Abstract
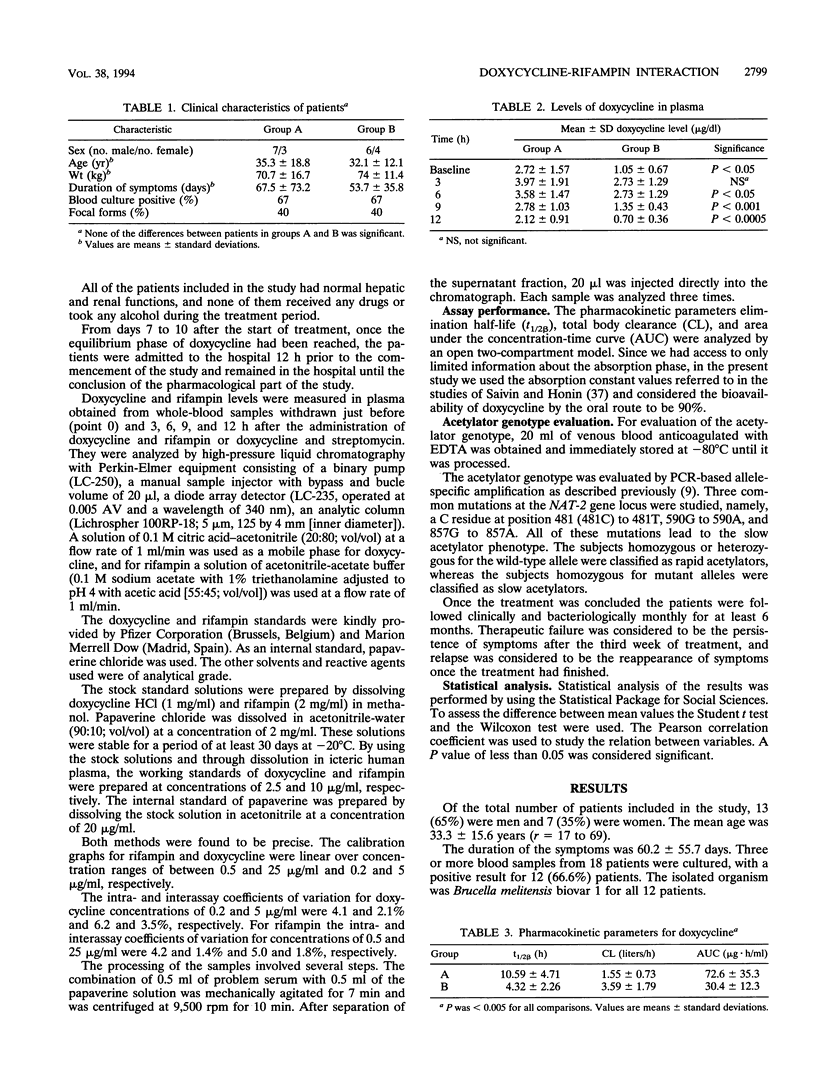
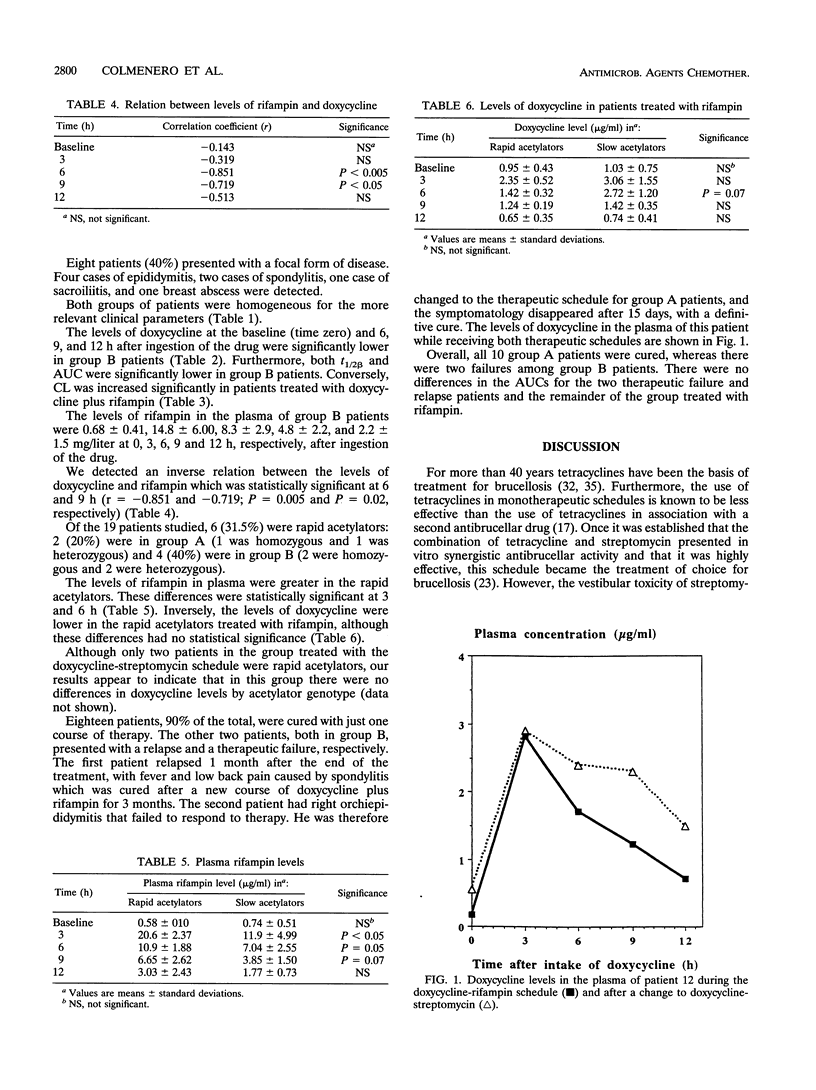
We studied the possible interaction between rifampin and doxycycline in 20 patients with brucellosis treated randomly with either doxycycline and streptomycin or doxycycline and rifampin. The doxycycline levels in the plasma of patients in the group treated with rifampin were significantly lower than those in the plasma of patients treated with doxycycline and streptomycin. Furthermore, clearance in patients treated with rifampin was significantly higher than that in patients treated with doxycycline and streptomycin, and consequently, the elimination half-life and the area under the concentration-time curve were significantly lower. There was no therapeutic failure or relapse in the group treated with doxycycline and streptomycin, whereas 2 of 10 patients in the group treated with doxycycline and rifampin had a therapeutic failure or relapse. The plasma doxycycline levels had an inverse correlation with plasma rifampin levels. In the group treated with rifampin, those who were rapid acetylators had lower levels of doxycycline. In conclusion, combined treatment with rifampin reduces the levels of doxycycline in plasma. These data suggest that therapeutic failures or relapses may result from this interaction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariza J., Gudiol F., Pallares R., Viladrich P. F., Rufi G., Corredoira J., Miravitlles M. R. Treatment of human brucellosis with doxycycline plus rifampin or doxycycline plus streptomycin. A randomized, double-blind study. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Jul 1;117(1):25–30. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariza J., Gudiol F., Pallarés R., Rufí G., Fernández-Viladrich P. Comparative trial of rifampin-doxycycline versus tetracycline-streptomycin in the therapy of human brucellosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):548–551. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariza J., Gudiol F., Valverde J., Pallarés R., Fernández-Viladrich P., Rufí G., Espadaler L., Fernández-Nogues F. Brucellar spondylitis: a detailed analysis based on current findings. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):656–664. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.5.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baciewicz A. M., Self T. H., Bekemeyer W. B. Update on rifampin drug interactions. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Mar;147(3):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baciewicz A. M., Self T. H. Rifampin drug interactions. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Aug;144(8):1667–1671. doi: 10.1001/archinte.144.8.1667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand A., Jonquet O. Traitement antibiotique de la brucellose. Sem Hop. 1982 Feb 4;58(5):281–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand A., Roux J., Janbon F., Jourdan J., Jonquet O. Traitement de la brucellose par la rifampicine. Résultats préliminaires. Nouv Presse Med. 1979 Nov 12;8(44):3635–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum M., Demierre A., Grant D. M., Heim M., Meyer U. A. Molecular mechanism of slow acetylation of drugs and carcinogens in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5237–5241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J., Liñares J., López de Goicoechea M. J., Ariza J., Cisnal M. C., Martin R. In-vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone and five other antimicrobial agents against 95 strains of Brucella melitensis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):459–461. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisneros J. M., Viciana P., Colmenero J., Pachón J., Martinez C., Alarcón A. Multicenter prospective study of treatment of Brucella melitensis brucellosis with doxycycline for 6 weeks plus streptomycin for 2 weeks. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):881–883. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmenero Castillo J. D., Hernandez Marquez S., Reguera Iglesias J. M., Cabrera Franquelo F., Rius Diaz F., Alonso A. Comparative trial of doxycycline plus streptomycin versus doxycycline plus rifampin for the therapy of human brucellosis. Chemotherapy. 1989;35(2):146–152. doi: 10.1159/000238662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J. Determination of the in vitro sensitivity of Brucella strains to rifampicin. Br Vet J. 1976 May-Jun;132(3):266–275. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)34686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiz J. M., Sabbaghian H., Sohrabi F. A comparative study of therapeutic agents used for treatment of acute brucellosis. Br J Clin Pract. 1973 Nov;27(11):410–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garraffo A., Dellamonica P., Fournier J. P., Lapalus P., Bernard E. The effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of doxycycline. Infection. 1988 Sep-Oct;16(5):297–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01645076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garraffo R., Dellamonica P., Fournier J. P., Lapalus P., Bernard E., Beziau H., Chichmanian R. M. Effet de la rifampicine sur la pharmacocinétique de la doxycycline. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1987 Jun;35(5 Pt 2):746–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeau P., Fuchs G., Guillevin L., Philippon A., Tucat G., Cabane J., Herson S. Traitement de la brucellose humaine par la rifampicine. Sem Hop. 1984 Jan 12;60(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaney D., Eknoyan G. Minocycline and doxycycline kinetics in chronic renal failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Aug;24(2):233–239. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978242233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jezequel A. M., Orlandi F., Tenconi L. T. Changes of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum induced by rifampicin in human and guinea-pig hepatocytes. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):984–987. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karreth S., Lenk W. The metabolism of 4-aminobiphenyl in rat. I. Reaction of N-hydroxy-4-aminobiphenyl with rat blood in vivo. Xenobiotica. 1991 Mar;21(3):417–428. doi: 10.3109/00498259109039481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land S. J., Zukowski K., Lee M. S., Debiec-Rychter M., King C. M., Wang C. Y. Metabolism of aromatic amines: relationships of N-acetylation, O-acetylation, N,O-acetyltransfer and deacetylation in human liver and urinary bladder. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Apr;10(4):727–731. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R. M., Fox W. R., Baty J. D., Willis R. G. In vitro studies on the deacetylation-reacetylation of arylamides and the transacetylation of arylamines by human and rat whole blood. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1671–1678. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens-Terol J., Busquets R. M. Brucellosis treated with rifampicin. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Jun;55(6):486–488. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.6.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGILL G. B., KILLOUGH J. H. Oxytetracycline-streptomycin therapy in brucellosis due to Brucella melitensis. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1953 Feb;91(2):204–211. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1953.00240140064005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFISCHNER W. C., Jr, ISHAK K. G., NEPTUNE E. M., Jr, FOX S. M., 3rd, FARID Z., EL DIN G. N. Brucellosis in Egypt; a review of experience with 228 patients. Am J Med. 1957 Jun;22(6):915–929. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttilå O., Neuvonen P. J., Aho K., Lehtovaara R. Interaction between doxycycline and some antiepileptic drugs. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 1;2(5917):470–472. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5917.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Plommet M. G., Kazmierczak A., Marly J. L., Nevot P. A. Rifampin in the treatment of experimental brucellosis in mice and guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):481–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn K. H., Mooy J., Böhm R., vd Vet A. Reduction of bioavailability of verapamil by rifampin. N Engl J Med. 1985 Apr 4;312(14):920–921. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198504043121413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo-Naudi J., Griscti-Soler N., Ganado W. Human brucellosis: an evaluation of antibiotics in the treatment of brucellosis. Postgrad Med J. 1967 Aug;43(502):520–526. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.43.502.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson L., Farrell I. D., Hinchliffe P. M. The sensitivity of Brucella abortus to chemotherapeutic agents. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):549–557. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPINK W. W. Some biologic and clinical problems related to intracellular parasitism in brucellosis. N Engl J Med. 1952 Oct 16;247(16):603–610. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195210162471605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saivin S., Houin G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of doxycycline and minocycline. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Dec;15(6):355–366. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198815060-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda M., Vree T. B., Beneken Kolmer E. W., Arts T. H. The role of plasma protein binding on the metabolism and renal excretion of sulphadimethoxine and its metabolite N4-acetylsulphadimethoxine in pigs. Vet Q. 1990 Apr;12(2):87–97. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1990.9694250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solera J., Martínez-Alfaro E., Sáez L. Metaanálisis sobre la eficacia de la combinación de rifampicina y doxiciclina en el tratamiento de la brucelosis humana. Med Clin (Barc) 1994 May 21;102(19):731–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solera J., Medrano F., Rodríguez M., Geijo P., Paulino J. Ensayo terapéutico comparativo y multicéntrico de rifampicina y doxiciclina frente a estreptomicina y doxiciclina en la brucelosis humana. Med Clin (Barc) 1991 May 4;96(17):649–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twum-Barima Y., Carruthers S. G. Quinidine-rifampin interaction. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1466–1469. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. J. Human brucellosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):821–842. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



