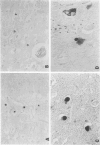
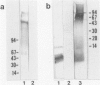
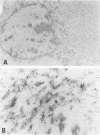
Abstract
Lewy bodies (LB) are intraneuronal, cytoplasmic inclusion bodies. They are invariably present in Parkinson's and diffuse LB diseases. Their composition by direct biochemical methods is unknown, although LBs are immunoreactive with a number of antibodies, including anti-ubiquitin and anti-neurofilament antibodies. Familial amyloidosis, Finnish type (FAF), is an autosomal-dominant form of systemic amyloidosis. The authors have isolated and partially sequenced the amyloid. The protein has significant sequence identity with gelsolin, an actin-modulating protein. Rabbit polyclonal antibodies raised to the FAF amyloid not only immunostain the amyloid but also LBs in the cortex and substantia nigra of Parkinson's and diffuse LB disease brains. Immunoreactivity is absorbed by the purified amyloid but is unaffected by ubiquitin. This provides a link between the LB and one of the human amyloidoses, FAF.
Full text
PDF

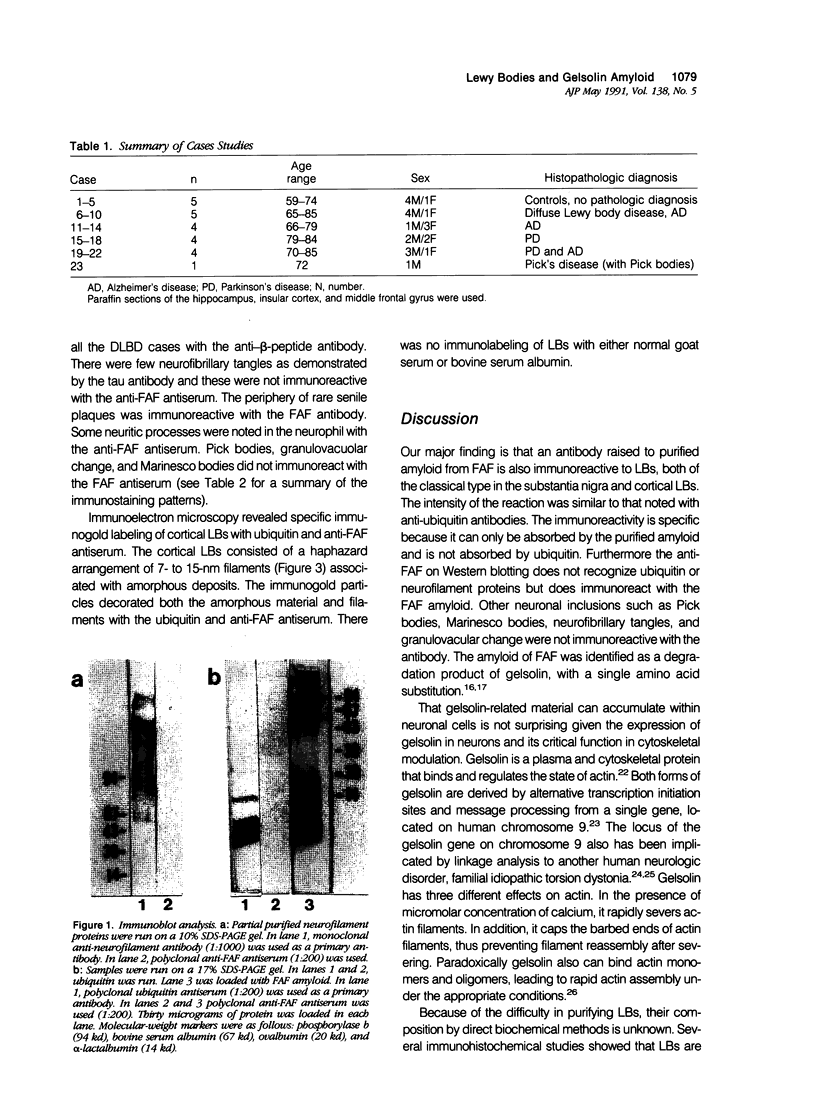
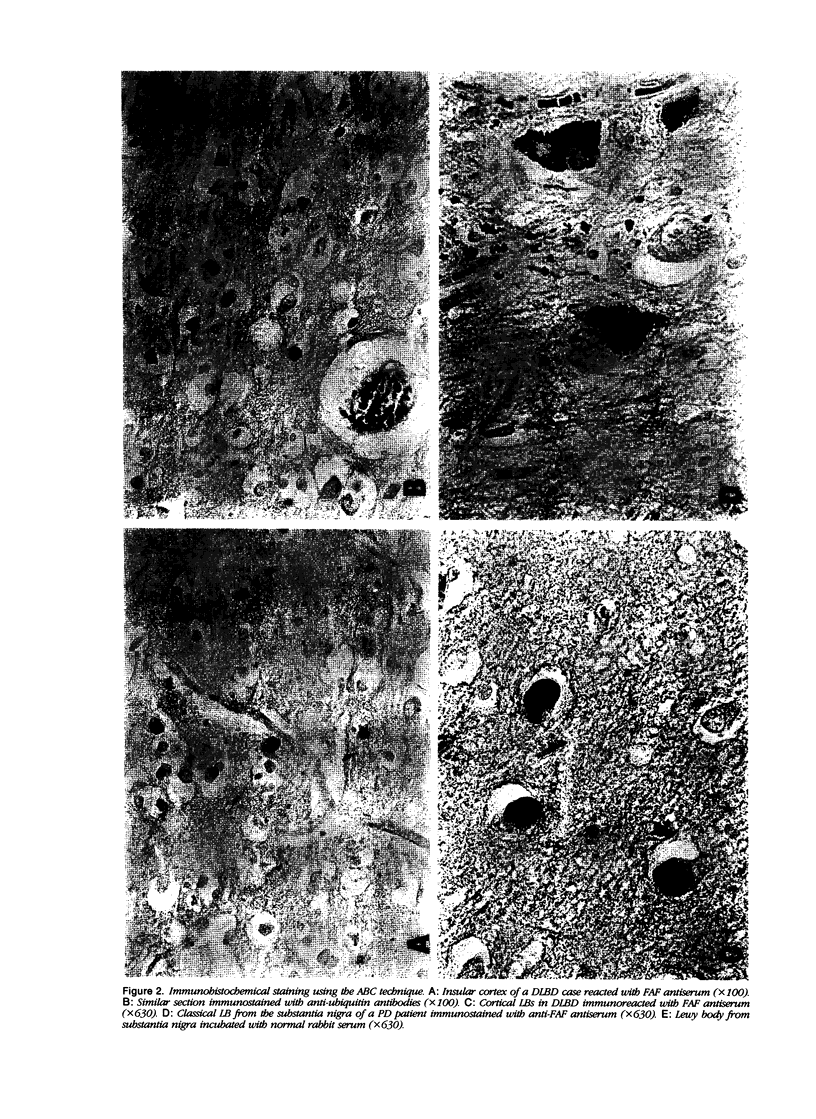
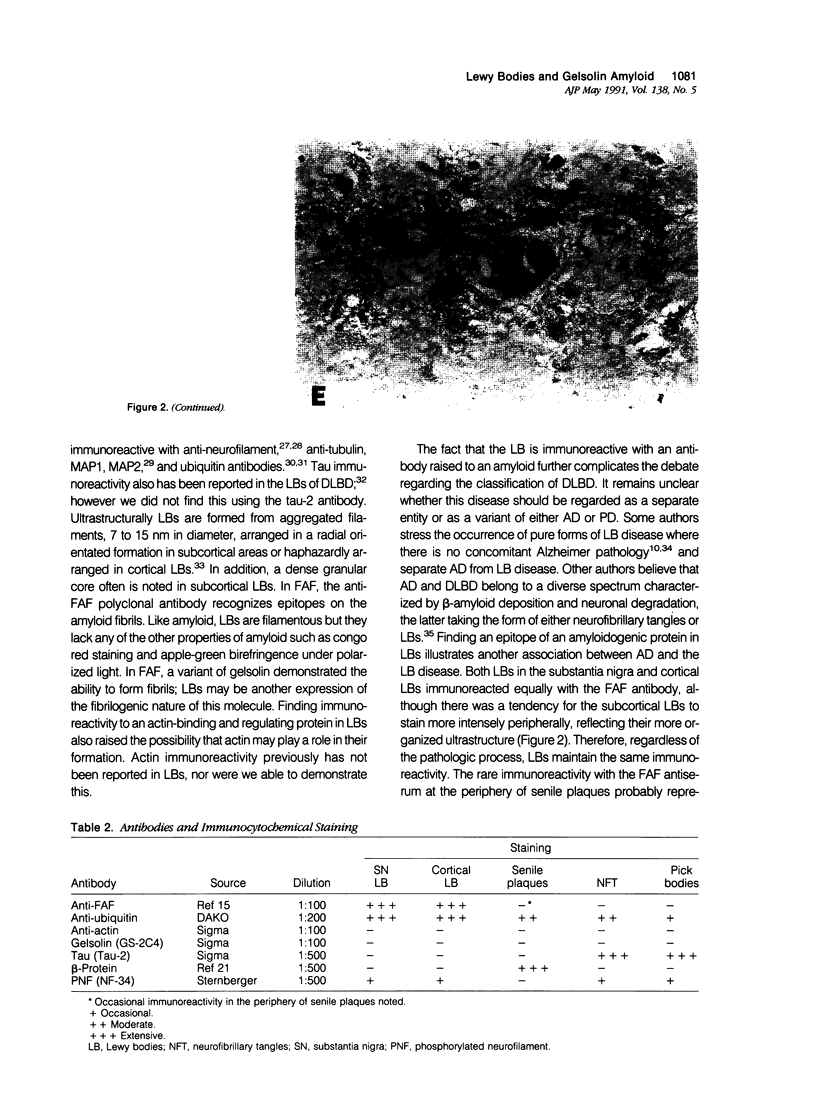


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agamanolis D. P., Greenstein J. I. Ataxia-telangiectasia. Report of a case with Lewy bodies and vascular abnormalities within cerebral tissue. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1979 Sep;38(5):475–489. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197909000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancher C., Lassmann H., Budka H., Jellinger K., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Wiche G., Seitelberger F., Wisniewski H. M. An antigenic profile of Lewy bodies: immunocytochemical indication for protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Jan;48(1):81–93. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198901000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Norton W. T. Bulk preparation of CNS cytoskeleton and the separation of individual neurofilament proteins by gel filtration: dye-binding characteristics and amino acid compositions. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1252–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Crystal H., Mattiace L. A., Kress Y., Schwagerl A., Ksiezak-Reding H., Davies P., Yen S. H. Diffuse Lewy body disease: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(6):572–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00691284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooling E. C., Schoene W. C., Richardson E. P., Jr Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1974 Jan;30(1):70–83. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490310072012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forno L. S., Sternberger L. A., Sternberger N. H., Strefling A. M., Swanson K., Eng L. F. Reaction of Lewy bodies with antibodies to phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated neurofilaments. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Mar 14;64(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Bergeron C., Perry G. The presence of tau distinguishes Lewy bodies of diffuse Lewy body disease from those of idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90651-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Perry G. Lewy bodies contain epitopes both shared and distinct from Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;47(6):654–663. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Haltia M., Prelli F., Novello J., Frangione B. Gelsolin variant (Asn-187) in familial amyloidosis, Finnish type. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):827–830. doi: 10.1042/bj2720827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb W. R., Lees A. J. The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Jun;51(6):745–752. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb W. R., Lees A. J. The significance of the Lewy body in the diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Jan-Feb;15(1):27–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb W. R., Scaravilli F., Michund J. Lewy bodies and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;53(8):710–711. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.8.710-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Yen S. H., Chiu F. C., Peress N. S. Lewy bodies of Parkinson's disease contain neurofilament antigens. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1082–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.6308771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltia M., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Gallo G., Kiuru S., Somer H., Palo J., Frangione B. Amyloid in familial amyloidosis, Finnish type, is antigenically and structurally related to gelsolin. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1223–1228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltia M., Prelli F., Ghiso J., Kiuru S., Somer H., Palo J., Frangione B. Amyloid protein in familial amyloidosis (Finnish type) is homologous to gelsolin, an actin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):927–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90612-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L., Salmon D., Galasko D., Masliah E., Katzman R., DeTeresa R., Thal L., Pay M. M., Hofstetter R., Klauber M. The Lewy body variant of Alzheimer's disease: a clinical and pathologic entity. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka K. Diffuse Lewy body disease in Japan. J Neurol. 1990 Jun;237(3):197–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00314594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. L., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Risch N., Bressman S. B., Brin M. F., Schuback D. E., Burke R. E., Kwiatkowski D. J., Shale H. Dystonia gene in Ashkenazi Jewish population is located on chromosome 9q32-34. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):114–120. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Mehl R., Yin H. L. Genomic organization and biosynthesis of secreted and cytoplasmic forms of gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):375–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Westbrook C. A., Bruns G. A., Morton C. C. Localization of gelsolin proximal to ABL on chromosome 9. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;42(4):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Haltia M., Fernandez-Madrid I., Koivunen O., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Frangione B. Mutation in gelsolin gene in Finnish hereditary amyloidosis. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1865–1867. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Blanchard A., Morrell K., Lennox G., Reynolds L., Billett M., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament inclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as Rosenthal fibres in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol. 1988 May;155(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretoja J. Familial systemic paramyloidosis with lattice dystrophy of the cornea, progressive cranial neuropathy, skin changes and various internal symptoms. A previously unrecognized heritable syndrome. Ann Clin Res. 1969 Dec;1(4):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretoja J. Genetic aspects of familial amyloidosis with corneal lattice dystrophy and cranial neuropathy. Clin Genet. 1973;4(3):173–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L., Kramer P. L., Moskowitz C. B., Kwiatkowski D. J., Brin M. F., Bressman S. B., Schuback D. E., Falk C. T., Risch N., de Leon D. Human gene for torsion dystonia located on chromosome 9q32-q34. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1427–1434. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow P. S., Finley D., Varshavsky A. Enhancement of immunoblot sensitivity by heating of hydrated filters. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODARD J. S. Concentric hyaline inclusion body formation in mental disease analysis of twenty-seven cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1962 Jul;21:442–449. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196207000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M. Cortical changes in the parkinsonian brain: a contribution to the delineation of "diffuse Lewy body disease". J Neurol. 1983;229(1):17–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00313493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M. Cortical changes in the parkinsonian brain: a contribution to the delineation of "diffuse Lewy body disease". J Neurol. 1983;229(1):17–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00313493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]