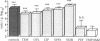Abstract
We compared the prophylactic activities of six fluoroquinolones against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in immunosuppressed rats. Pefloxacin was the only agent which was as effective as the reference drug trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Clinical trials with pefloxacin in patients at risk for P. carinii pneumonia appear to be justified.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azoulay-Dupuis E., Bedos J. P., Vallée E., Hardy D. J., Swanson R. N., Pocidalo J. J. Antipneumococcal activity of ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and temafloxacin in an experimental mouse pneumonia model at various stages of the disease. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):319–324. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochereau-Massin I., Bauchet J., Faurisson F., Vallois J. M., Lacombe P., Pocidalo J. J. Ocular kinetics of pefloxacin after intramuscular administration in albino and pigmented rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1112–1115. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Watanabe T. T., Hasegawa G. K., Goralnik G. N., Roertgen K. E., Kaizu T., Reiser K. M., Gorin A. B., Last J. A. Biochemical assays in lung homogenates: artifacts caused by trapped blood after perfusion. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 30;48(1 Pt 1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(79)80012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debs R. J., Blumenfeld W., Brunette E. N., Straubinger R. M., Montgomery A. B., Lin E., Agabian N., Papahadjopoulos D. Successful treatment with aerosolized pentamidine of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg L. A., Lerner C. W., Tapper M. L. Clinical features of Pneumocystis pneumonia in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):689–694. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard P. M., Brun-Pascaud M., Farinotti R., Tamisier L., Kernbaum S. Pentamidine aerosol in prophylaxis and treatment of murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):978–981. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosey L. L., Howard R. M., Witebsky F. G., Ognibene F. P., Wu T. C., Gill V. J., MacLowry J. D. Advantages of a modified toluidine blue O stain and bronchoalveolar lavage for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.803-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Swanson R. N., Hensey D. M., Ramer N. R., Bower R. R., Hanson C. W., Chu D. T., Fernandes P. B. Comparative antibacterial activities of temafloxacin hydrochloride (A-62254) and two reference fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1768–1774. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopewell P. C., Luce J. M. Pulmonary involvement in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Chest. 1985 Jan;87(1):104–112. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Gray V. L., Gutteridge W. E., Latter V. S., Pudney M. Efficacy of a hydroxynaphthoquinone, 566C80, in experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):225–228. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith-McCain B. L. Effects of sulfonylurea compounds on Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):944–947. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith B. L. Efficacy of diaminodiphenylsulfone and other drugs in murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):436–440. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmerich B., Borner K., Pennington J. E. Comparative evaluation of enoxacin, ofloxacin, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol for treatment of experimental Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):417–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Beaver J., Boarman D., Lewis M., Parrillo J. E., Chabner B., Masur H. Characterization of de novo folate synthesis in Pneumocystis carinii and Toxoplasma gondii: potential for screening therapeutic agents. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):312–320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montay G., Goueffon Y., Roquet F. Absorption, distribution, metabolic fate, and elimination of pefloxacin mesylate in mice, rats, dogs, monkeys, and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):463–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Kurobe N., Kashimoto S., Ohue T., Takase Y., Shimizu M. Pharmacokinetics of AT-2266 administered orally to mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Kurobe N., Ohue T., Hashimoto M., Shimizu M. Pharmacokinetics of a novel quinolone, AT-4140, in animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Richardson J. D., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. Activity of clindamycin with primaquine against Pneumocystis carinii in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D., Deloron P., Gaudin C., Malhotra K., Lebras J., Pocidalo J. J. Activities of pefloxacin and ciprofloxacin against experimental malaria in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2327–2330. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Kim C. K., Foy J. M., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Inhibitors of folic acid synthesis in the treatment of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Rutledge M. E., Yoneda K., Stahr B. J. Pneumocystis carinii: new separation method from lung tissue. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Jun;47(3):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Ikai T. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: epidemiology in Japan, and cyst concentration method. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Jul;244(2-3):405–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]