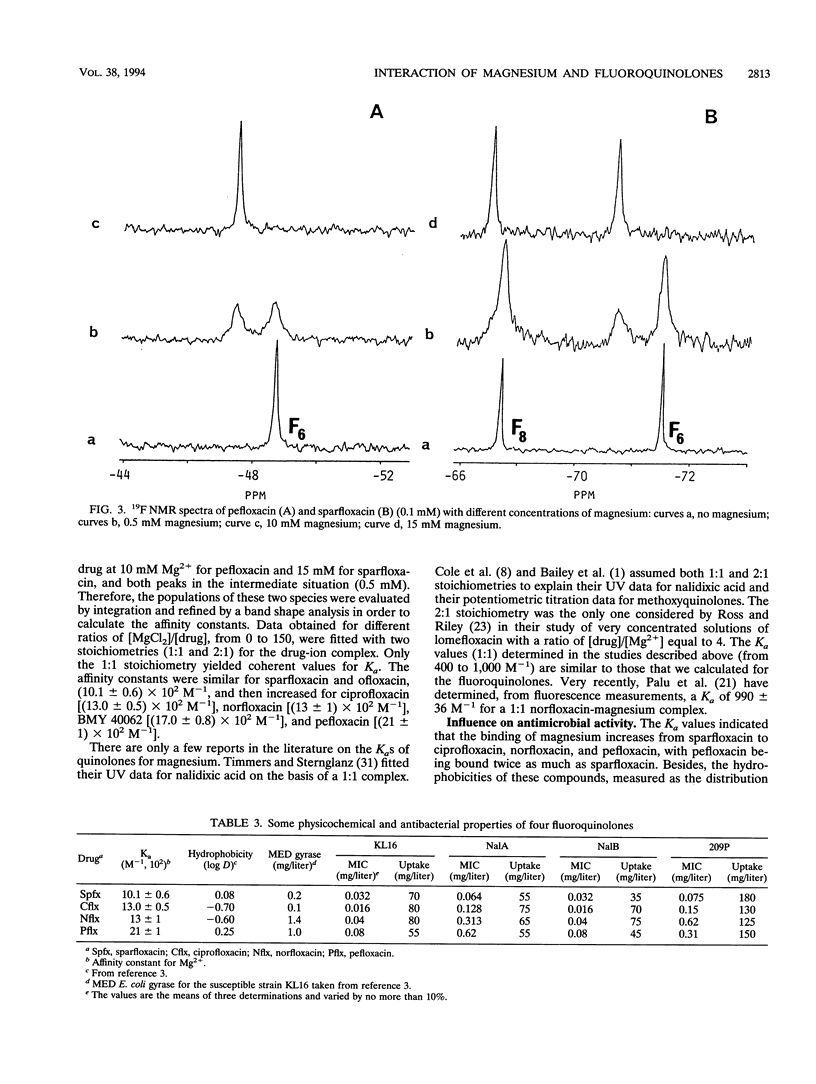
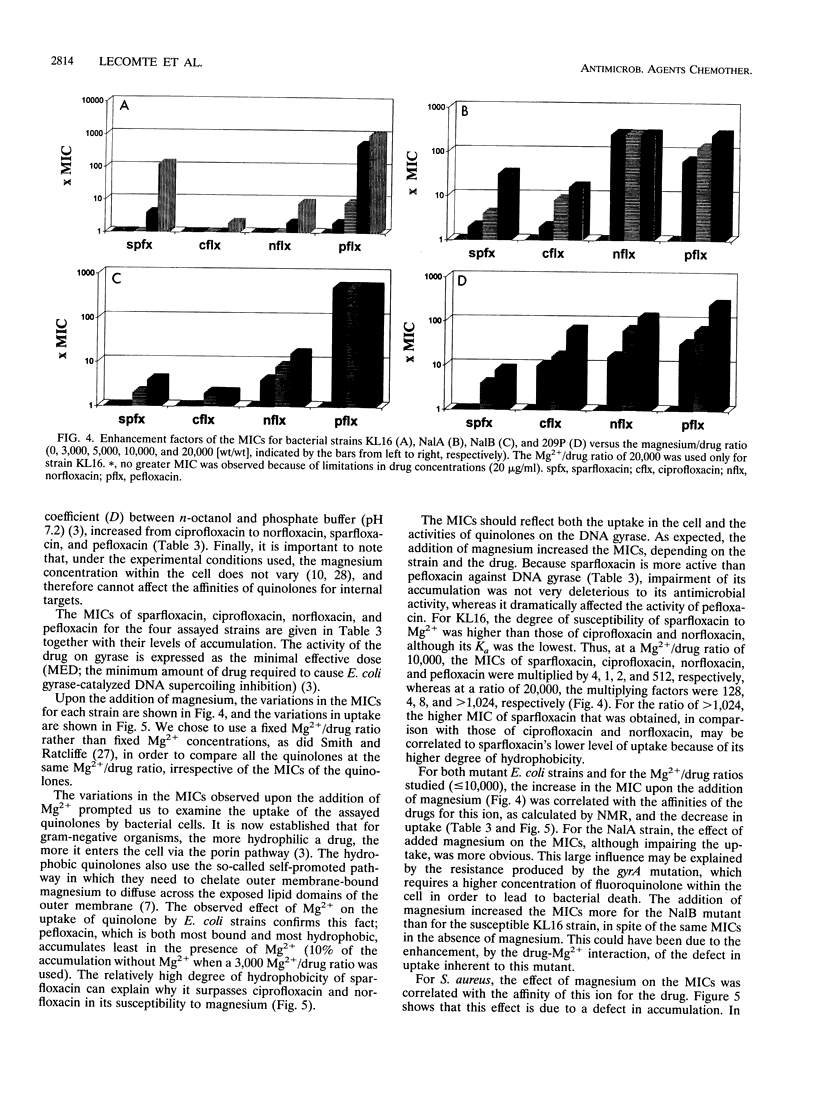
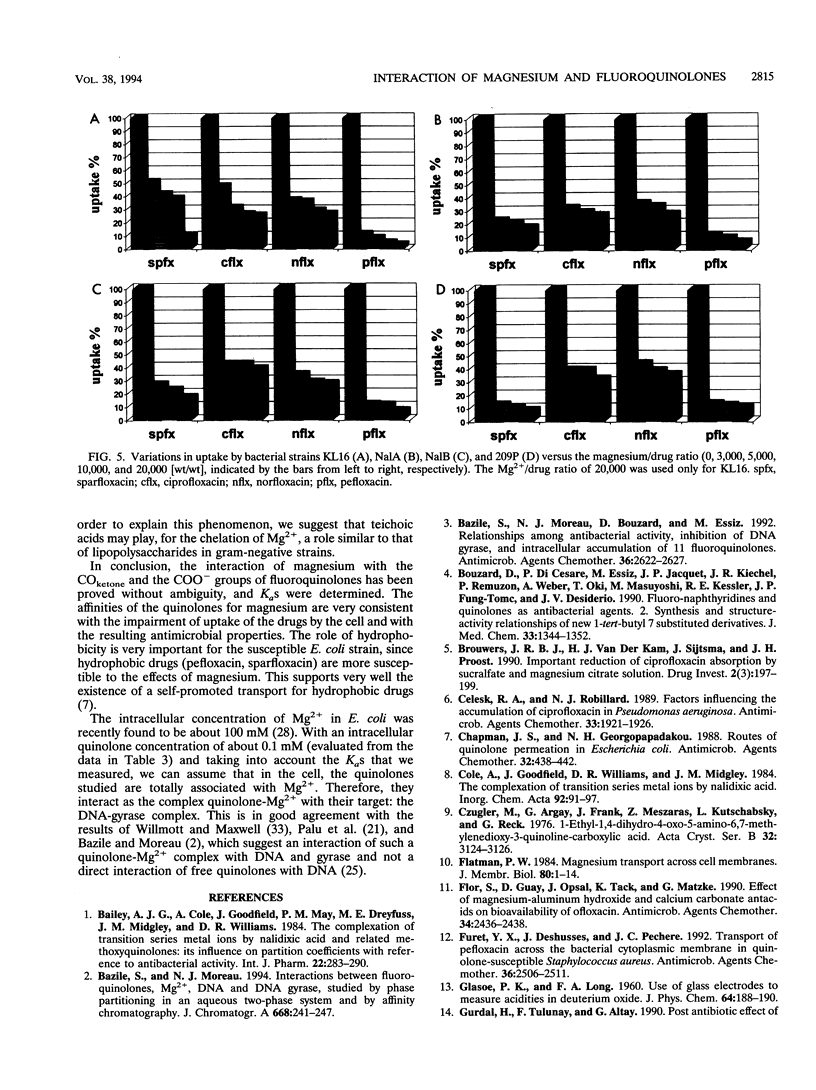
Abstract
By using infrared and 19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopies, we localized the binding site and measured the affinity of magnesium for six fluoroquinolones. It was proven that magnesium is situated between the ketone and the carboxylate groups. We determined the binding constants for the 1:1 Mg(2+)-drug complex in solution. Sparfloxacin and pefloxacin, with affinity constants (Ka) of (10.1 +/- 0.6) x 10(2) M-1 and (21 +/- 1) x 10(2) M-1, respectively, were the least and the most bound, respectively. The trend of the affinities of the assayed fluoroquinolones for magnesium was correlated with their antimicrobial activities against four bacteria and with their accumulation by these bacteria. The reference strain, Escherichia coli KL16, and two resistant mutants, NalA (gyrase mutation) and NalB (uptake defect), plus Staphylococcus aureus 209P were used. It appeared that, in every case, an impairment of accumulation is responsible for the increase in the MICs observed upon the addition of magnesium.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazile S., Moreau N., Bouzard D., Essiz M. Relationships among antibacterial activity, inhibition of DNA gyrase, and intracellular accumulation of 11 fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2622–2627. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzard D., Di Cesare P., Essiz M., Jacquet J. P., Kiechel J. R., Remuzon P., Weber A., Oki T., Masuyoshi M., Kessler R. E. Fluoronaphthyridines and quinolones as antibacterial agents. 2. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of new 1-tert-butyl 7-substituted derivatives. J Med Chem. 1990 May;33(5):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/jm00167a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Factors influencing the accumulation of ciprofloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1921–1926. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S., Georgopapadakou N. H. Routes of quinolone permeation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):438–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W. Magnesium transport across cell membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01868686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor S., Guay D. R., Opsahl J. A., Tack K., Matzke G. R. Effects of magnesium-aluminum hydroxide and calcium carbonate antacids on bioavailability of ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2436–2438. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furet Y. X., Deshusses J., Pechère J. C. Transport of pefloxacin across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane in quinolone-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2506–2511. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khac S. B., Moreau N. J. Interactions between fluoroquinolones, Mg2+, DNA and DNA gyrase, studied by phase partitioning in an aqueous two-phase system and by affinity chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 1994 May 6;668(1):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(94)80114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A. The molecular basis of quinolone action. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Oct;30(4):409–414. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.4.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey C., Bertasso A., Pace J., Georgopapadakou N. H. Quinolone accumulation in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1601–1605. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Yamamoto M., Arita T. Interactions of aluminum, magnesium, and calcium ions with nalidixic acid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1978 May;26(5):1505–1510. doi: 10.1248/cpb.26.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane barrier as a mechanism of antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palù G., Valisena S., Ciarrocchi G., Gatto B., Palumbo M. Quinolone binding to DNA is mediated by magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9671–9675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Giraldo C., Hurtado C., Morán F. J., Blanco M. T., Gómez-García A. C. The influence of magnesium on ofloxacin activity against different growth phases of Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jun;25(6):1021–1022. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.6.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Mitscher L. A., Sharma P. N., O'Donnell T. J., Chu D. W., Cooper C. S., Rosen T., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: a cooperative drug--DNA binding model. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3886–3894. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by analogues of nalidixic acid: the target of the drugs is DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):307–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takács-Novák K., Noszál B., Hermecz I., Keresztúri G., Podányi B., Szász G. Protonation equilibria of quinolone antibacterials. J Pharm Sci. 1990 Nov;79(11):1023–1028. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600791116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K., Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation dissociation constants of nalidixic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem. 1978 Aug;9(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornaletti S., Pedrini A. M. Studies on the interaction of 4-quinolones with DNA by DNA unwinding experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 31;949(3):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmott C. J., Maxwell A. A single point mutation in the DNA gyrase A protein greatly reduces binding of fluoroquinolones to the gyrase-DNA complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jan;37(1):126–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Nakamura M., Bogaki M., Ito H., Kojima T., Hattori H., Nakamura S. Mechanism of action of quinolones against Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):839–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]