Abstract
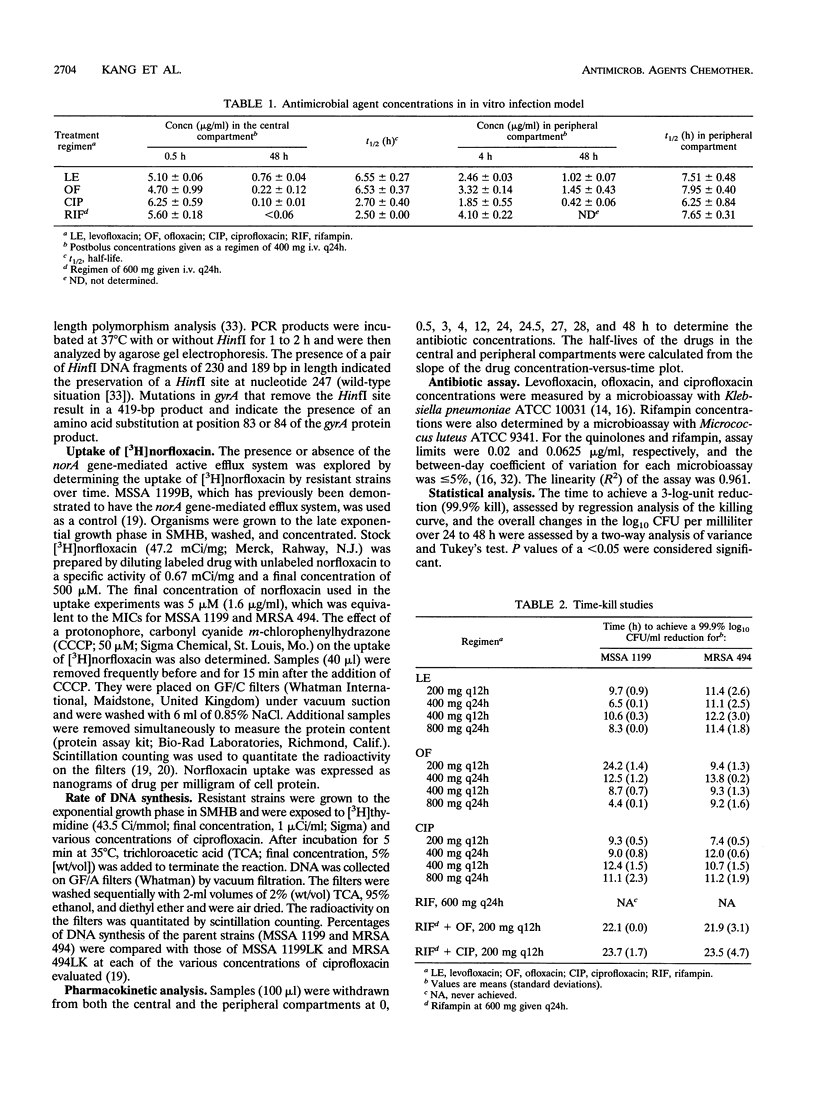
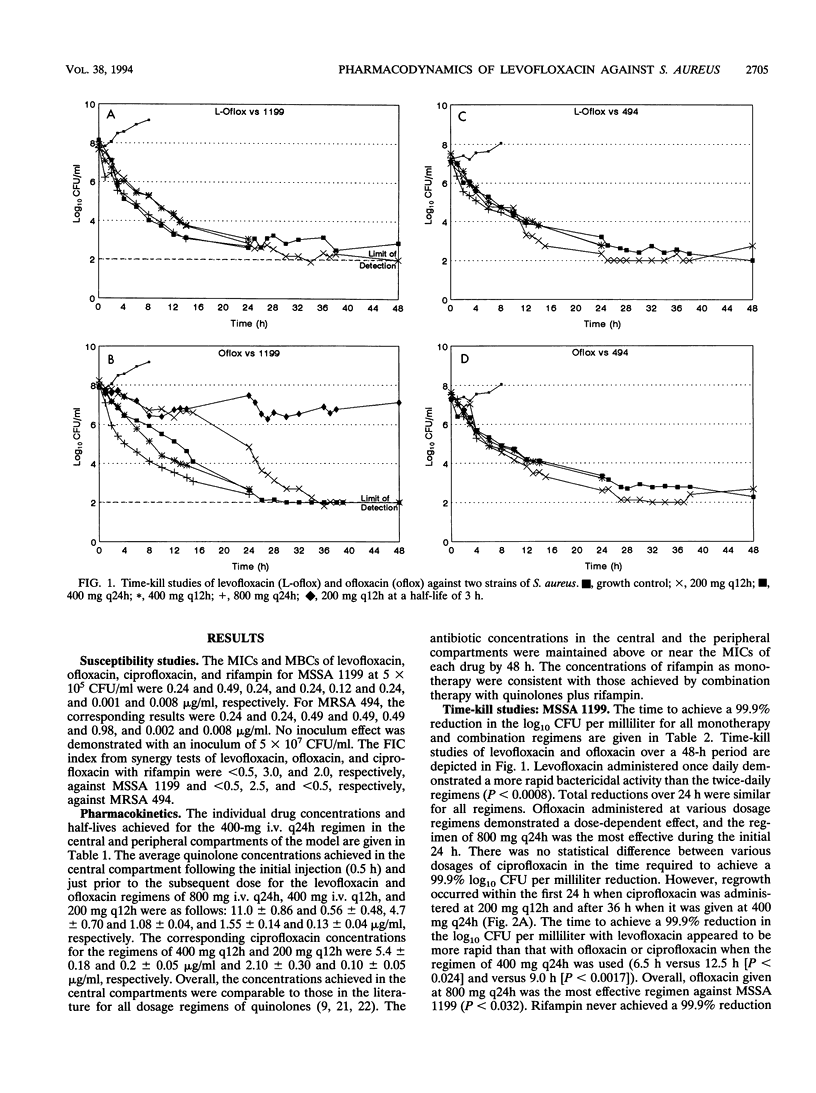
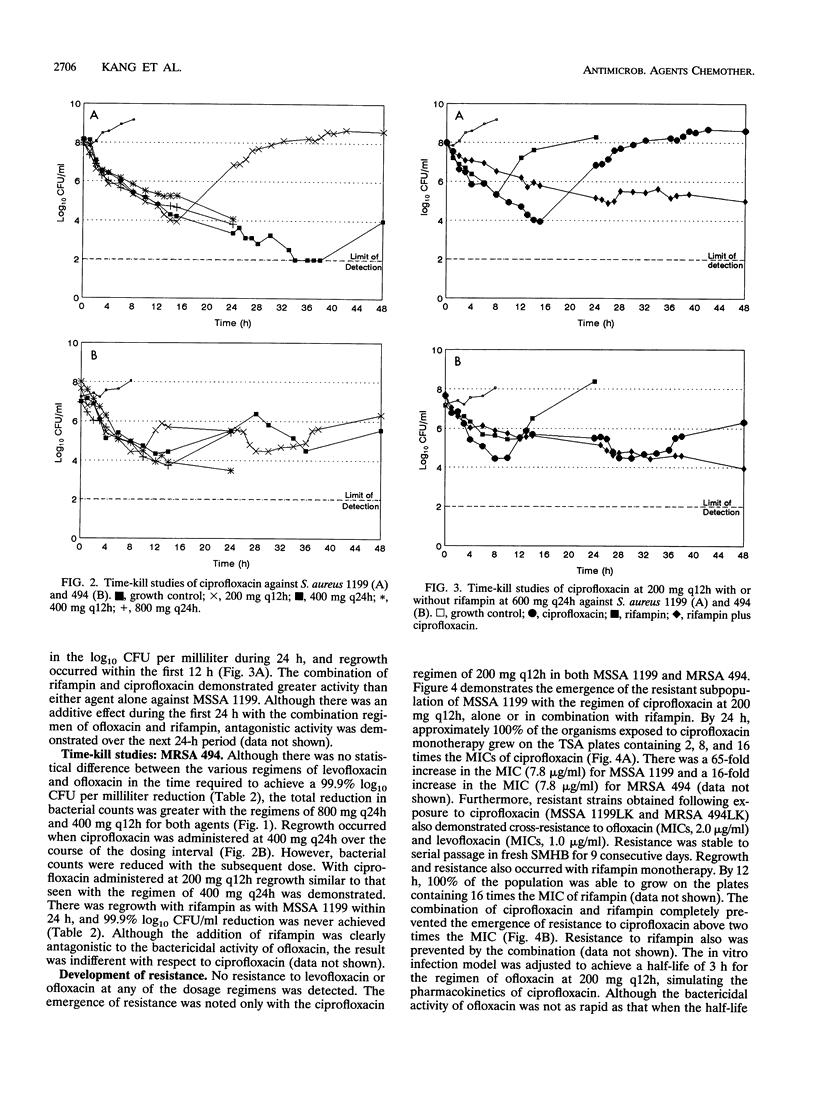
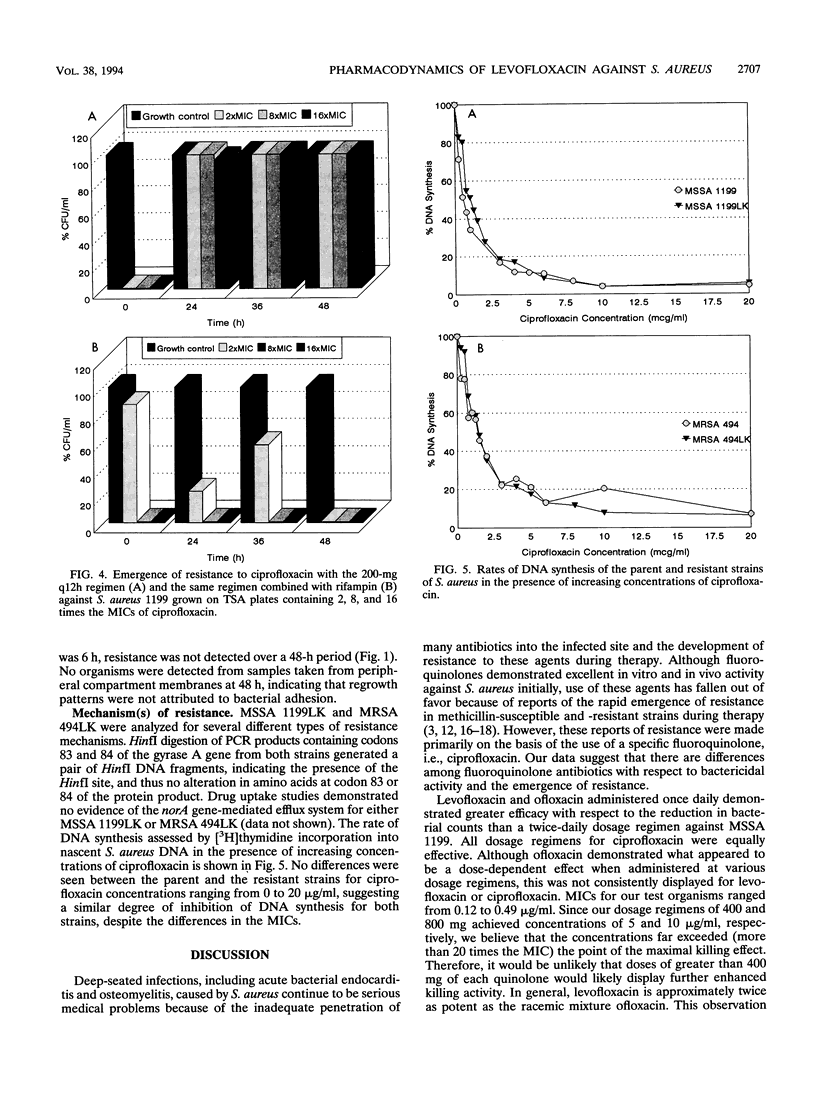
The pharmacodynamic properties of levofloxacin (an optically active isomer of ofloxacin), ofloxacin, and ciprofloxacin, alone and in combination with rifampin, were evaluated over 24 to 48 h against clinical isolates of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA 1199 and MRSA 494, respectively) in an in vitro infection model. The incidence of the emergence of resistance among the test strains was also determined. The fluoroquinolones were administered to simulate dosage regimens of 200 mg, 400 mg given intravenously (i.v.) every 12 h (q12h), and 400 and 800 mg given i.v. q24h. Rifampin was dosed at 600 mg i.v. q24h. Although the MICs and MBCs of the quinolones were similar (< or = 0.49 microgram/ml), levofloxacin was the most potent agent in time-kill studies on the basis of the time required to achieve a 99.9% reduction in the number of log10 CFU per milliliter (e.g., with the regimen of levofloxacin [400 mg q24h, 6.5 h] versus ofloxacin [12.5 h], P < 0.024, and levofloxacin versus ciprofloxacin [6.5 versus 9.0 h], P < 0.0017) against MSSA 1199. The killing activity of levofloxacin was similar to that of ofloxacin against MRSA 494 (time to achieve a 99.9% reduction in the number of log10 CFU per milliliter, 11.1 versus 13.8 h, respectively). Levofloxacin and ofloxacin dosed once daily demonstrated greater bactericidal activity than when they were dosed twice daily against MSSA 1199. Resistance to levofloxacin or ofloxacin was not observed with any dosage regimen. Furthermore, resistance to ofloxacin was not detected when the half-life was reduced from 6 to 3 h. Regrowth and stable resistance (65-fold increase in the MIC for MSSA 1199; 16-fold increase in the MIC for MRSA 494) were noted within 24 h of exposure to ciprofloxacin at 200 mg q12h. Combination therapy with rifampin prevented the emergence of resistance to ciprofloxacin. Neither DNA gyrase alteration nor an energy-dependent efflux process mediated by the norA gene appeared to be responsible for the resistance observed. Our data suggest that with levofloxacin there is a more rapid onset of bactericidal activity than with ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin against MSSA 1199 and that the activity of levofloxacin is similar to that of ofloxacin but better than that of ciprofloxacin against MRSA 494. Resistance was noted only after exposure to the low dose of ciprofloxacin. Resistance to ofloxacin did not develop even when the pharmacokinetics of the drug were set to equal those of ciprofloxacin, suggesting that ofloxacin differs from ciprofloxacin irrespective of time of exposure. The resistance to ciprofloxacin that developed in our vitro model may be mediated by the cfx-ofx locus, which has been shown to be associated with low-level fluoroquinolone resistance. Overall, levofloxacin demonstrated potent bactericidal activity against S. aureus, without the emergence of resistance in our infection model. Quinolones dosed once daily were more effective than equivalent dosages administered twice daily. The addition of rifampin was not synergistic but prevented the emergence of ciprofloxacin resistance.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser J. In-vitro model for simultaneous simulation of the serum kinetics of two drugs with different half-lives. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):125–130. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H. M., Rimland D., Carroll D. J., Terry P., Wachsmuth I. K. Rapid development of ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1279–1285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Combination of ofloxacin and other antimicrobial agents. J Chemother. 1990 Dec;2(6):343–347. doi: 10.1080/1120009x.1990.11739040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Lafredo S. C., Foleno B., Isaacson D. M., Barrett J. F., Tobia A. J., Rosenthale M. E. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of levofloxacin (l-ofloxacin), an optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):860–866. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison M. W., Vance-Bryan K., Larson T. A., Toscano J. P., Rotschafer J. C. Assessment of effects of protein binding on daptomycin and vancomycin killing of Staphylococcus aureus by using an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1925–1931. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswitz J. J., Willard K. E., Fasching C. E., Peterson L. R. Detection of gyrA gene mutations associated with ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: analysis by polymerase chain reaction and automated direct DNA sequencing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1166–1169. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay D. R., Opsahl J. A., McMahon F. G., Vargas R., Matzke G. R., Flor S. Safety and pharmacokinetics of multiple doses of intravenous ofloxacin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):308–312. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa I., Atarashi S., Yokohama S., Imamura M., Sakano K., Furukawa M. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):163–164. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori S., Ohshita Y., Utsui Y., Hiramatsu K. Sequential acquisition of norfloxacin and ofloxacin resistance by methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2278–2284. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys H., Mulvihill E. Ciprofloxacin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1985 Aug 17;2(8451):383–383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura M., Shibamura S., Hayakawa I., Osada Y. Inhibition of DNA gyrase by optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):325–327. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos B., Ledergerber B., Flepp M., Bettex J. D., Lüthy R., Siegenthaler W. Comparison of high-pressure liquid chromatography and bioassay for determination of ciprofloxacin in serum and urine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):353–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Barriere S. L., Schaberg D. R., Fekety R. The emergence of resistance to ciprofloxacin during treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):753–758. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Ciprofloxacin and rifampin, alone and in combination, for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1184–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Efficacy of ofloxacin in experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):257–260. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Lamp K. C., Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J. CI-960, a new fluoroquinolone, for therapy of experimental ciprofloxacin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1192–1197. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Ruble C. A. Efflux-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):1086–1094. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Ruble C. A. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1080–1086. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamp K. C., Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J. Ofloxacin clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992 Jan;22(1):32–46. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199222010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel M. Ciprofloxacin: chemistry, mechanism of action, resistance, antimicrobial spectrum, pharmacokinetics, clinical trials, and adverse reactions. Pharmacotherapy. 1988;8(1):3–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1875-9114.1988.tb04058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel M., Vallée F., Bergeron M. G. Tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin after single and multiple doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):501–505. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin C. S., Smith J. T. Bactericidal mechanisms of ofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):1–8. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Höffken G., Olschewski P., Sievers B., Kirch A., Borner K., Koeppe P. Comparative pharmacokinetics of intravenous ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):73–79. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey C., Bertasso A., Pace J., Georgopapadakou N. H. Quinolone accumulation in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1601–1605. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath B. J., Bailey E. M., Lamp K. C., Rybak M. J. Pharmacodynamics of once-daily amikacin in various combinations with cefepime, aztreonam, and ceftazidime against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vitro infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2741–2746. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N., Yoshida S., Wakebe H., Inoue M., Yamaguchi T., Mitsuhashi S. Mechanisms of clinical resistance to fluoroquinolones in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2562–2567. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X. In vitro activity of S-ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1105–1107. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segreti J., Gvazdinskas L. C., Trenholme G. M. In vitro activity of minocycline and rifampin against staphylococci. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;12(3):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. J., Yin E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):573–579. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S., Peterson L. R., Fisher L. M. Ciprofloxacin resistance in coagulase-positive and -negative staphylococci: role of mutations at serine 84 in the DNA gyrase A protein of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2151–2154. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucksis M., Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. A novel locus conferring fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5854–5860. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5854-5860.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Fujimoto T., Sato K., Osada Y. In vitro activity of DR-3355, an optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1336–1340. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Joly P. Comparative in-vitro activities of teicoplanin, vancomycin, coumermycin and ciprofloxacin, alone and in combination with rifampicin or LM 427, against Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Mar;19(3):313–320. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Lagast H., Klastersky J. Antistaphylococcal activity of rifampin with other antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):365–371. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]