Abstract
This study addressed the effects of fluconazole and 5-fluorocytosine on the candidacidal activity of amphotericin B in the presence of human serum. A Candida albicans isolate that was susceptible to all three agents according to standard testing procedures was employed. Fungicidal activity was estimated by using a flow cytometric procedure that exploited the fact that yeast cells killed by amphotericin B diminish in size and take up propidium iodide. The following findings were made. (i) Fluconazole and 5-fluorocytosine each failed to inhibit pseudohyphal formation and cell aggregation even when applied at 10 and 50 micrograms/ml, respectively, for up to 10 h. Hence, these agents were not fungistatic when tested in the presence of serum. (ii) Simultaneous application of 5-fluorocytosine had neither enhancing nor inhibitory effects on the fungicidal activity of amphotericin B. However, yeasts that were preincubated for 20 h with 5-fluorocytosine became less susceptible to killing by amphotericin B. (iii) Fluconazole exerted a frank antagonistic effect on the fungicidal activity of amphotericin B. Thus, under our in vitro conditions, both fluconazole and 5-fluorocytosine can overtly antagonize the candidacidal action of amphotericin B.
Full text
PDF

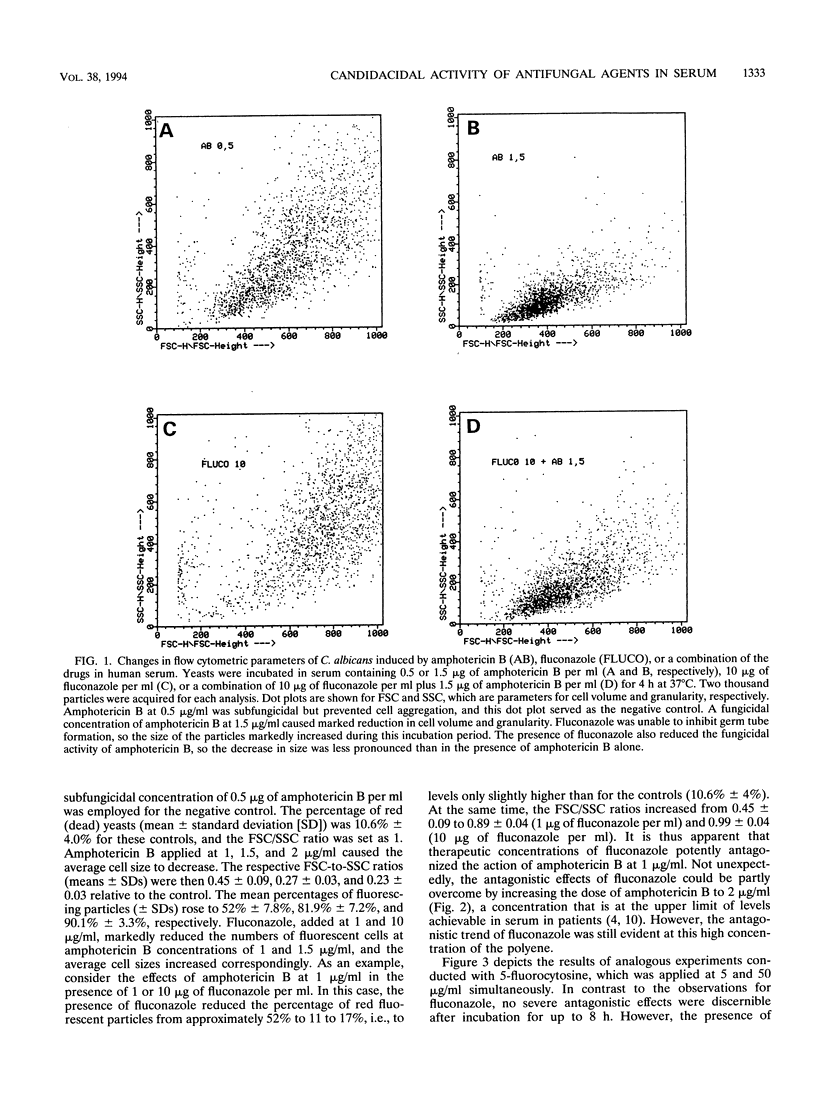
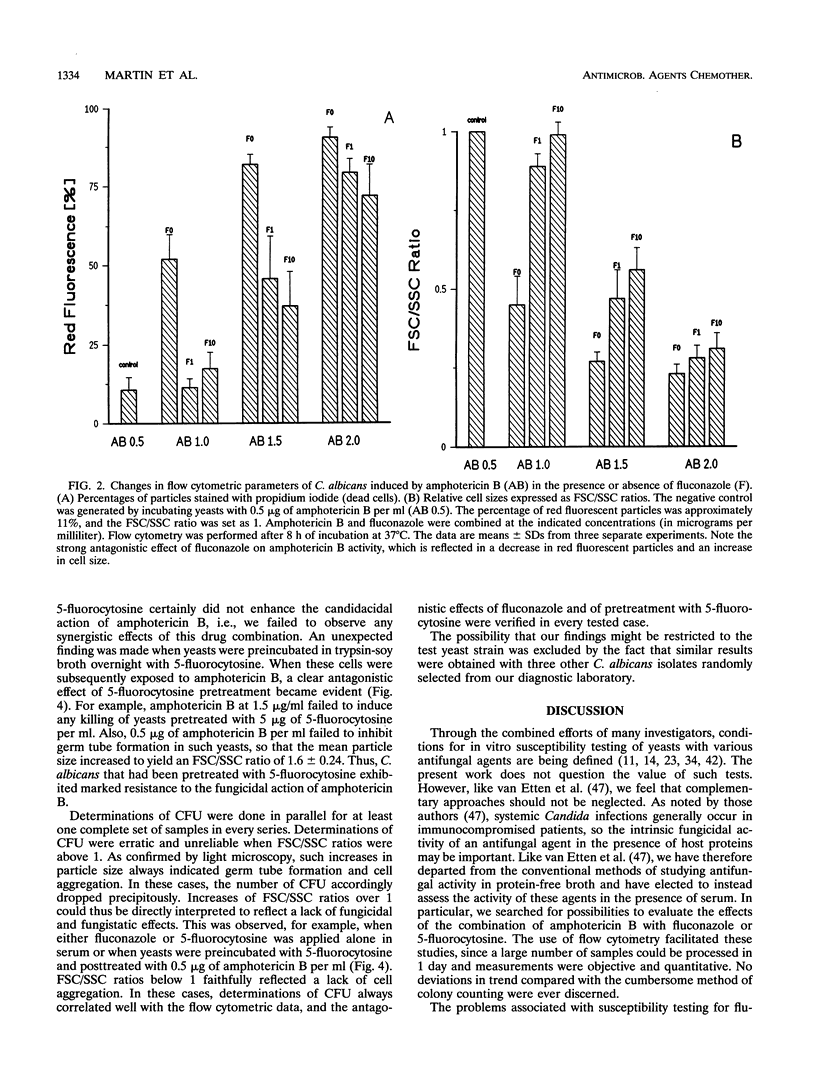
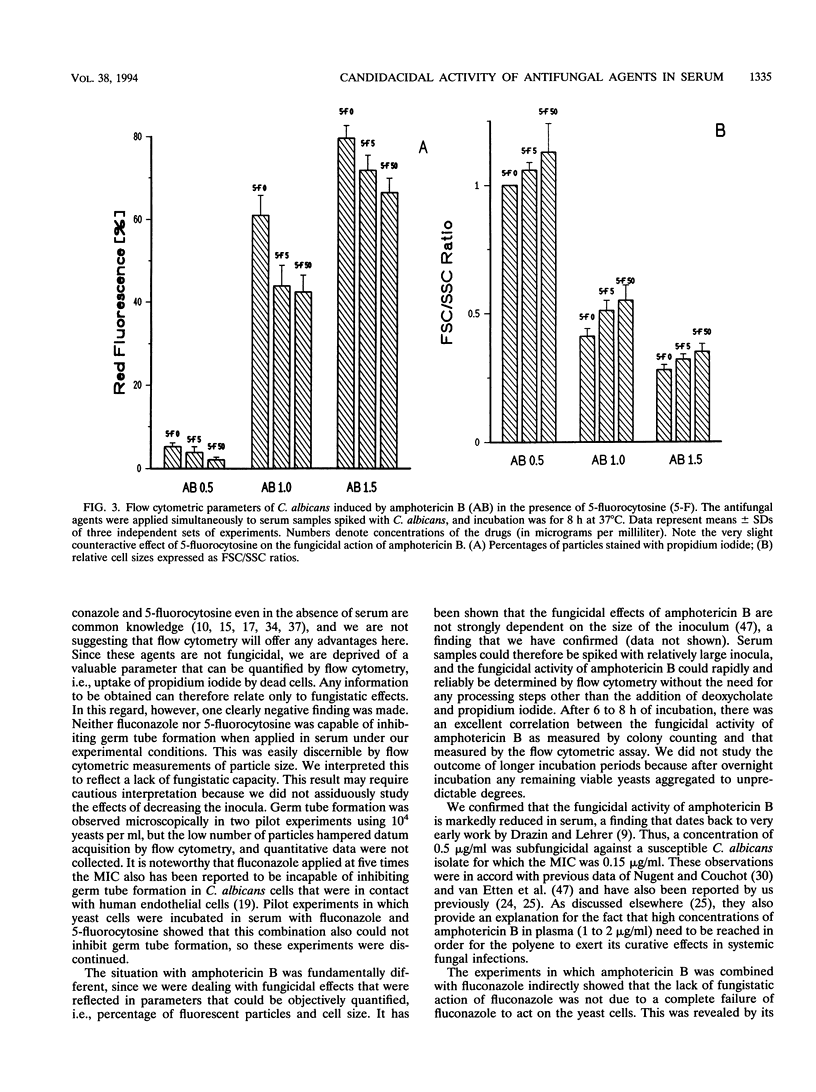
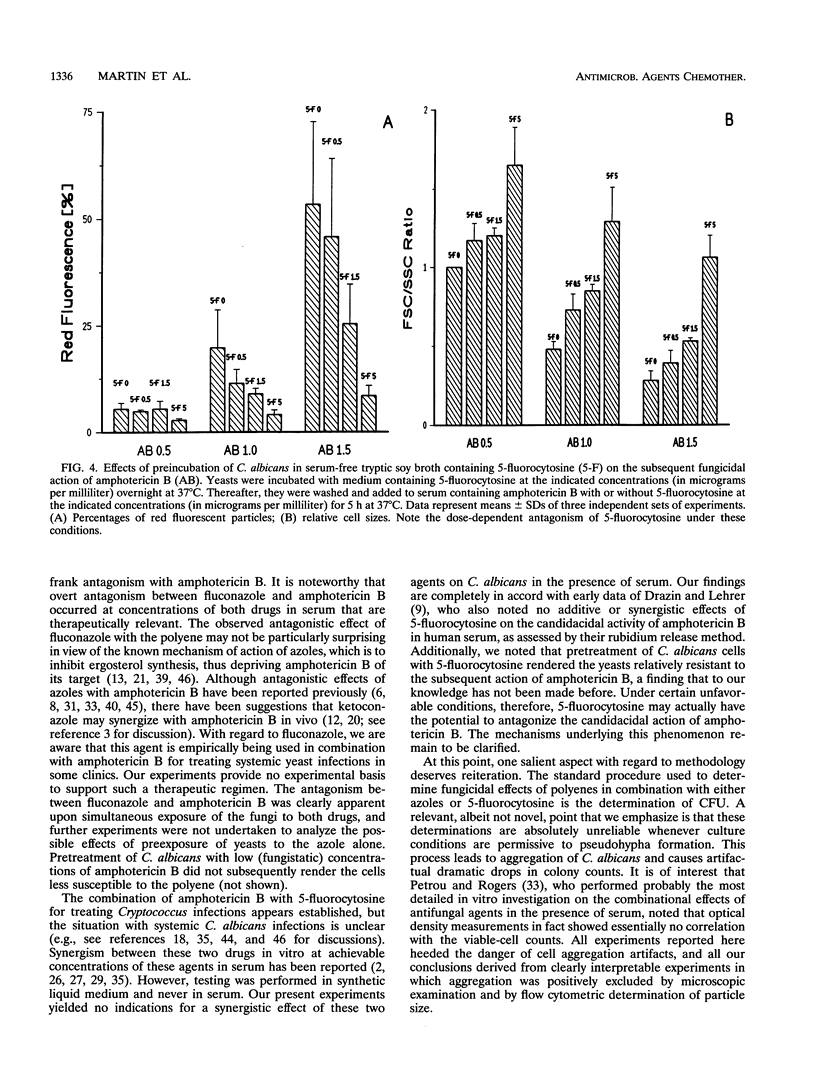


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson A. J., Jr, Bennett J. E. Amphotericin B pharmacokinetics in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs W. H., Andrews F. A., Sarosi G. A. Combined action of amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine on pathogenic yeasts susceptible to either drug alone. Chemotherapy. 1981;27(4):247–251. doi: 10.1159/000237987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. M., Nahata M. C. Clinical use of systemic antifungal agents. Clin Pharm. 1988 Jun;7(6):424–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindschadler D. D., Bennett J. E. A pharmacologic guide to the clinical use of amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):427–436. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Effects of serum lipoproteins on damage to erythrocytes and Candida albicans cells by polyene antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):623–626. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Kobayashi D., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Antifungal action of amphotericin B in combination with other polyene or imidazole antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):138–146. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brammer K. W., Farrow P. R., Faulkner J. K. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of fluconazole in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12 (Suppl 3):S318–S326. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_3.s318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove R. F., Beezer A. E., Miles R. J. In vitro studies of amphotericin B in combination with the imidazole antifungal compounds clotrimazole and miconazole. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):681–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R. E., Lehrer R. I. Rubidium release: a rapid and sensitive assay for amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1976 Sep;134(3):238–244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.3.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinel-Ingroff A., Kish C. W., Jr, Kerkering T. M., Fromtling R. A., Bartizal K., Galgiani J. N., Villareal K., Pfaller M. A., Gerarden T., Rinaldi M. G. Collaborative comparison of broth macrodilution and microdilution antifungal susceptibility tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3138–3145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3138-3145.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. F., Henson D. M. Amphotericin B resistance in Candida. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Apr;102(4):563–564. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-4-563_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Galgiani J. N., Pfaller M. A., Espinel-Ingroff A., Bartizal K. F., Bartlett M. S., Body B. A., Frey C., Hall G., Roberts G. D. Multicenter evaluation of a broth macrodilution antifungal susceptibility test for yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jan;37(1):39–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A. Overview of medically important antifungal azole derivatives. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):187–217. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Antifungal susceptibility tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1867–1870. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Reiser J., Brass C., Espinel-Ingroff A., Gordon M. A., Kerkering T. M. Comparison of relative susceptibilities of Candida species to three antifungal agents as determined by unstandardized methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1343–1347. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Susceptibility of Candida albicans and other yeasts to fluconazole: relation between in vitro and in vivo studies. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12 (Suppl 3):S272–S275. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_3.s272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallis H. A., Drew R. H., Pickard W. W. Amphotericin B: 30 years of clinical experience. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12(2):308–329. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Filler S. G., Ibrahim A. S., Fu Y., Edwards J. E., Jr Modulation of interactions of Candida albicans and endothelial cells by fluconazole and amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2239–2244. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz M. B., Jones J. M. Combined ketoconazole and amphotericin B treatment of acute disseminated histoplasmosis in a renal allograft recipient. South Med J. 1985 Nov;78(11):1368–1370. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198511000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. M., Clissold S. P. Fluconazole. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in superficial and systemic mycoses. Drugs. 1990 Jun;39(6):877–916. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199039060-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Craven P. C. Antifungal agents used in systemic mycoses. Activity and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1983 Jan;25(1):41–62. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198325010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinet R., Nerson D., de Closets F., Dupouy-Camet J., Kures L., Marjollet M., Poirot J. L., Ros A., Texier-Maugein J., Volle P. J. Collaborative evaluation in seven laboratories of a standardized micromethod for yeast susceptibility testing. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2307–2312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2307-2312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E., Bhakdi S. Quantitative analysis of opsonophagocytosis and of killing of Candida albicans by human peripheral blood leukocytes by using flow cytometry. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2013–2023. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2013-2023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E., Schlasius U., Bhakdi S. Flow cytometric assay for estimating fungicidal activity of amphotericin B in human serum. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(3):117–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00202051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Brajtburg J., Kobayashi G. S., Bolard J. Antifungal agents useful in therapy of systemic fungal infections. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:303–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Kwan C. N., Schlessinger D., Venkov P. Potentiation of rifampicin and 5-fluorocytosine as antifungal antibiotics by amphotericin B (yeast-membrane permeability-ribosomal RNA-eukaryotic cell-synergism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):196–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Edwards J. E., Jr, Guze L. B. Synergism of amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine for candida species. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):82–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. M., Couchot K. R. Effects of sublethal concentrations of amphotericin B on Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):665–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Cheesman S. L., Abbott A. B. Antifungal effects of fluconazole (UK 49858), a new triazole antifungal, in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18(4):473–478. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Interactions among amphotericin B, 5-fluorocytosine, ketoconazole, and miconazole against pathogenic fungi in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):763–770. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrou M. A., Rogers T. R. Interactions in vitro between polyenes and imidazoles against yeasts. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Apr;27(4):491–506. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Rinaldi M. G., Galgiani J. N., Bartlett M. S., Body B. A., Espinel-Ingroff A., Fromtling R. A., Hall G. S., Hughes C. E., Odds F. C. Collaborative investigation of variables in susceptibility testing of yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1648–1654. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak A. Synergism of polyene antibiotics with 5-fluorocytosine. Chemotherapy. 1978;24(1):2–16. doi: 10.1159/000237753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rex J. H., Pfaller M. A., Rinaldi M. G., Polak A., Galgiani J. N. Antifungal susceptibility testing. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Oct;6(4):367–381. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. E., Galgiani J. N. Activity of fluconazole (UK 49,858) and ketoconazole against Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):418–422. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Dismukes W. E. Azole antifungal agents: emphasis on new triazoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter L. P., Owellen R. J., Rathbun H. K., Buchanan B. Letter: Antagonism between miconazole and amphotericin B. Lancet. 1976 Aug 7;2(7980):318–318. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90774-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shawar R., Paetznick V., Witte Z., Ensign L. G., Anaissie E., LaRocco M. Collaborative investigation of broth microdilution and semisolid agar dilution for in vitro susceptibility testing of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1976–1981. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1976-1981.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa O., Nakayama H. Increased sensitivity of Candida albicans cells accumulating 14 alpha-methylated sterols to active oxygen: possible relevance to in vivo efficacies of azole antifungal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1626–1629. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smego R. A., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Combined therapy with amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine for Candida meningitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Nov-Dec;6(6):791–801. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.6.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Effect of ketoconazole on the fungicidal action of amphotericin B in Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):185–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van 't Wout J. W., Meynaar I., Linde I., Poell R., Mattie H., Van Furth R. Effect of amphotericin B, fluconazole and itraconazole on intracellular Candida albicans and germ tube development in macrophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 May;25(5):803–811. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.5.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf A. R., Polak A. Mechanisms of action of 5-fluorocytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):79–85. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Lee J., Aoki S., Mechinaud F., Bacher J., Lecciones J., Thomas V., Rubin M., Pizzo P. A. Experimental basis for use of fluconazole for preventive or early treatment of disseminated candidiasis in granulocytopenic hosts. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12 (Suppl 3):S307–S317. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_3.s307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Etten E. W., van de Rhee N. E., van Kampen K. M., Bakker-Woudenberg I. A. Effects of amphotericin B and fluconazole on the extracellular and intracellular growth of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2275–2281. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



