Abstract
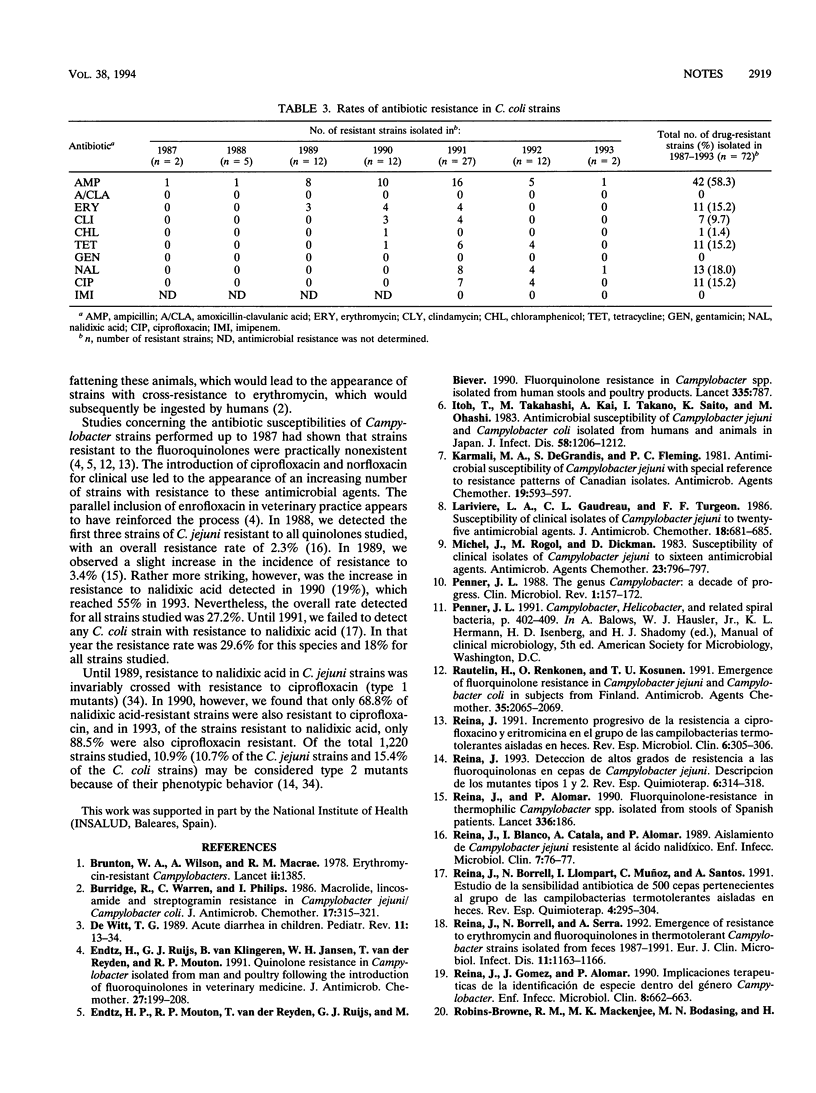
We report the in vitro antibiotic susceptibility of 1,220 strains belonging to the thermotolerant Campylobacter species, isolated from the feces of pediatric patients with diarrhea in the period from 1987 to 1993. The strains were identified as 1,148 C. jejuni isolates and 72 C. coli isolates. The overall results show that the strains showed drug resistance as follows: 51.8% to ampicillin, 4.4% to clindamycin, 2.6% to chloramphenicol, 21.2% to tetracycline, and 1% to gentamicin. Twenty-one strains (1.7%) displayed resistance to the combination of amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, and 3.2% of the strains were resistant to erythromycin (MIC of > or = 4 micrograms/ml), with a notable difference according to the species under consideration. While C. jejuni remained stable at 0.9 to 4% resistance to erythromycin, for C. coli the percentages detected ranged from 0 to 33%, with overall rates of 2.5 and 15.2% for the two species, respectively. Resistance to nalidixic acid (MIC of > or = 32 micrograms/ml) was found in 27.2% of the strains (27.8% for C. jejuni and 18% for C. coli), and resistance to ciprofloxacin (MIC of > or = 4 micrograms/ml) was found in 24.2% of the strains for C. jejuni and 15.2% for C. coli). Cross-resistance between nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin was found in 89.1% of the strains (type 1 mutants), while 10.9% were resistant to nalidixic acid but susceptible to ciprofloxacin (type 2 mutants).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunton W. A., Wilson A. M., Macrae R. M. Erythromycin-resistant campylobacters. Lancet. 1978 Dec 23;2(8104-5):1385–1385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge R., Warren C., Phillips I. Macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Mar;17(3):315–321. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.3.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endtz H. P., Mouton R. P., van der Reyden T., Ruijs G. J., Biever M., van Klingeren B. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter spp isolated from human stools and poultry products. Lancet. 1990 Mar 31;335(8692):787–787. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90897-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endtz H. P., Ruijs G. J., van Klingeren B., Jansen W. H., van der Reyden T., Mouton R. P. Quinolone resistance in campylobacter isolated from man and poultry following the introduction of fluoroquinolones in veterinary medicine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Feb;27(2):199–208. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Takahashi M., Kai A., Takano I., Saito K., Ohashi M. [Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from human and animals in Japan]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1984 Nov;58(11):1206–1212. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.58.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., De Grandis S., Fleming P. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni with special reference to resistance patterns of Canadian isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):593–597. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lariviere L. A., Gaudreau C. L., Turgeon F. F. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni to twenty-five antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Dec;18(6):681–685. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J., Rogol M., Dickman D. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni to sixteen antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):796–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautelin H., Renkonen O. V., Kosunen T. U. Emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in subjects from Finland. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2065–2069. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reina J., Alomar P. Fluoroquinolone-resistance in thermophilic Campylobacter spp isolated from stools of Spanish patients. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):186–186. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91715-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reina J., Borrell N., Serra A. Emergence of resistance to erythromycin and fluoroquinolones in thermotolerant Campylobacter strains isolated from feces 1987-1991. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;11(12):1163–1166. doi: 10.1007/BF01961137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reina J., Gómez J., Alomar P. Implicaciones terapéuticas de la identificación de especie dentro del género Campylobacter. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1990 Dec;8(10):662–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Mackenjee M. K., Bodasing M. N., Coovadia H. M. Treatment of Campylobacter-associated enteritis with erythromycin. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Mar;137(3):282–285. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140290068018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara H., Mochizuki A., Okamura N., Nakaya R. Antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli with special reference to plasmid profiles of Japanese clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):713–719. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severin W. P. Campylobacter en enteritis. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1978 Apr 15;122(15):499–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. A demographic survey of campylobacter, salmonella and shigella infections in England. A Public Health Laboratory Service Survey. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Dec;99(3):647–657. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800066504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Chang N., Garner R. S., Sherburne R., Mueller L. Incidence of antibiotic resistance and characterization of plasmids in Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from clinical sources in Alberta, Canada. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jan;32(1):28–32. doi: 10.1139/m86-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Courvalin P. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1107–1112. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., De Grandis S. A., Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Transmissible plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):831–835. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Garner R. S., Allan B. J. Characterization of tetracycline resistance plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):930–935. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Blaser M. J., Echeverria P., Pitarangsi C., Bodhidatta L., Wang W. L. Erythromycin-resistant Campylobacter infections in Thailand. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):438–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Bronsdon M. A., Gordon K. P., Plorde J. J. Isolation of plasmids encoding tetracycline resistance from Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from simians. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):320–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Survey of plasmids and resistance factors in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoof R., Vanderlinden M. P., Dierickx R., Lauwers S., Yourassowsky E., Butzler J. P. Susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni to twenty-nine antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):553–556. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder M., Forsgren A. Erythromycin-resistant Campylobacters. Lancet. 1978 Dec 2;2(8101):1201–1201. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. L., Reller L. B., Blaser M. J. Comparison of antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):351–353. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Huang W. M., Taylor D. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Campylobacter jejuni gyrA gene and characterization of quinolone resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):457–463. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



