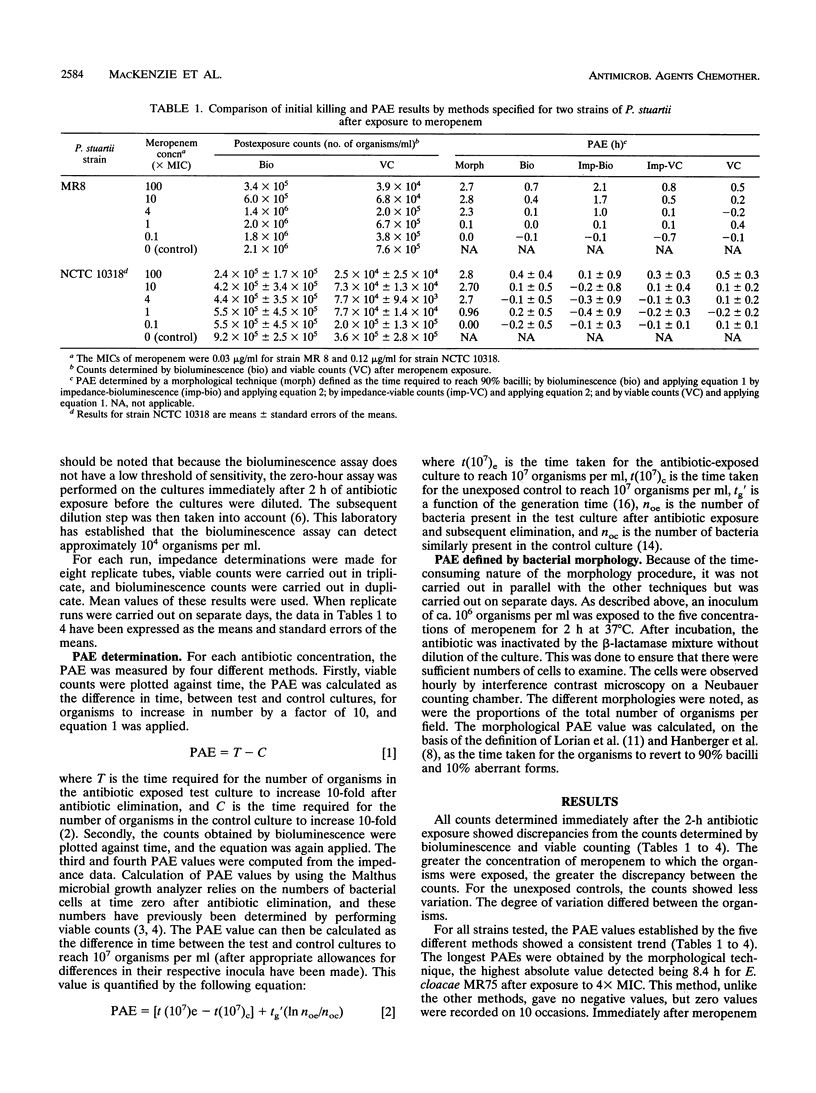
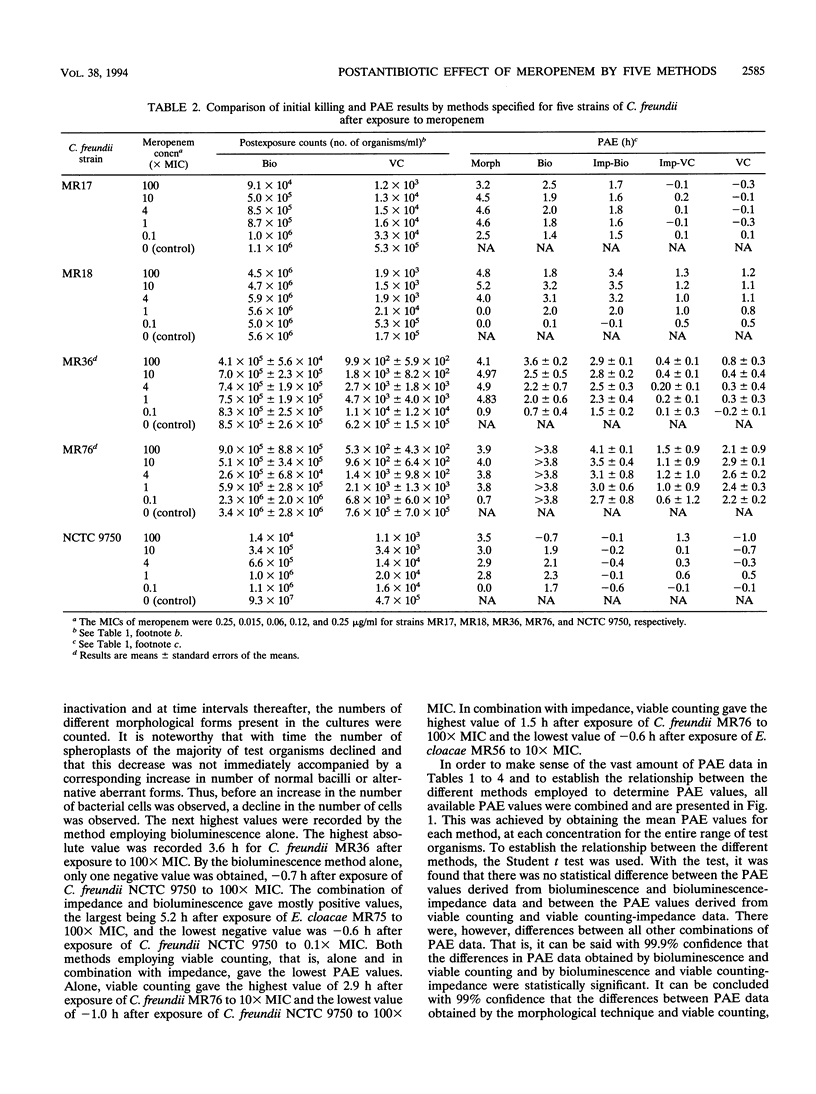
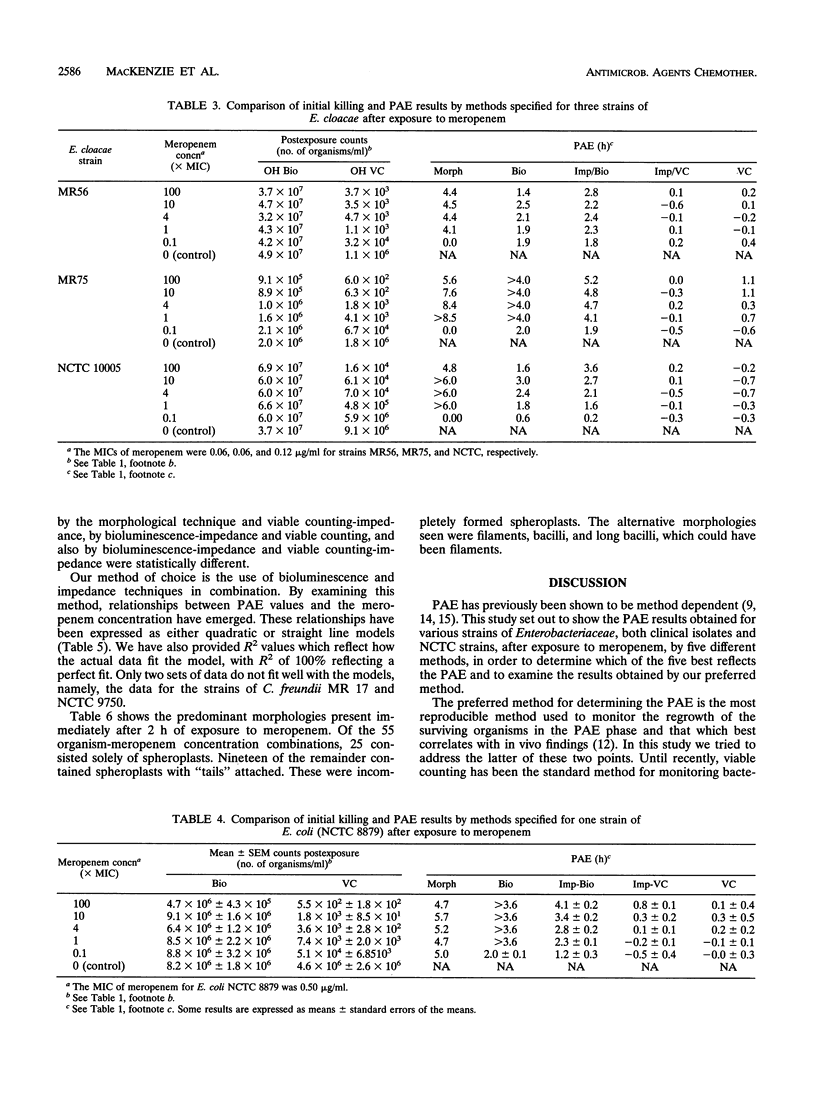
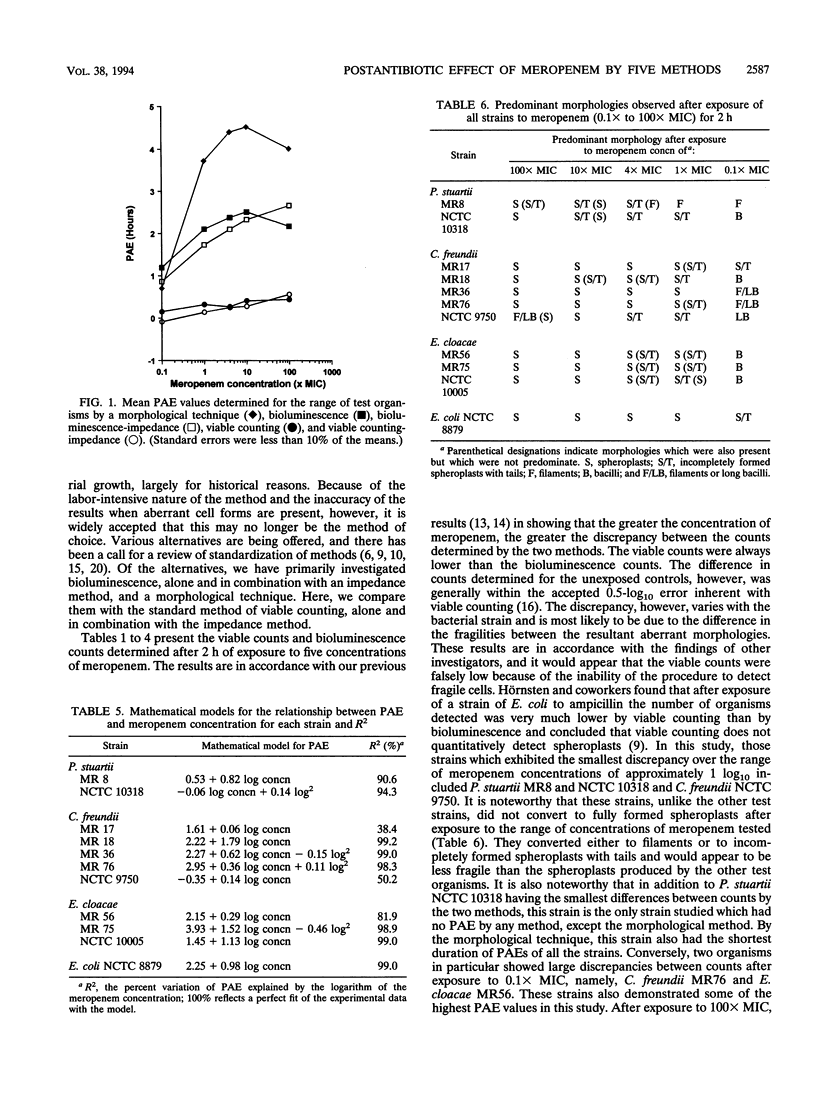
Abstract
The postantibiotic effect (PAE) of meropenem was determined for 11 strains, both clinical isolates and reference strains of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The study compares PAE results obtained by five methods used to monitor bacterial regrowth, including viable counting, alone and in combination with impedance; bioluminescence, alone and in combination with impedance; and a morphological technique. After exposure of the test organisms to meropenem (0.1 x to 100 x MIC) for 2 h, concentration-dependent differences in counts by bioluminescence and viable counts were observed, the latter always being lower. The differences varied with the test organism. For example, after exposure of Providentia stuartii NCTC 10318 to 0.1 x MIC, the counts were 5.5 x 10(5) and 2.0 x 10(5) whereas after exposure of Citrobacter freundii MR76 to 0.1 x MIC of meropenem the counts were 2.3 x 10(6) and 6.8 x 10(3) by bioluminescence and viable counting, respectively. The discrepancies were probably due to the relative inability of the viable counting procedure to detect fragile aberrant morphologies and resulted in differences in the calculated PAE values. With methods which do not detect fragile morphologies, the PAE may be underestimated. A general trend was observed for the order of magnitude of the PAEs by the following methods (in order of decreasing magnitude of PAE): (i) morphological technique, (ii) bioluminescence technique alone, (iii) bioluminescence in combination with impedance, (iv) viable counting in combination with impedance, and (v) viable counting alone. It is our opinion that of the methods examined in this study, bioluminescence in combination with impedance best reflects the true values for PAEs, and these results were examined more closely.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gould I. M., Jason A. C., Milne K. Use of the Malthus Microbial Growth Analyser to study the post antibiotic effect of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Oct;24(4):523–531. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould I. M., Wilson D., Milne K., Paterson A., Golder D., Russell D. Interaction of imipenem with erythromycin and tetracycline assessed by microdilution checkerboard techniques. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2407–2409. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Nilsson L. E., Kihlström E., Maller R. Postantibiotic effect of beta-lactam antibiotics on Escherichia coli evaluated by bioluminescence assay of bacterial ATP. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Nilsson L. E., Nilsson M., Maller R. Post-antibiotic effect of beta-lactam antibiotics on gram-negative bacteria in relation to morphology, initial killing and MIC. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;10(11):927–934. doi: 10.1007/BF02005446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Svensson E., Nilsson M., Nilsson L. E., Hörnsten E. G., Maller R. Effects of imipenem on Escherichia coli studied using bioluminescence, viable counting and microscopy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Feb;31(2):245–260. doi: 10.1093/jac/31.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörnsten E. G., Nilsson L. E., Elwing H., Lundström I. Effects of Escherichia coli spheroplast formation on assays of H2 and adenosine triphosphate based ampicillin susceptibility tests. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;12(2):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson B., Hanberger H., Maller R., Nilsson L. E., Nilsson M. Synergic post-antibiotic effect of amikacin in combination with beta-lactam antibiotics on gram-negative bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Jul;28(1):25–34. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Ernst J., Amaral L. The post-antibiotic effect defined by bacterial morphology. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Apr;23(4):485–491. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.4.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie F. M., Gould I. M., Chapman D. G., Jason D. Comparison of methodologies used in assessing the postantibiotic effect. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994 Aug;34(2):223–230. doi: 10.1093/jac/34.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie F. M., Gould I. M. The post-antibiotic effect. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Oct;32(4):519–537. doi: 10.1093/jac/32.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. R., Roberts D. E., Ingold A., Want S. V. Osmotically stable L forms of Haemophilus influenzae and their significance in testing sensitivity to penicillins. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jul;27(7):560–564. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.7.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenholt I., Isaksson B., Nilsson L., Cars O. Postantibiotic and bactericidal effect of imipenem against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;8(2):136–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01963897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. C., Jason A. C., Hobbs G., Gibson D. M., Christie R. H. Electronic measurement of bacterial growth. J Phys E. 1978 Jun;11(6):560–568. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/11/6/017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D., Higgs E., Rutman A., Cole P. Isolation of spheroplastic forms of Haemophilus influenzae from sputum in conventionally treated chronic bronchial sepsis using selective medium supplemented with N-acetyl-D-glucosamine: possible reservoir for re-emergence of infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Nov 24;289(6456):1409–1412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6456.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley T., Edwards C., Hastings M. Post-antibiotic effect of teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 May;27(5):683–684. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



