguyen M. H., Cannon D. L., McMillan A., Ilksoy N., Chu C. K., Liotta D. C., Bazmi H. Z., Mellors J. W. Characterization of human immunodeficiency viruses resistant to oxathiolane-cytosine nucleosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):875–881. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., McMillan A., Cannon D., Mathis R., Lloyd R. M., Peck A., Sommadossi J. P., St Clair M., Wilson J., Furman P. A. Selective inhibition of human immunodeficiency viruses by racemates and enantiomers of cis-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2423–2431. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewach D. S., Liotta D. C., Schinazi R. F. Affinity of the antiviral enantiomers of oxathiolane cytosine nucleosides for human 2'-deoxycytidine kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Apr 6;45(7):1540–1543. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui M. A., Driscoll J. S., Marquez V. E., Roth J. S., Shirasaka T., Mitsuya H., Barchi J. J., Jr, Kelley J. A. Chemistry and anti-HIV properties of 2'-fluoro-2',3'-dideoxyarabinofuranosylpyrimidines. J Med Chem. 1992 Jun 12;35(12):2195–2201. doi: 10.1021/jm00090a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Carlisle R. Toxicity of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine for normal human hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):452–454. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P. Nucleoside analogs: similarities and differences. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;16 (Suppl 1):S7–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/16.supplement_1.s7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Maga G., Focher F., Ciarrocchi G., Manservigi R., Arcamone F., Capobianco M., Carcuro A., Colonna F., Iotti S. L-thymidine is phosphorylated by herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and inhibits viral growth. J Med Chem. 1992 Oct 30;35(22):4214–4220. doi: 10.1021/jm00100a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Kemp S. D., Parry N. R., Larder B. A. Rapid in vitro selection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistant to 3'-thiacytidine inhibitors due to a mutation in the YMDD region of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5653–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Vartanian J. P., Henry M., Chenciner N., Cheynier R., Delassus S., Martins L. P., Sala M., Nugeyre M. T., Guétard D. LAV revisited: origins of the early HIV-1 isolates from Institut Pasteur. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):961–965. doi: 10.1126/science.2035026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



