Abstract
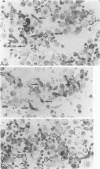
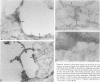
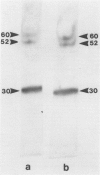
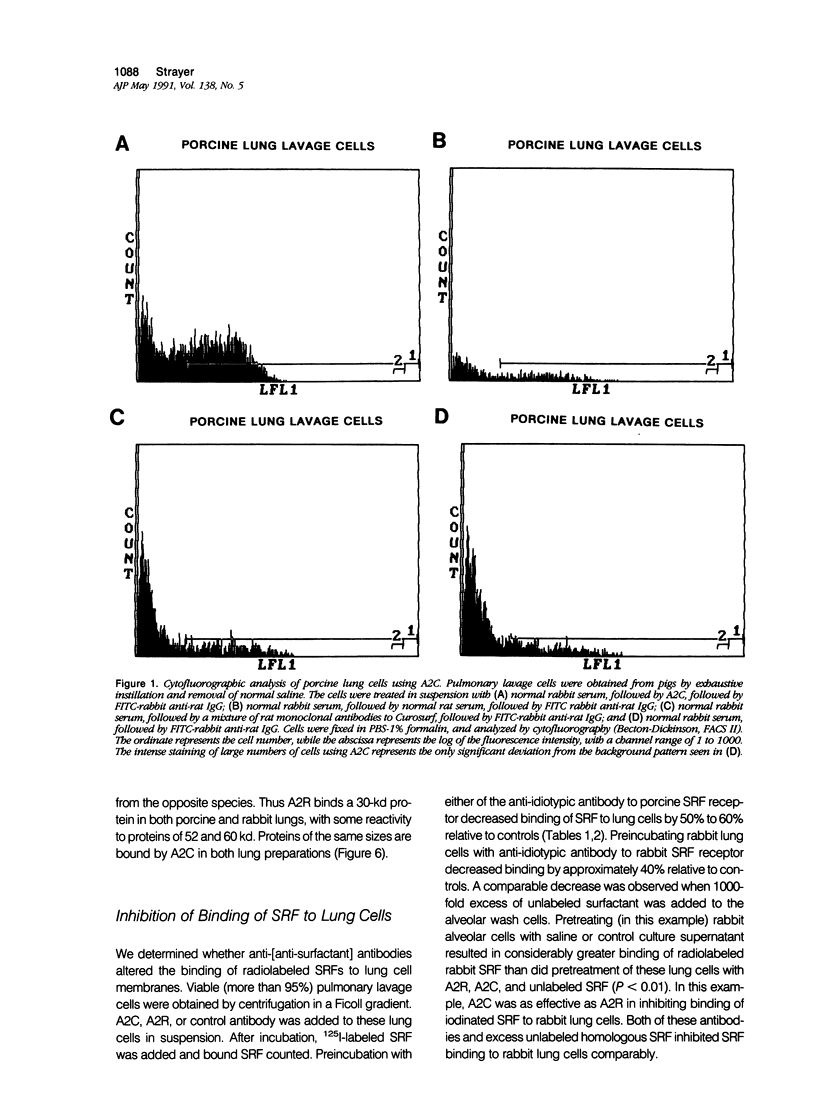
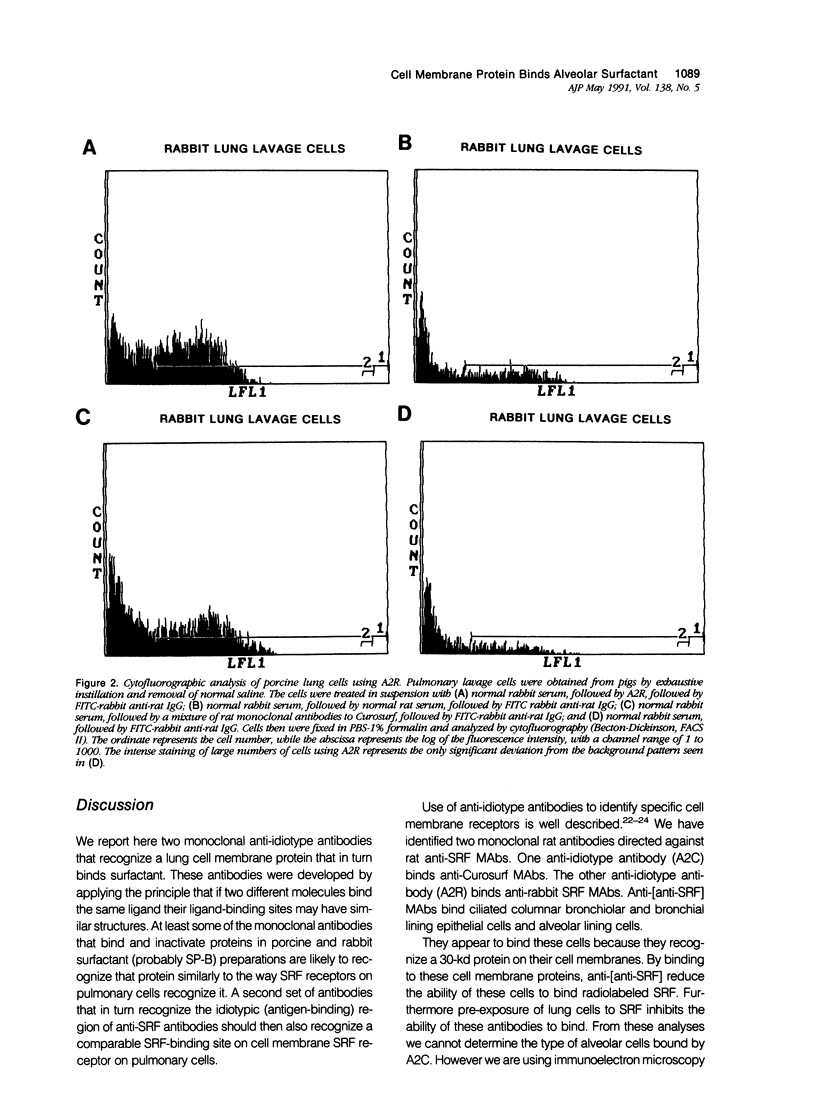
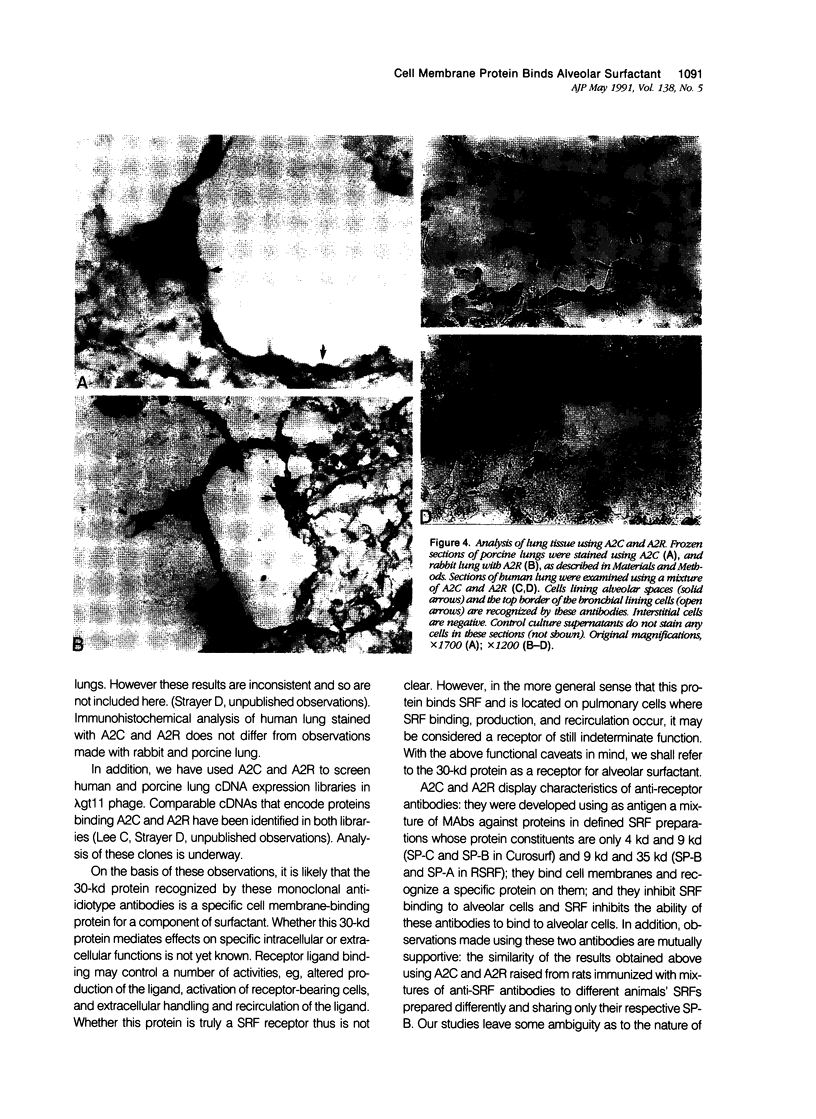
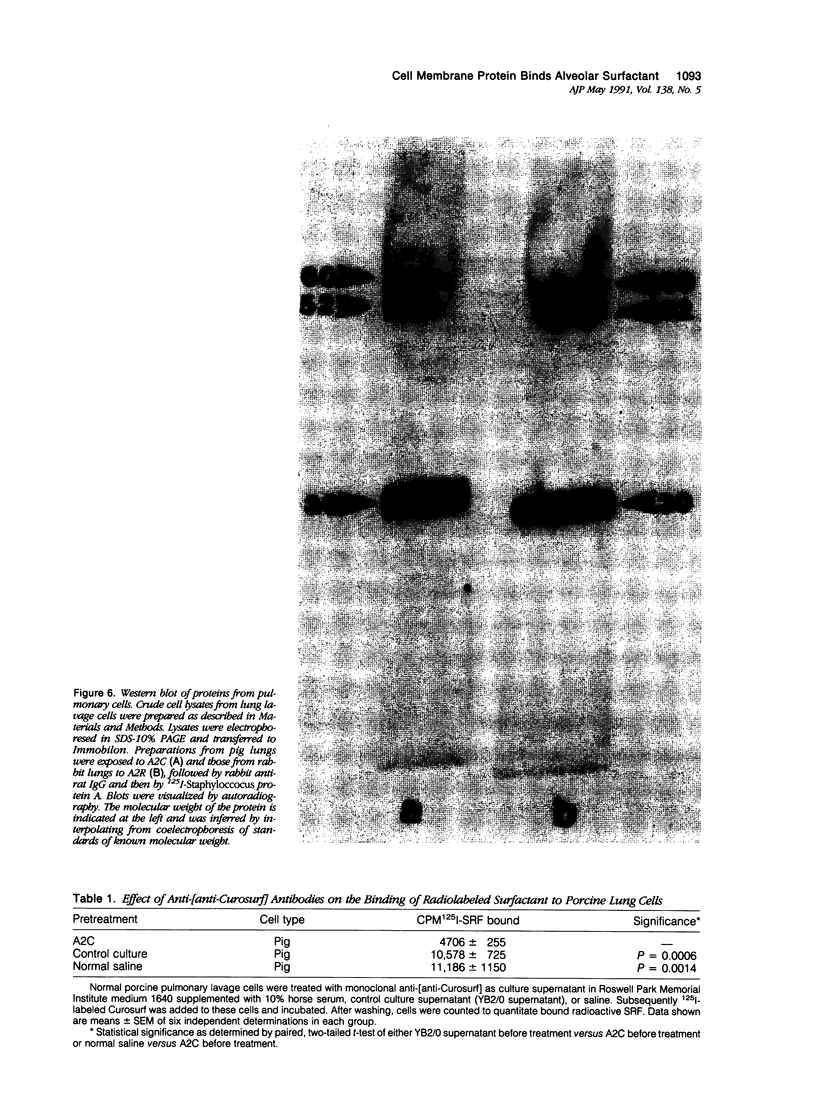
Alveolar surfactants are complex mixtures of proteins and phospholipids produced by type II alveolar cells and responsible for lowering pulmonary surface tension. The process by which surfactant is produced and exported and by which its production by pulmonary cells is regulated are not well understood. This study was designed to identify a cellular receptor for surfactant constituents. To do so, monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies directed against antibodies to porcine and rabbit surfactant proteins were prepared. These monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies bind both alveolar lining and bronchial epithelial cells in rabbit, porcine, and human lungs. Macrophages and other nonepithelial cells do not react with these antibodies. Western blot analysis indicates that both A2R and A2C recognize the same proteins in both pig and rabbit lungs: a 30-kd protein and additional proteins at 52 and 60 kd. Preincubating lung wash cells with A2C or A2R prevents binding of porcine or rabbit surfactant preparations, respectively, by these cells. Preincubating frozen sections of lung tissue with surfactant inhibits binding of A2R and A2C to the lung. Antibody directed to a cell membrane protein that recognizes alveolar surfactant may be useful in elucidating the structure and function of this receptor and in understanding the cellular physiology and pathophysiology of the surfactant system.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curstedt T., Jörnvall H., Robertson B., Bergman T., Berggren P. Two hydrophobic low-molecular-mass protein fractions of pulmonary surfactant. Characterization and biophysical activity. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene M. I., Co M. S. Shared structural features of an internal image bearing monoclonal anti-idiotype and the external antigen. Monogr Allergy. 1987;22:120–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene M. I., Kokai Y., Gaulton G. N., Powell M. B., Geller H., Cohen J. A. Receptor systems in tissues of the nervous system. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:153–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Merritt T. A., Schneider H., Epstein B. L., Mannino F., Edwards D. K., Gluck L. Isolation of human surfactant from amniotic fluid and a pilot study of its efficacy in respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1983 Apr;71(4):473–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Alveolar type II cells express a high-affinity receptor for pulmonary surfactant protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5566–5570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter R. H., Shapiro D. L., Ohning B., Whitsett J. A. Biophysical activity of synthetic phospholipids combined with purified lung surfactant 6000 dalton apoprotein. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987 Jun;44(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(87)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettenazzo A., Jobe A., Humme J., Seidner S., Ikegami M. Clearance of surfactant phosphatidylcholine via the upper airways in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Nov;65(5):2151–2155. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.5.2151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Harding H. P. Immunohistochemical localization of a low molecular weight surfactant-associated protein in human lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Nov;35(11):1339–1342. doi: 10.1177/35.11.3309049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possmayer F. A proposed nomenclature for pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):990–998. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Merritt T. A., Degryse E., Stefani L., Courtney M., Hallman M., Cochrane C. G. Use of human surfactant low molecular weight apoproteins in the reconstitution of surfactant biologic activity. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):826–833. doi: 10.1172/JCI113391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Ross G. F., Singleton F. M., Dingle S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):692–698. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. S., Hallman M., Merritt T. A. Immunogenicity of surfactant. I. Human alveolar surfactant. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):35–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. S., Hallman M., Merritt T. A. Immunogenicity of surfactant. II. Porcine and bovine surfactants. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):41–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. S., Leibowitz J. L. Virus-lymphocyte interactions during the course of immunosuppressive virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):463–472. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. S., Vitetta E. S., Köhler H. Anti-receptor antibody. I. Isolation and characterization of the immunoglobulin receptor for phosphorylcholine. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Kobayashi T., Nilsson R., Nohara K., Robertson B. The role of the low-molecular weight (less than or equal to 15,000 daltons) apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;69(5):336–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Borchelt J. D., Hawgood S. Lung surfactant apoprotein SP-A (26-36 kDa) binds with high affinity to isolated alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5410–5414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):426–444. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Wager R. E., Hawgood S., Dobbs L., Clements J. A. Surfactant apoprotein Mr = 26,000-36,000 enhances uptake of liposomes by type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2888–2894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Cellular uptake and processing of surfactant lipids and apoprotein SP-A by rat lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1336–1342. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. H., Chung W., Olafson R. W., Harding P. G., Possmayer F. Characterization of the small hydrophobic proteins associated with pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 17;921(3):437–448. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]