Abstract
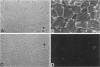
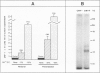
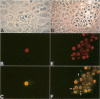
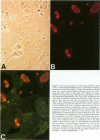
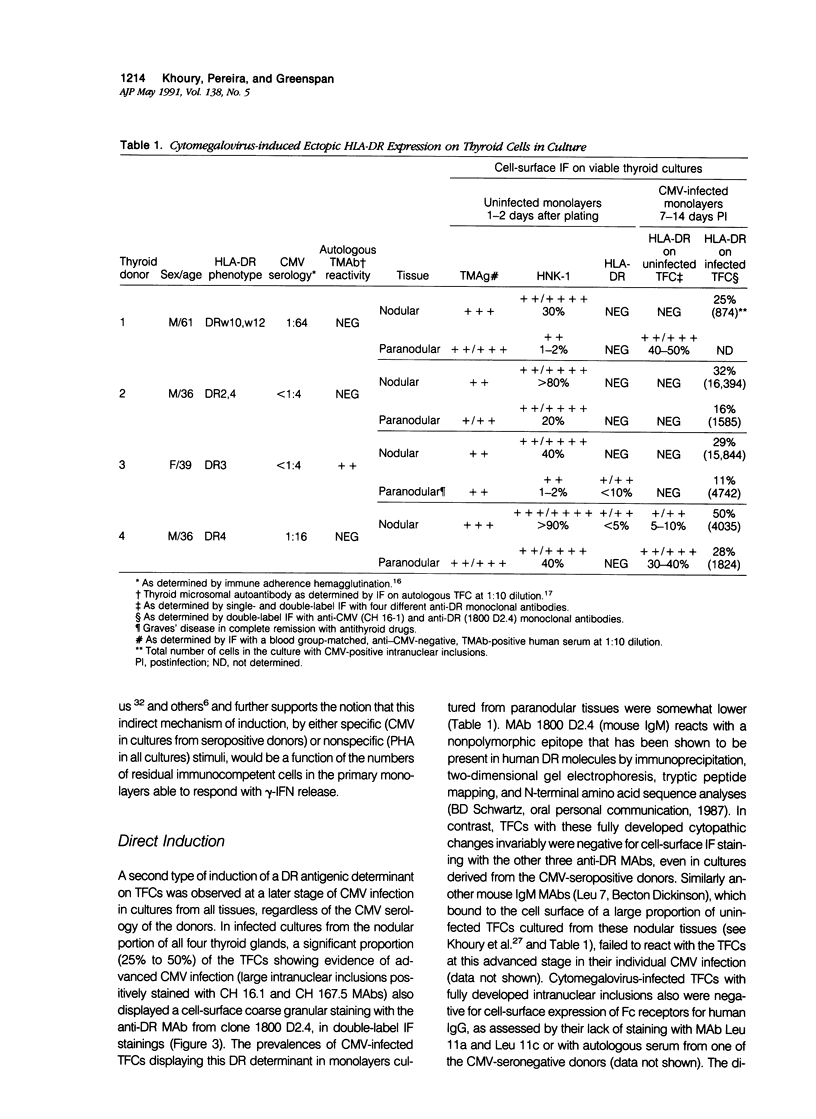
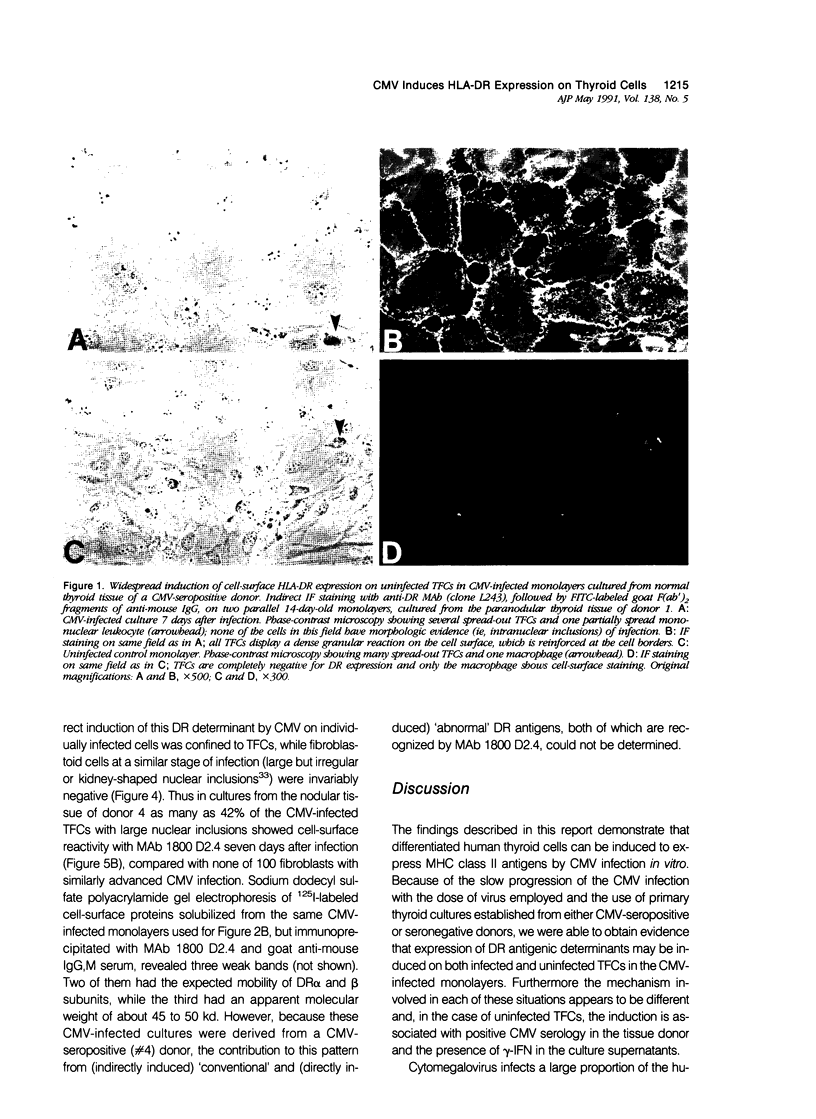
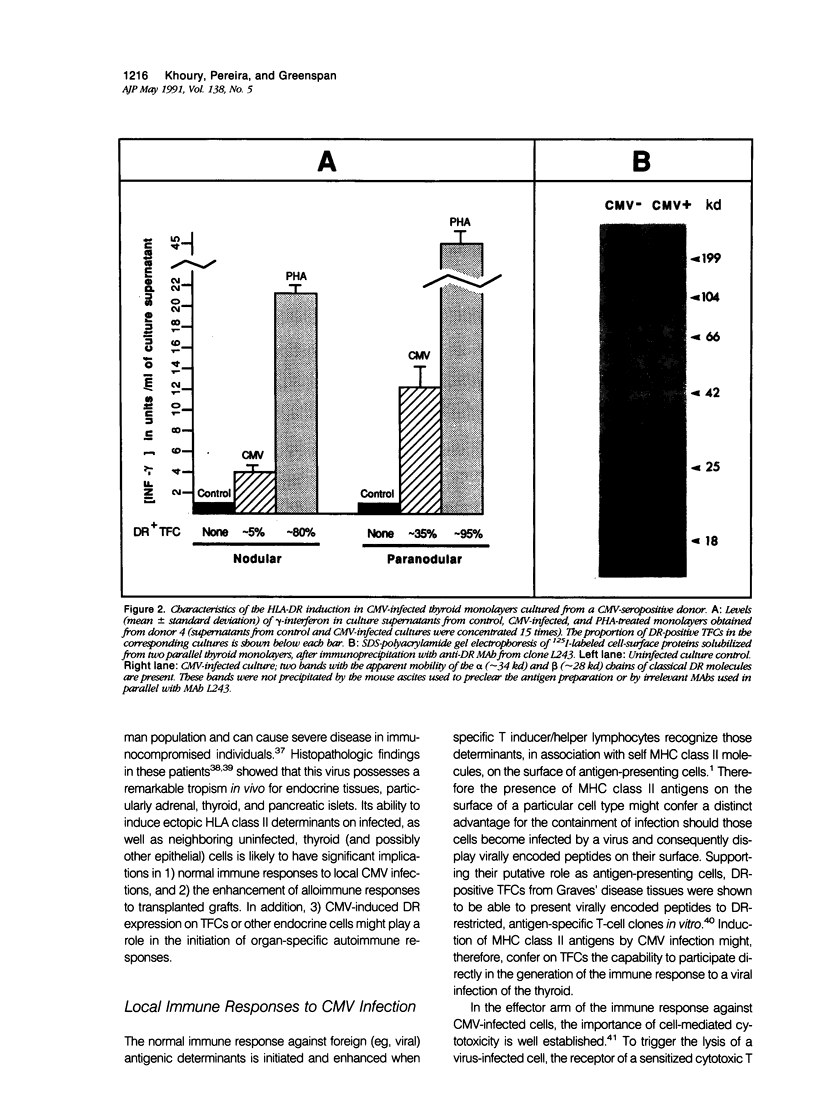
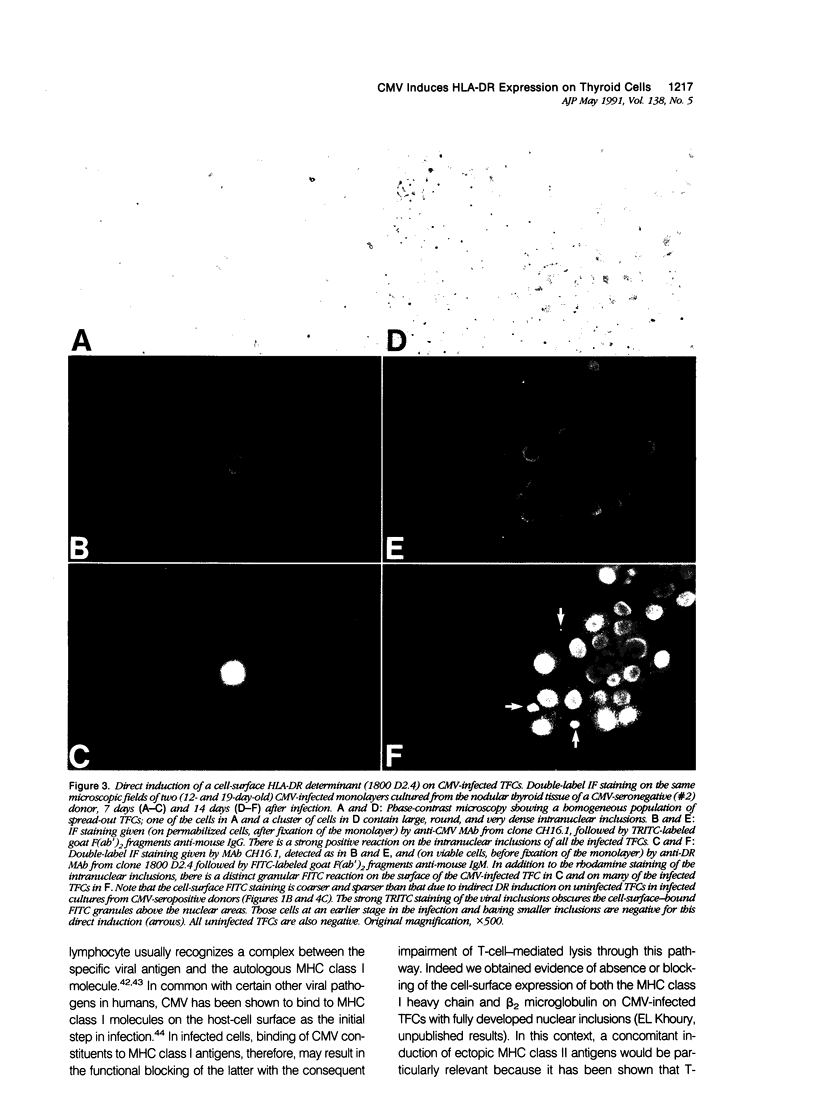
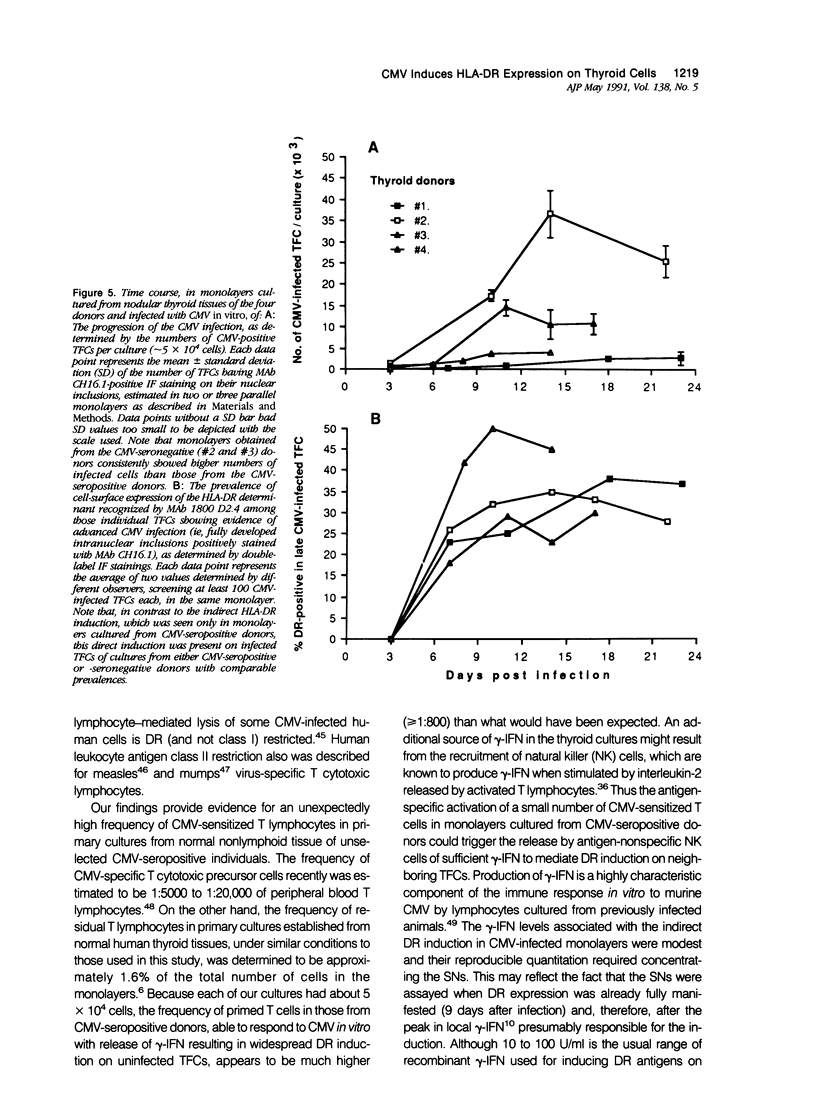
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection of primary cultures established from human thyroid nodular and normal (paranodular) tissues resulted in induction of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR expression on thyroid follicular cells (TFC), as detected by cell-surface immunofluorescence staining with monoclonal antibodies (MAb). Two distinct modalities of induction were observed. The first type occurred in cultures of normal tissue obtained from CMV-seropositive but not seronegative donors, was detected on 30% to 50% of the TFCs, even though the vast majority of these cells failed to show any morphologic or antigenic evidence of individual CMV infection, and was associated with production of gamma-interferon (gamma-IFN) in vitro. The induced molecules displayed the characteristic DR polypeptide profile on immunoprecipitation and electrophoretic analysis. These results demonstrate that CMV infection of normal thyroid cultures may induce DR expression on TFCs in the absence of pre-existing lymphoid infiltrates and suggest that the induction is the result of an in vitro response to CMV by previously sensitized immunocompetent cells present in these primary cultures. Such a response, associated with the release of gamma-IFN, would induce DR expression on neighboring uninfected cells. The second mode of induction occurred in all CMV-infected cultures, regardless of their tissue origin (nodular or normal) or the serologic status of the donors. Up to 50% of infected TFCs at a late stage of infection, having fully developed CMV antigen-positive intranuclear inclusions, also displayed the cell-surface DR-related determinant recognized by one of the four anti-DR MAbs used. This induction was restricted to TFCs, while CMV-infected fibroblastoid cells present in the monolayers were invariably negative. Induction by CMV of major histocompatibility class II antigens on human epithelial cells may have significant implications in the development of normal immune responses against local viral infection, the enhancement of alloimmune rejection of grafted organs, and the generation of organ-specific autoimmune responses.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht T., Cavallo T., Cole N. L., Graves K. Cytomegalovirus: development and progression of cytopathic effects in human cell culture. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Andersen H. K. Smooth-muscle antibodies and other tissue antibodies in cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):22–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomaeus W. N., O'Donoghue H., Foti D., Lawson C. M., Shellam G. R., Reed W. D. Multiple autoantibodies following cytomegalovirus infection: virus distribution and specificity of autoantibodies. Immunology. 1988 Jul;64(3):397–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Graham S., Hickling J. K., Mason P. D., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T cells: their precursor frequency and stage specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Feb;18(2):269–275. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Feldmann M. Role of aberrant HLA-DR expression and antigen presentation in induction of endocrine autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1115–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D. Selective induction of chromosomal gene expression by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Cline W. L., Purcell R. H. Detection of cytomegalovirus antibody by immune adherence hemagglutination. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Dec;153(3):543–548. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach I., Perrin J. Distribution of microsomal antigen in various types of thyroid tumour. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 May;14(1):77–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Nelson J. A., Walker L., Oldstone M. B. Sequence homology and immunologic cross-reactivity of human cytomegalovirus with HLA-DR beta chain: a means for graft rejection and immunosuppression. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.100-105.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Stein M. E., Safko B., Stadecker M. J. Direct induction of Ia antigen on murine thyroid-derived epithelial cells by reovirus. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3821–3825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., McKeating J. A., Ward P. J., Sanderson A. R., Griffiths P. D. Beta 2 microglobulin enhances the infectivity of cytomegalovirus and when bound to the virus enables class I HLA molecules to be used as a virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):793–803. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Pujol-Borrell R., Chiovato L., Russell R. C., Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigen on thyrocytes in Graves' disease: relevance for autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90628-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., von Willebrand E. The influence of the pattern of inflammation and administration of steroids on class II MHC antigen expression in renal transplants. Transplantation. 1986 Oct;42(4):358–363. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198610000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatani Y., Gerstein H. C., Iitaka M., Row V. V., Volpé R. Thyrocyte HLA-DR expression and interferon-gamma production in autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Sep;63(3):695–708. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-3-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Sekaly R. P., Jacobson C. L., McFarland H. F., Long E. O. HLA class II-restricted presentation of cytoplasmic measles virus antigens to cytotoxic T cells. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1756–1762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1756-1762.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemble G. W., McCormick A. L., Pereira L., Mocarski E. S. A cytomegalovirus protein with properties of herpes simplex virus ICP8: partial purification of the polypeptide and map position of the gene. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3143–3151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3143-3151.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury E. L., Greenspan J. S., Greenspan F. S. Adrenocortical cells of the zona reticularis normally express HLA-DR antigenic determinants. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jun;127(3):580–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury E. L., Greenspan J. S., Greenspan F. S. Ectopic expression of HLA class II antigens on thyroid follicular cells: induction and transfer in vitro by autologous mononuclear leukocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Nov;67(5):992–1004. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-5-992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury E. L., Hammond L., Bottazzo G. F., Doniach D. Presence of the organ-specific 'microsomal' autoantigen on the surface of human thyroid cells in culture: its involvement in complement-mediated cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):316–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. A. In-vitro cultivation of human cytomegalovirus in thyroid epithelial cells. Arch Virol. 1976;50(1-2):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01318006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley M. D., Torpey D. J., 3rd, Rinaldo C. R., Jr HLA-DR-restricted cytotoxicity of cytomegalovirus-infected monocytes mediated by Leu-3-positive T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3045–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski M., Braham K., Caillaud J. M., Carlu C., Tursz T. HNK-1 antibody detects an antigen expressed on neuroectodermal cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1775–1780. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei M., Lamb J. R., Bottazzo G. F., Feldmann M. Epithelial cells expressing aberrant MHC class II determinants can present antigen to cloned human T cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):639–641. doi: 10.1038/312639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa P. T., Dörries R., ter Meulen V. Viral particles induce Ia antigen expression on astrocytes. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):543–546. doi: 10.1038/320543a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Ting A., Zweerink H. J., Askonas B. A. HLA restriction of cell-mediated lysis of influenza virus-infected human cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):524–526. doi: 10.1038/270524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Pereira L., Michael N. Precise localization of genes on large animal virus genomes: use of lambda gt11 and monoclonal antibodies to map the gene for a cytomegalovirus protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1266–1270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld D. S., Platzer M., Davies T. F. Reovirus induction of MHC class II antigen in rat thyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):543–545. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedt G. W., Schinella R. A. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clinicopathologic study of 56 autopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Aug;109(8):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Maehlen J., Löve A., Klareskog L., Norrby E., Kristensson K. Induction of class I and class II transplantation antigens in rat brain during fatal and non-fatal measles virus infection. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Oct;16(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90076-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak C. Y., Eun H. M., McArthur R. G., Yoon J. W. Association of cytomegalovirus infection with autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 1988 Jul 2;2(8601):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92941-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Cremer N. Electrophoretic analysis of polypeptides immune precipitated from cytomegalovirus-infected cell extracts by human sera. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):933–942. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.933-942.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Balfour H. H., Jr, Marker S. C., Fryd D. S., Howard R. J., Simmons R. L. Cytomegalovirus disease in renal allograft recipients: a prospective study of the clinical features, risk factors and impact on renal transplantation. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 Jul;59(4):283–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Babcock G. F. NKP-15: a monoclonal antibody reactive against purified human natural killer cells and granulocytes. Immunol Lett. 1983 Mar;6(3):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(83)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccinini L. A., Mackenzie W. A., Platzer M., Davies T. F. Lymphokine regulation of HLA-DR gene expression in human thyroid cell monolayers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Mar;64(3):543–548. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Chiovato L., Bottazzo G. F. Lectin-induced expression of DR antigen on human cultured follicular thyroid cells. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):71–73. doi: 10.1038/304071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma S., Furukawa T., Plotkin S. A. The characterization of IgG receptor induced by human cytomegalovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jun;155(2):168–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkurt E. E. Induction of immune interferon by murine cytomegalovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Sep;155(4):611–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasappa J., Garzelli C., Onodera T., Ray U., Notkins A. L. Virus-induced thyroiditis. Endocrinology. 1988 Feb;122(2):563–566. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-2-563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd I., Pujol-Borrell R., Belfiore A., Bottazzo G. F. Thyrocyte HLA class II expression and regulation in relation to thyroid autoimmunity. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1987;281:27–34. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.114s027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd I., Pujol-Borrell R., Hammond L. J., Bottazzo G. F., Feldmann M. Interferon-gamma induces HLA-DR expression by thyroid epithelium. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Aug;61(2):265–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Volkman D. J., Burman K. D., Gerrard T. L., Fauci A. S. The in vitro regulation of human thyrocyte HLA-DR antigen expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Nov;61(5):817–824. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-5-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K., Finkbeiner W., Alpers C. E., Blumenfeld W., Davis R. L., Smuckler E. A., Beckstead J. H. Autopsy findings in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1984 Sep 7;252(9):1152–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacheis M., Giacoletto K., Schwartz B. D. Analysis of normal human tonsil class II antigen glycosylation by lectin affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17004–17010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Willebrand E., Pettersson E., Ahonen J., Häyry P. CMV infection, class II antigen expression, and human kidney allograft rejection. Transplantation. 1986 Oct;42(4):364–367. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198610000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]