Abstract
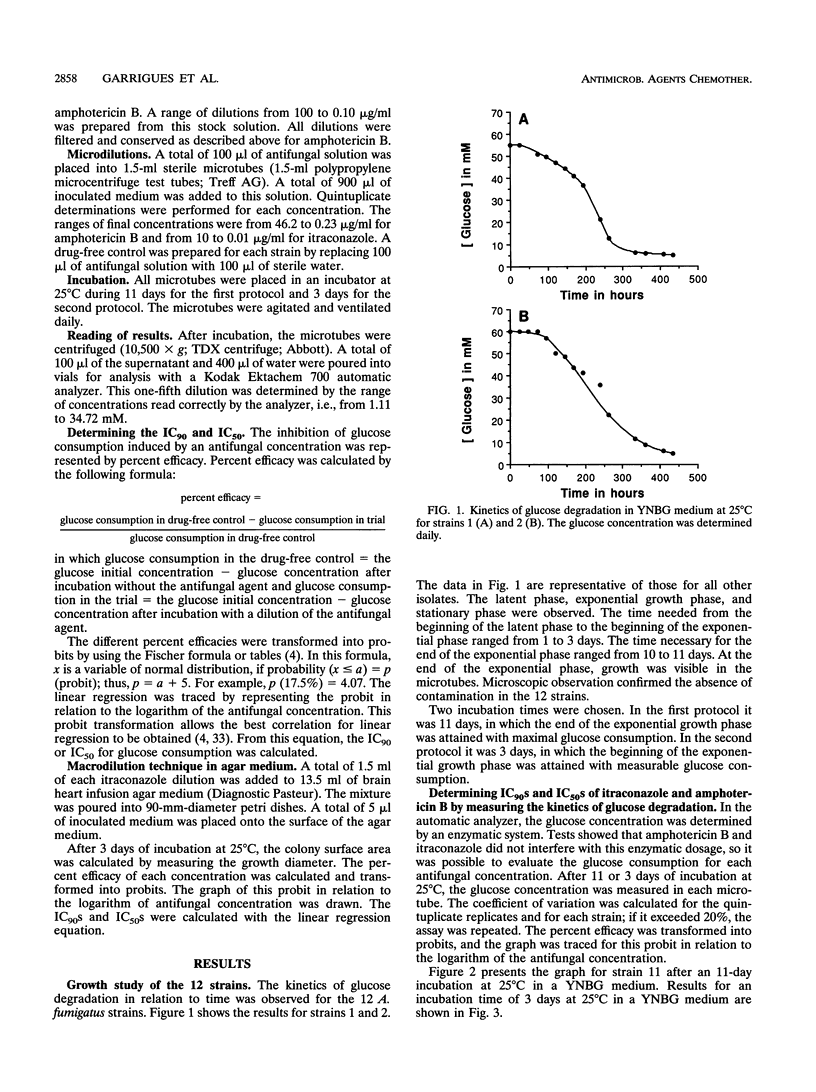
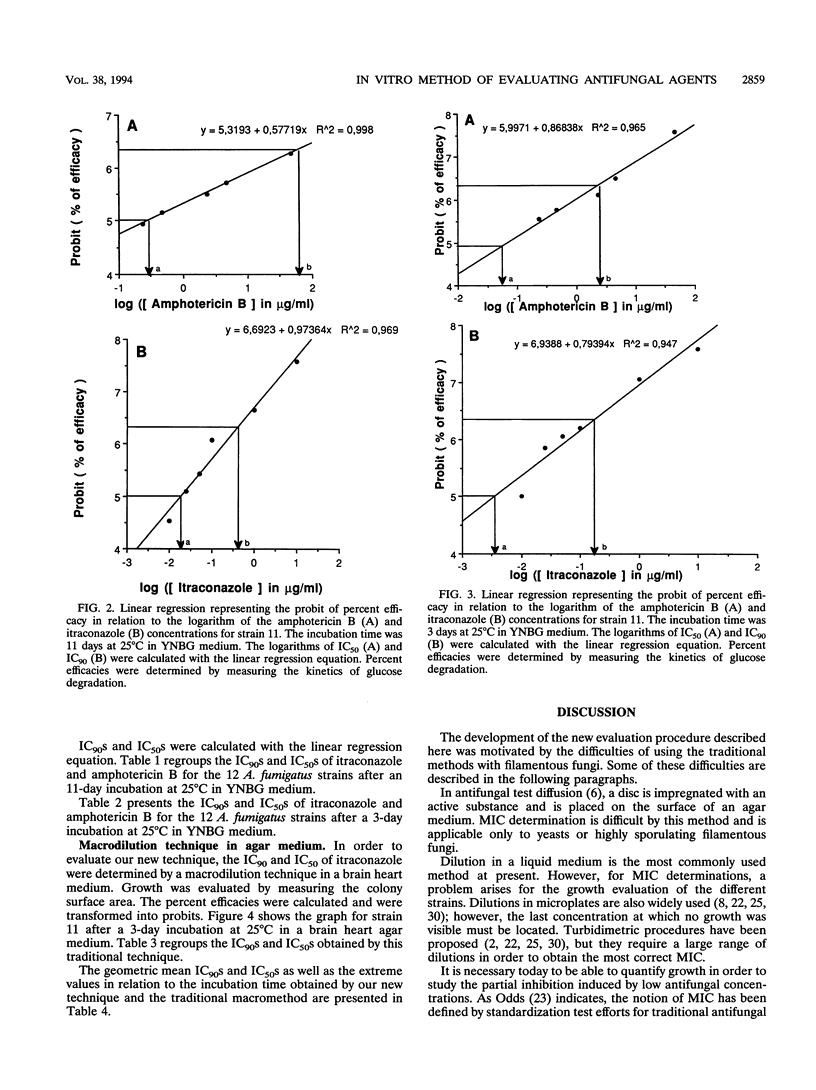
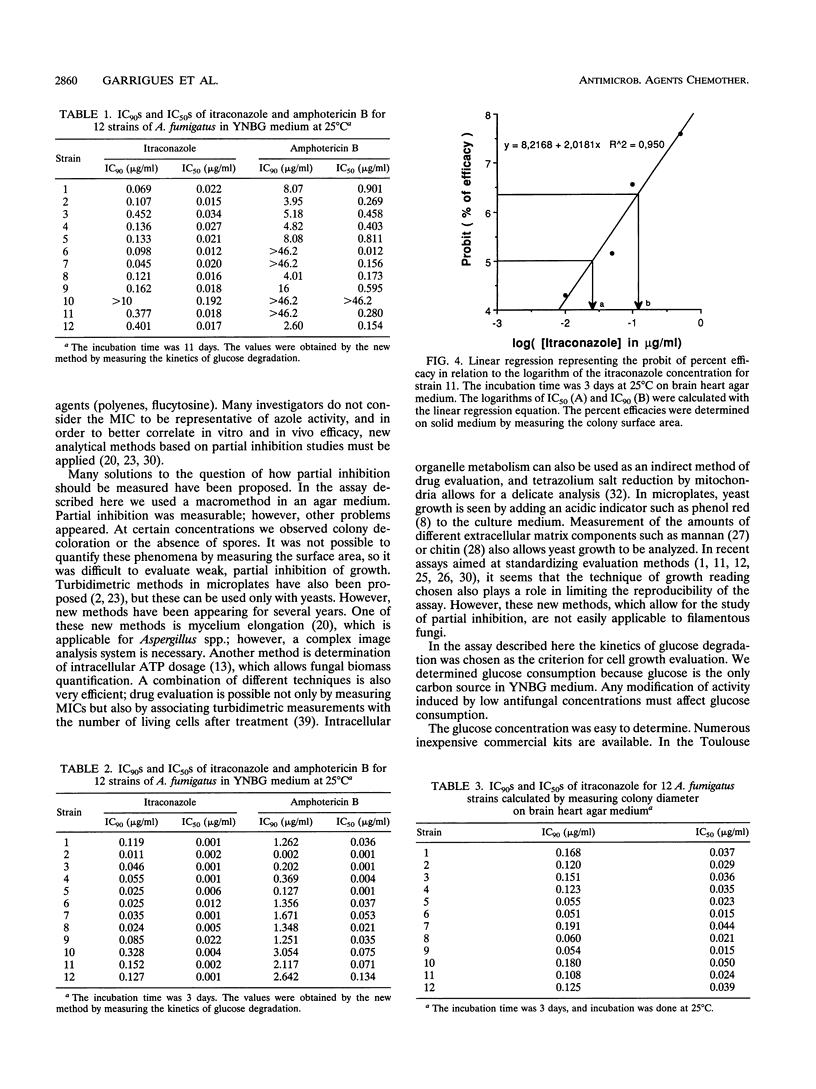
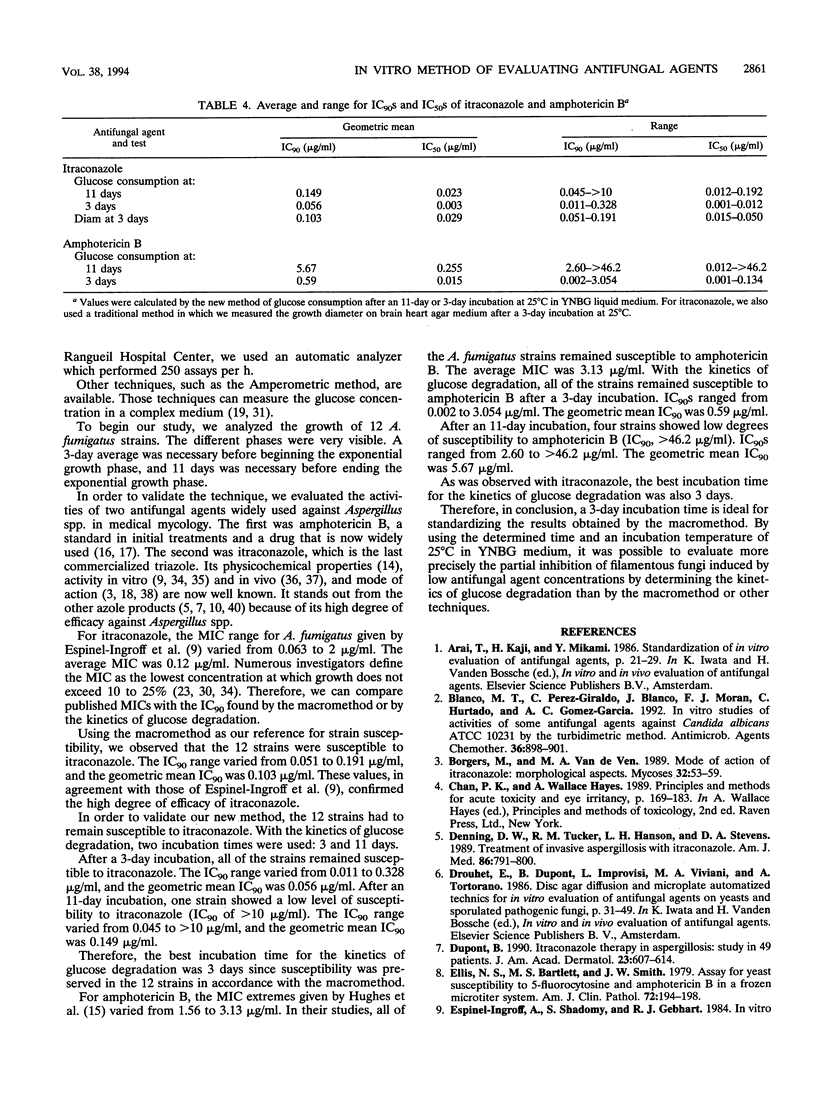
We developed a new in vitro method of evaluating antifungal molecules. Fungal growth was determined by measuring glucose consumption, the only carbon source in a synthetic medium. First, the growth of 12 Aspergillus fumigatus strains was studied. Glucose consumption was an excellent indicator of fungal growth. Second, the partial inhibition of growth was calculated in terms of the 90% or 50% inhibitory concentration for the 12 strains after treatment with itraconazole and amphotericin B. With a 3-day incubation time, the calculated 90% and 50% inhibitory concentrations agreed with those obtained by a macromethod and with those reported in previous publications. In each case the high degrees of efficacy of itraconazole and amphotericin B against A. fumigatus were confirmed. Partial inhibition induced by low concentrations of antifungal agents was quantifiable by this new method.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanco M. T., Pérez-Giraldo C., Blanco J., Morán F. J., Hurtado C., Gómez-García A. C. In vitro studies of activities of some antifungal agents against Candida albicans ATCC 10231 by the turbidimetric method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):898–901. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgers M., Van de Ven M. A. Mode of action of itraconazole: morphological aspects. Mycoses. 1989;32 (Suppl 1):53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1989.tb02294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Tucker R. M., Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis with itraconazole. Am J Med. 1989 Jun;86(6 Pt 2):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B. Itraconazole therapy in aspergillosis: study in 49 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Sep;23(3 Pt 2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70263-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis N. S., Bartlett M. S., Smith J. W. Assay for yeast susceptibility to 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B in a frozen microtiter system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;72(2):194–198. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B. D., Armstrong D., Yu B., Gold J. W. Invasive aspergillosis. Progress in early diagnosis and treatment. Am J Med. 1981 Oct;71(4):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Antifungal susceptibility tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1867–1870. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Rinaldi M. G., Polak A. M., Pfaller M. A. Standardization of antifungal susceptibility testing. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30 (Suppl 1):213–224. doi: 10.1080/02681219280000911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. M., Clissold S. P. Itraconazole. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in superficial and systemic mycoses. Drugs. 1989 Mar;37(3):310–344. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198937030-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. E., Harris C., Moody J. A., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. In vitro activities of amphotericin B in combination with four antifungal agents and rifampin against Aspergillus spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):560–562. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka H., Ii Y., Takekawa Y., Teraoka T. Evaluation of antifungal volatile compounds on the basis of the elongation rate of a single hypha. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3779–3784. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3779-3784.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millon L., Manteaux A., Reboux G., Drobacheff C., Monod M., Barale T., Michel-Briand Y. Fluconazole-resistant recurrent oral candidiasis in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients: persistence of Candida albicans strains with the same genotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Apr;32(4):1115–1118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.4.1115-1118.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Relative inhibition factors--a novel approach to the assessment of antifungal antibiotics in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13(1):31–43. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida spp. by relative growth measurement at single concentrations of antifungal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1727–1737. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Quantitative microculture system with standardized inocula for strain typing, susceptibility testing, and other physiologic measurements with Candida albicans and other yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2735–2740. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2735-2740.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Dupont B., Kobayashi G. S., Müller J., Rinaldi M. G., Espinel-Ingroff A., Shadomy S., Troke P. F., Walsh T. J., Warnock D. W. Standardized susceptibility testing of fluconazole: an international collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):1805–1809. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Rinaldi M. G., Galgiani J. N., Bartlett M. S., Body B. A., Espinel-Ingroff A., Fromtling R. A., Hall G. S., Hughes C. E., Odds F. C. Collaborative investigation of variables in susceptibility testing of yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1648–1654. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike I. H., Evans E. G., Carney J. A. Mannan estimation as a measure of the growth of Candida albicans. J Med Vet Mycol. 1991;29(2):83–91. doi: 10.1080/02681219180000151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rementeria A., Ezkurra P., Hernando F., Ponton J., Sevilla M. J., Cisterna R. Chitin assay to estimate the growth of Candida albicans in organs of infected mice. J Med Vet Mycol. 1991;29(1):15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandven P., Bjørneklett A., Maeland A. Susceptibilities of Norwegian Candida albicans strains to fluconazole: emergence of resistance. The Norwegian Yeast Study Group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2443–2448. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shawar R., Paetznick V., Witte Z., Ensign L. G., Anaissie E., LaRocco M. Collaborative investigation of broth microdilution and semisolid agar dilution for in vitro susceptibility testing of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1976–1981. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1976-1981.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellier R., Krajden M., Grigoriew G. A., Campbell I. Innovative endpoint determination system for antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1619–1625. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem J. The in-vitro antifungal spectrum of itraconazole. Mycoses. 1989;32 (Suppl 1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem J., Van Gerven F., Janssen P. A. Activity of orally, topically, and parenterally administered itraconazole in the treatment of superficial and deep mycoses: animal models. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9 (Suppl 1):S15–S32. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_1.s15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Ceuppens A. M., Heymans C., Meunier F. In vitro evaluation of various antifungal agents alone and in combination by using an automatic turbidimetric system combined with viable count determinations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):997–1004. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viviani M. A., Tortorano A. M., Pagano A., Vigevani G. M., Gubertini G., Cristina S., Assaisso M. L., Suter F., Farina C., Minetti B. European experience with itraconazole in systemic mycoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Sep;23(3 Pt 2):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70260-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


