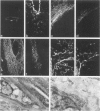
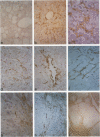
Abstract
It has been suggested that perisinusoidal liver cells (PSC) play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of fibrocontractive changes. Using light and electron microscopic immunolocalization techniques, a series of 207 normal and pathologic human liver specimens were evaluated for the expression of alpha smooth muscle (SM) actin and desmin in this and other nonparenchymal cell types. In normal adult liver tissue, PSCs were practically devoid of desmin and exceptionally stained for alpha-SM actin, whereas this actin isoform frequently was encountered in PSCs from the embryonic to the adolescent period. A broad spectrum of pathologic conditions was accompanied by the presence of alpha-SM actin containing PSCs; these were detected preferentially in periportal or perivenular zones according to the predominant location of the underlying hepatocellular damage. The occurrence of this PSC phenotype generally was associated with fibrogenesis and was in some cases detected earlier than overt collagen accumulation. Fibrous bands subdividing liver tissue in cirrhosis and focal nodular hyperplasia, as well as desmoplastic reaction to malignant tumors, contained alpha-SM actin-rich cells admixed with variable proportions of cells coexpressing desmin. In end stages, this population was less numerous than in active fibrotic or cirrhotic processes. Using immunogold electron microscopy, alpha-SM actin was localized in microfilament bundles of typical PSCs. Our results are compatible with the assumption that the appearance of alpha-SM actin and desmin-expressing myofibroblasts results at least in part from a phenotypic modulation of PSCs.
Full text
PDF

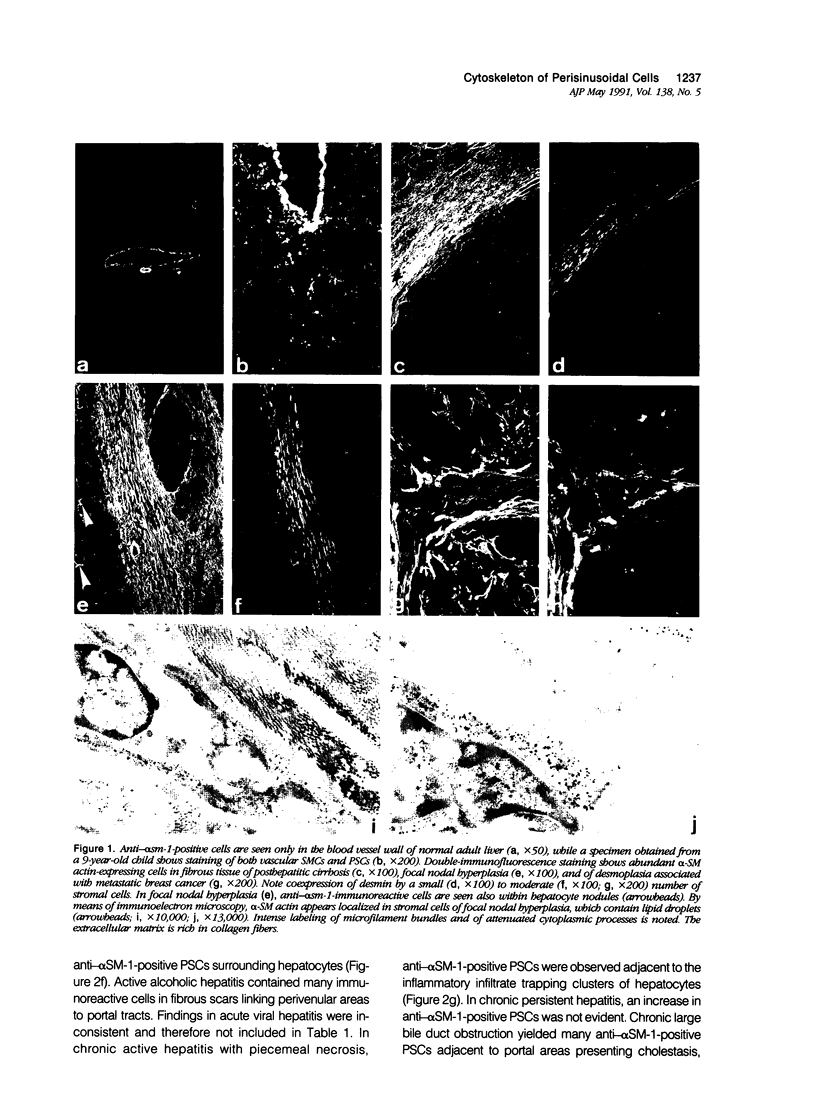
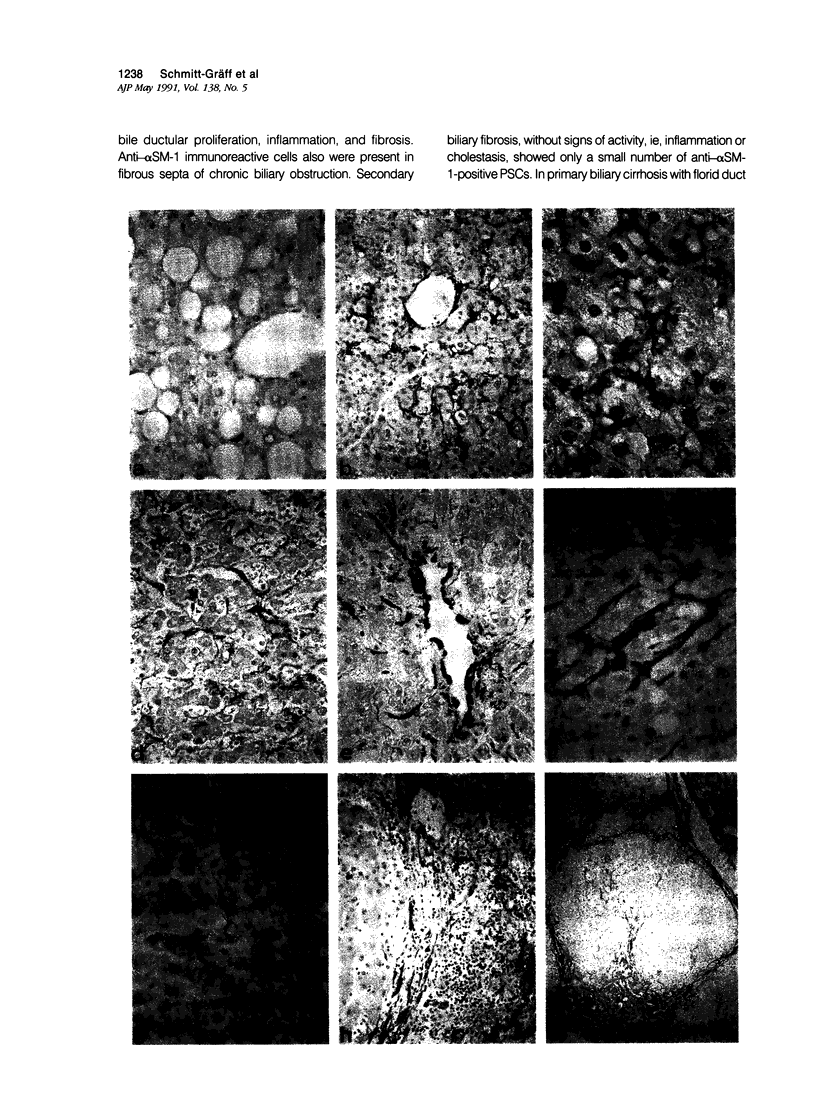




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aterman K. The parasinusoidal cells of the liver: a historical account. Histochem J. 1986 Jun;18(6):279–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01675207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballardini G., Fallani M., Biagini G., Bianchi F. B., Pisi E. Desmin and actin in the identification of Ito cells and in monitoring their evolution to myofibroblasts in experimental liver fibrosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1988;56(1):45–49. doi: 10.1007/BF02890000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt A. D., Robertson J. L., Heir J., MacSween R. N. Desmin-containing stellate cells in rat liver; distribution in normal animals and response to experimental acute liver injury. J Pathol. 1986 Sep;150(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/path.1711500106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chojkier M., Lyche K. D., Filip M. Increased production of collagen in vivo by hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):808–814. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Weiner F. R., Flanders K. C., Giambrone M. A., Wind R., Biempica L., Zern M. A. In vitro and in vivo association of transforming growth factor-beta 1 with hepatic fibrosis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2477–2482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby I., Skalli O., Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed by myofibroblasts during experimental wound healing. Lab Invest. 1990 Jul;63(1):21–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Moll R. Cytoskeletal components of lymphoid organs. I. Synthesis of cytokeratins 8 and 18 and desmin in subpopulations of extrafollicular reticulum cells of human lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen. Differentiation. 1987;36(2):145–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French S. W., Miyamoto K., Wong K., Jui L., Briere L. Role of the Ito cell in liver parenchymal fibrosis in rats fed alcohol and a high fat-low protein diet. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):73–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. L., Roll F. J., Boyles J., Bissell D. M. Hepatic lipocytes: the principal collagen-producing cells of normal rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8681–8685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser S. R., Julian J. Intermediate filament protein as a marker of uterine stromal cell decidualization. Biol Reprod. 1986 Sep;35(2):463–474. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod35.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Hellstrand M., Rymo L., Rubbia L., Gabbiani G. Interferon gamma inhibits both proliferation and expression of differentiation-specific alpha-smooth muscle actin in arterial smooth muscle cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1595–1608. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks H. F., Brouwer A., Knook D. L. The role of hepatic fat-storing (stellate) cells in retinoid metabolism. Hepatology. 1987 Nov-Dec;7(6):1368–1371. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO T., NEMOTO M. Uber die Kupfferschen Sternzellen und die Fettspeicherungszellen (fat storing cells) in der Blutkapillarenwand der memschlichen Leber. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1952 Oct;24(4):243–258. doi: 10.2535/ofaj1936.24.4_243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent G., Gay S., Inouye T., Bahu R., Minick O. T., Popper H. Vitamin A-containing lipocytes and formation of type III collagen in liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3719–3722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Skalli O., Bloom W. S., Gabbiani G. Cytoskeleton of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Normal conditions and experimental intimal thickening. Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;50(6):645–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette D. A. An improved mounting medium for immunofluorescence microscopy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;69(6):647–648. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo M. A., Lieber C. S. Hepatic fibrosis after long-term administration of ethanol and moderate vitamin A supplementation in the rat. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo M. A., Mak K. M., Savolainen E. R., Lieber C. S. Isolation and culture of myofibroblasts from rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Nov;180(2):382–391. doi: 10.3181/00379727-180-42193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Kalman J., Mayer L., Fillit H. M., Packer M. Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):236–241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher J. J., Friedman S. L., Roll F. J., Bissell D. M. Immunolocalization of laminin in normal rat liver and biosynthesis of laminin by hepatic lipocytes in primary culture. Gastroenterology. 1988 Apr;94(4):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak K. M., Leo M. A., Lieber C. S. Alcoholic liver injury in baboons: transformation of lipocytes to transitional cells. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak K. M., Lieber C. S. Lipocytes and transitional cells in alcoholic liver disease: a morphometric study. Hepatology. 1988 Sep-Oct;8(5):1027–1033. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Pham N. T., Tsukamoto H. Differential effects of interleukin-1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and transforming growth factor beta 1 on cell proliferation and collagen formation by cultured fat-storing cells. Liver. 1989 Apr;9(2):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1989.tb00382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Zhang M. Y., Tsukamoto H. Sensitization of hepatic lipocytes by high-fat diet to stimulatory effects of Kupffer cell-derived factors: implication in alcoholic liver fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):173–182. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milani S., Herbst H., Schuppan D., Hahn E. G., Stein H. In situ hybridization for procollagen types I, III and IV mRNA in normal and fibrotic rat liver: evidence for predominant expression in nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology. 1989 Jul;10(1):84–92. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milani S., Herbst H., Schuppan D., Kim K. Y., Riecken E. O., Stein H. Procollagen expression by nonparenchymal rat liver cells in experimental biliary fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jan;98(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91307-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato Y., Hasumura Y., Takeuchi J. The role of fat-storing cells in Disse space fibrogenesis in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):559–566. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Suzuki J., Mukai H., Mori M. Sequential changes of extracellular matrix and proliferation of Ito cells with enhanced expression of desmin and actin in focal hepatic injury. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):611–619. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okanoue T., Burbige E. J., French S. W. The role of the Ito cell in perivenular and intralobular fibrosis in alcoholic hepatitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983 Sep;107(9):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce R. A., Glaug M. R., Greco R. S., Mackenzie J. W., Boyd C. D., Deak S. B. Increased procollagen mRNA levels in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1652–1658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Collart M. A., Grau G. E., Sappino A. P., Vassalli P. Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):245–247. doi: 10.1038/344245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Warhol M. J., O'Connor E. M., Etheridge C. L., Fujiwara K. Immunohistochemical localization of smooth muscle myosin in human spleen, lymph node, and other lymphoid tissues. Unique staining patterns in splenic white pulp and sinuses, lymphoid follicles, and certain vasculature, with ultrastructural correlations. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jun;123(3):440–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph R., McClure W. J., Woodward M. Contractile fibroblasts in chronic alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Apr;76(4):704–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saber M. A., Zern M. A., Shafritz D. A. Use of in situ hybridization to identify collagen and albumin mRNAs in isolated mouse hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4017–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Dietrich P. Y., Skalli O., Widgren S., Gabbiani G. Colonic pericryptal fibroblasts. Differentiation pattern in embryogenesis and phenotypic modulation in epithelial proliferative lesions. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;415(6):551–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00718649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Schürch W., Gabbiani G. Differentiation repertoire of fibroblastic cells: expression of cytoskeletal proteins as marker of phenotypic modulations. Lab Invest. 1990 Aug;63(2):144–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Gräff A., Skalli O., Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is expressed in a subset of bone marrow stromal cells in normal and pathological conditions. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;57(5):291–302. doi: 10.1007/BF02899094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Schürch W., Seemayer T., Lagacé R., Montandon D., Pittet B., Gabbiani G. Myofibroblasts from diverse pathologic settings are heterogeneous in their content of actin isoforms and intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):275–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takase S., Leo M. A., Nouchi T., Lieber C. S. Desmin distinguishes cultured fat-storing cells from myofibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts in the rat. J Hepatol. 1988 Jun;6(3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toccanier-Pelte M. F., Skalli O., Kapanci Y., Gabbiani G. Characterization of stromal cells with myoid features in lymph nodes and spleen in normal and pathologic conditions. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):109–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Cachectin: a hormone that triggers acute shock and chronic cachexia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):413–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Lee P. C., Ells P. F., Bissell D. M., Smuckler E. A., Stern R. Collagen production by rat hepatocytes and sinusoidal cells in primary monolayer culture. Hepatology. 1982 Jan-Feb;2(1):13–18. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin typing on total cellular extracts: a highly sensitive protein-chemical procedure able to distinguish different actins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):595–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake K. Perisinusoidal stellate cells (fat-storing cells, interstitial cells, lipocytes), their related structure in and around the liver sinusoids, and vitamin A-storing cells in extrahepatic organs. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;66:303–353. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61977-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi Y., Namihisa T., Kuroda H., Komatsu I., Miyazaki A., Watanabe S., Usui K. Immunocytochemical detection of desmin in fat-storing cells (Ito cells). Hepatology. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):709–714. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Leeuw A. M., McCarthy S. P., Geerts A., Knook D. L. Purified rat liver fat-storing cells in culture divide and contain collagen. Hepatology. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):392–403. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]