Abstract
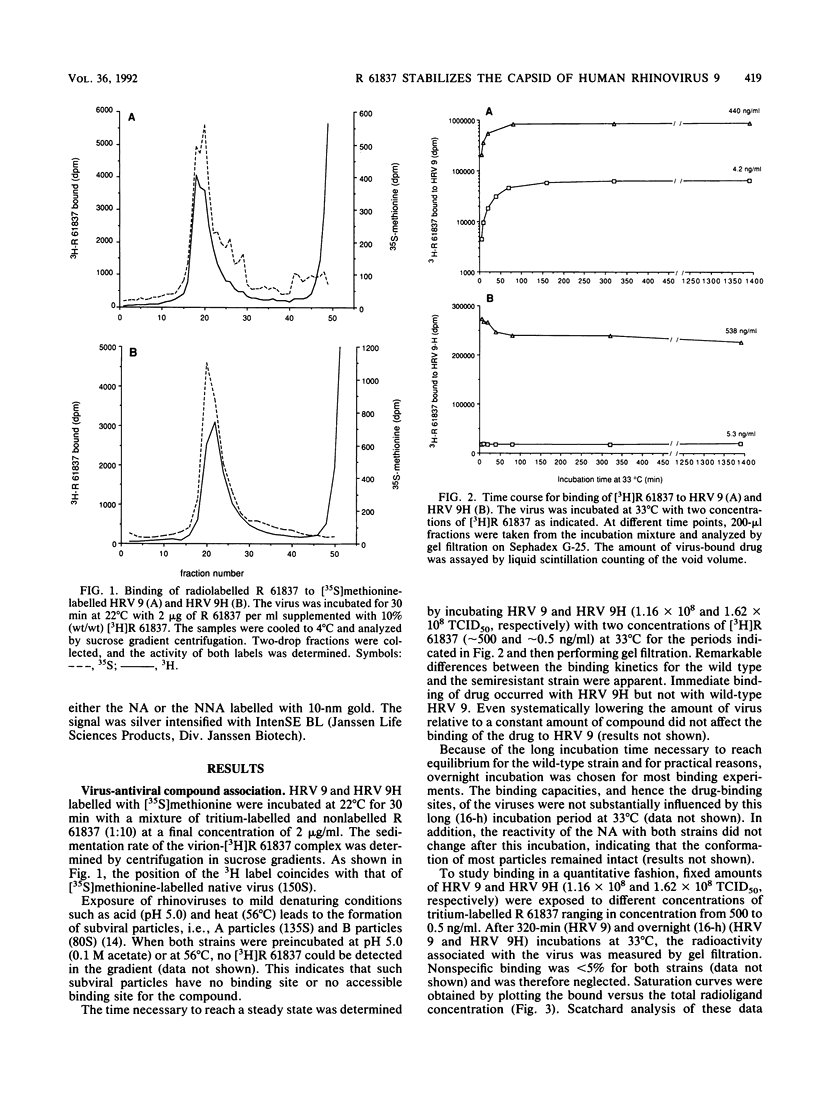
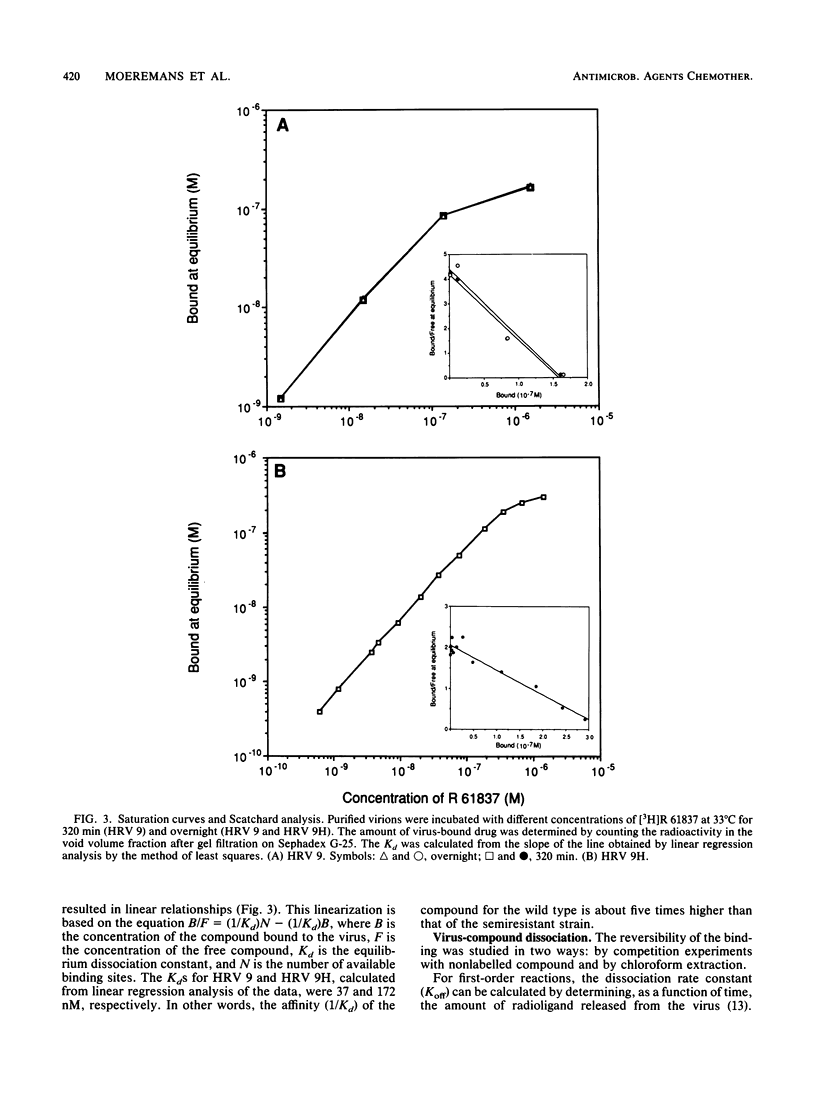
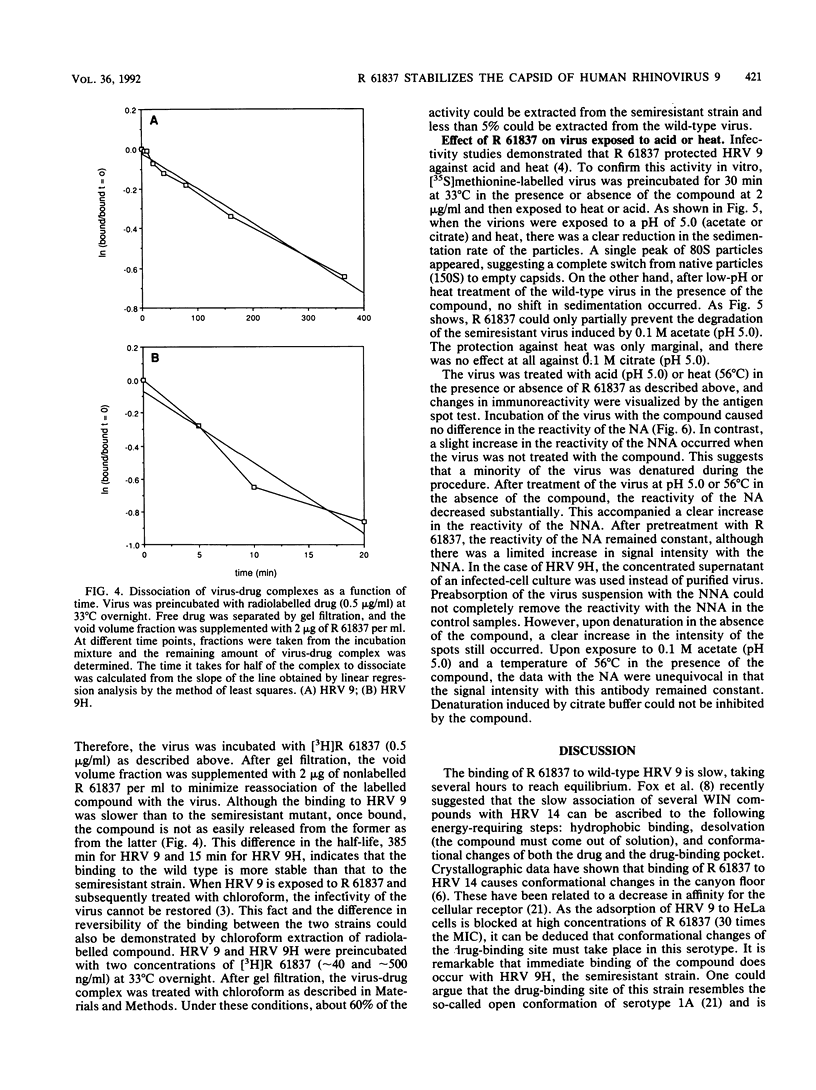
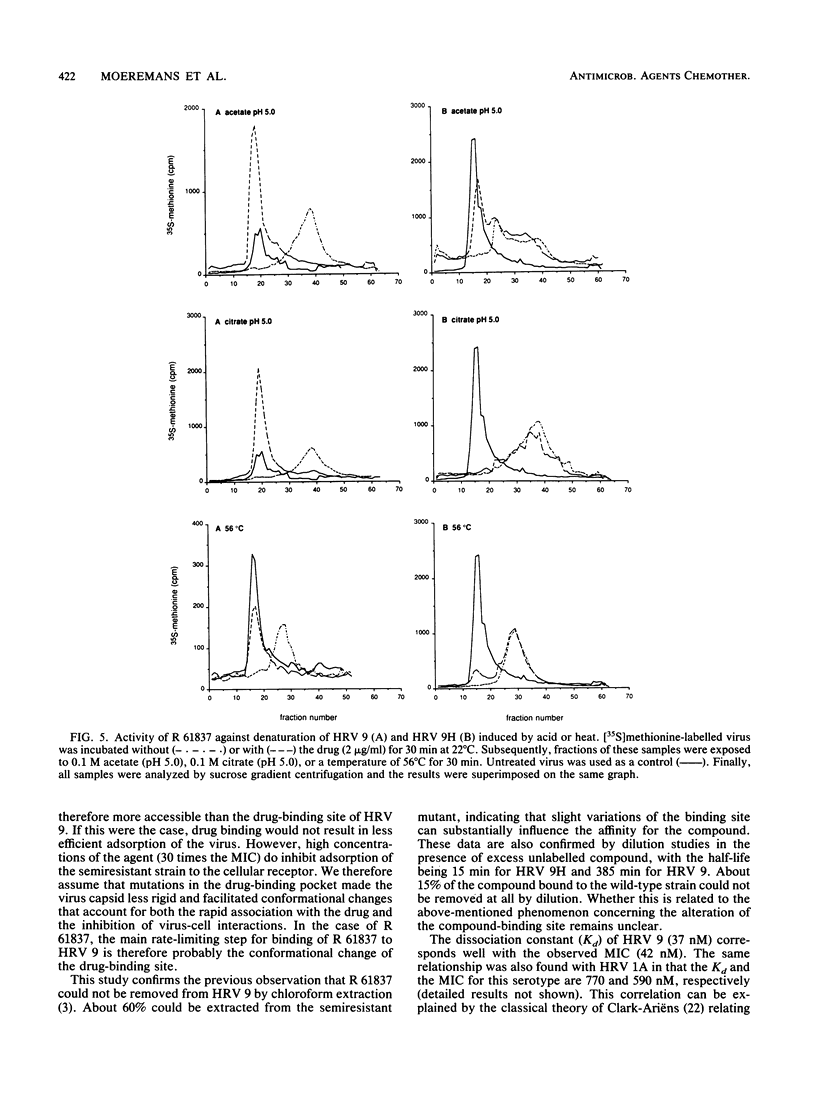
The binding of the antiviral compound R 61837 to human rhinovirus 9 (HRV 9) was studied quantitatively and compared with binding of R 61837 to HRV 9H, a semiresistant variant. For both strains, radiolabelled R 61387 bound to native particles only. The Kd values obtained by Scatchard analysis of saturation binding data were 37 nM for HRV 9 and 172 nM for HRV 9H, whereas the concentrations resulting in a 50% reduction of cytopathic effect were 42 nM and 840 nM, respectively. Reversibility experiments showed that 65% of the compound could be extracted with chloroform from HRV 9H but less than 5% could be extracted from HRV 9. Dissociation studies demonstrated that in the presence of excess unlabelled compound, the half-lives of the virus compound complex HRV 9 and HRV 9H were 385 and 15 min, respectively. The effect of this antirhinoviral compound on the formation of subviral particles induced by low pH or heat was also investigated. Rate zonal centrifugation experiments using [35S]methionine-labelled HRV 9 showed that binding of R 61837 protected the virus against heat (56 degrees C) and acid (pH 5.0) and that at the same concentration of R 61837 the semiresistant strain was stabilized to a lesser extent. This observation was confirmed immunochemically with nonneutralizing and neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Both 80S and 130S subviral particles have C antigenic determinants, whereas native particles (150S) have been designated D. R 61837 prevented the switch from D to C antigenicity which can be induced by exposure of rhinoviruses to mild denaturing conditions. These findings indicate that the compound is able to prevent a conformational change of the capsid which may be a prerequisite for infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andries K., Dewindt B., De Brabander M., Stokbroekx R., Janssen P. A. In vitro activity of R 61837, a new antirhinovirus compound. Arch Virol. 1988;101(3-4):155–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01310997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andries K., Dewindt B., Snoeks J., Willebrords R. Lack of quantitative correlation between inhibition of replication of rhinoviruses by an antiviral drug and their stabilization. Arch Virol. 1989;106(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1007/BF01311037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., McSharry J. J., Lawrence G. W. Effect of arildone on modifications of poliovirus in vitro. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. S., Minor I., Rossmann M. G., Diana G. D., Andries K. Human rhinovirus 14 complexed with antiviral compound R 61837. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90749-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers H. J. Selective inhibiton of uncoating of echovirus 12 by rhodanine. A study on early virus-cell interactions. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. P., Otto M. J., McKinlay M. A. Prevention of rhinovirus and poliovirus uncoating by WIN 51711, a new antiviral drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. T., Torney H. L., Dulworth J. K. Mechanism of action of the antiviral compound MDL 20,610. Antiviral Res. 1988 Jul;9(4):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(88)90056-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhrt M. F., Fancher M. J., McKinlay M. A., Lennert S. D. Virucidal activity of glutaric acid and evidence for dual mechanism of action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):924–927. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Noble-Harvey J. Comparison of in vitro and cell-mediated alteration of a human Rhinovirus and its inhibition by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):819–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.819-826.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Yin F. H. Antigenic determinants of infective and inactivated human rhinovirus type 2. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.114-123.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthe D. S. A simple technique for the preparation and storage of sucrose gradients. Anal Biochem. 1983 Nov;135(1):230–232. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90755-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Different pH requirements for entry of the two picornaviruses, human rhinovirus 2 and murine encephalomyocarditis virus. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):346–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischak H., Neubauer C., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Characteristics of the minor group receptor of human rhinoviruses. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeremans M., Daneels G., Van Dijck A., Langanger G., De Mey J. Sensitive visualization of antigen-antibody reactions in dot and blot immune overlay assays with immunogold and immunogold/silver staining. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Ohsawa C., Aoyama M., Umeda I., Suhara Y., Ishitsuka H. Antivirus agent, Ro 09-0410, binds to rhinovirus specifically and stabilizes the virus conformation. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Fancher M. J., Felock P. J., Rossmann M. G., Miller M. S., Diana G., Treasurywala A. M., McKinlay M. A., Dutko F. J. Conformational change in the floor of the human rhinovirus canyon blocks adsorption to HeLa cell receptors. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2002–2007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2002-2007.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Selway J. W. Effect of dichloroflavan (BW683C) on the stability and uncoating of rhinovirus type 1B. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Aug;14 (Suppl A):97–105. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_a.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Colonno R. J. Isolation of a receptor protein involved in attachment of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.290-295.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Nakib W., Higgins P. G., Barrow G. I., Tyrrell D. A., Andries K., Vanden Bussche G., Taylor N., Janssen P. A. Suppression of colds in human volunteers challenged with rhinovirus by a new synthetic drug (R61837). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):522–525. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]