Abstract
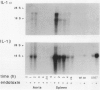
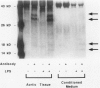
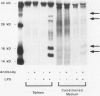
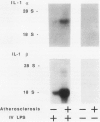
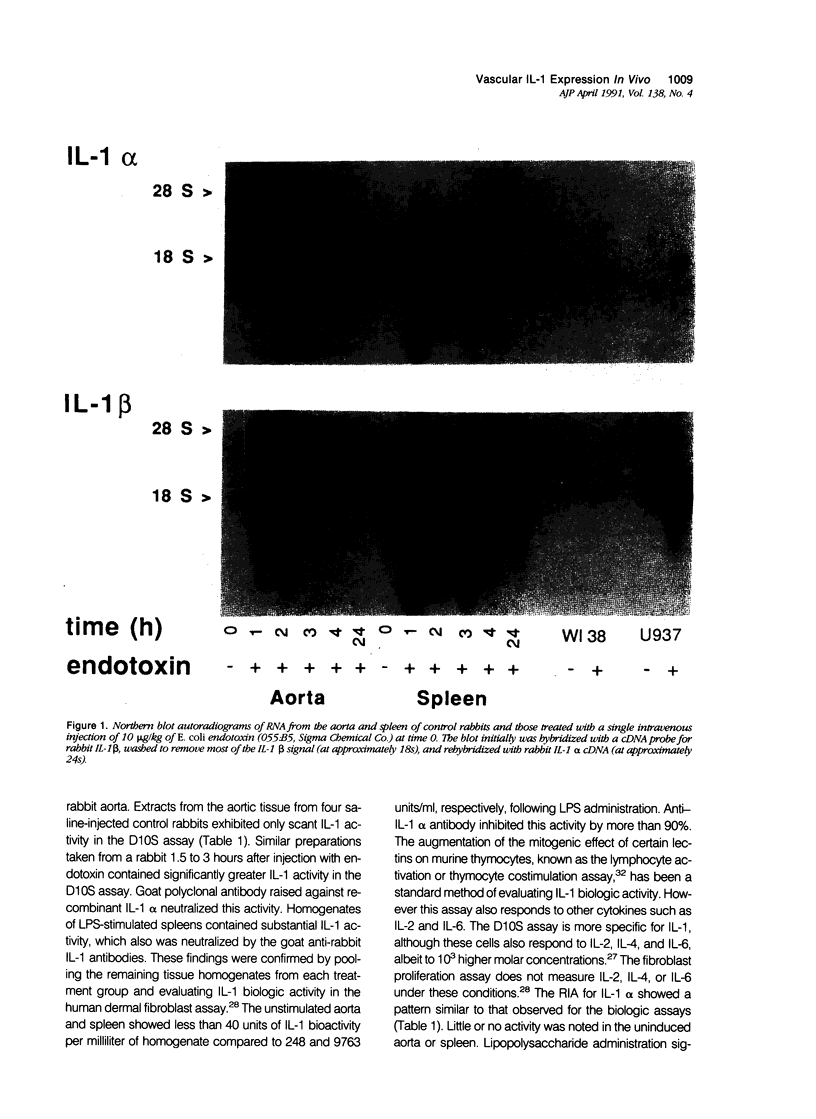
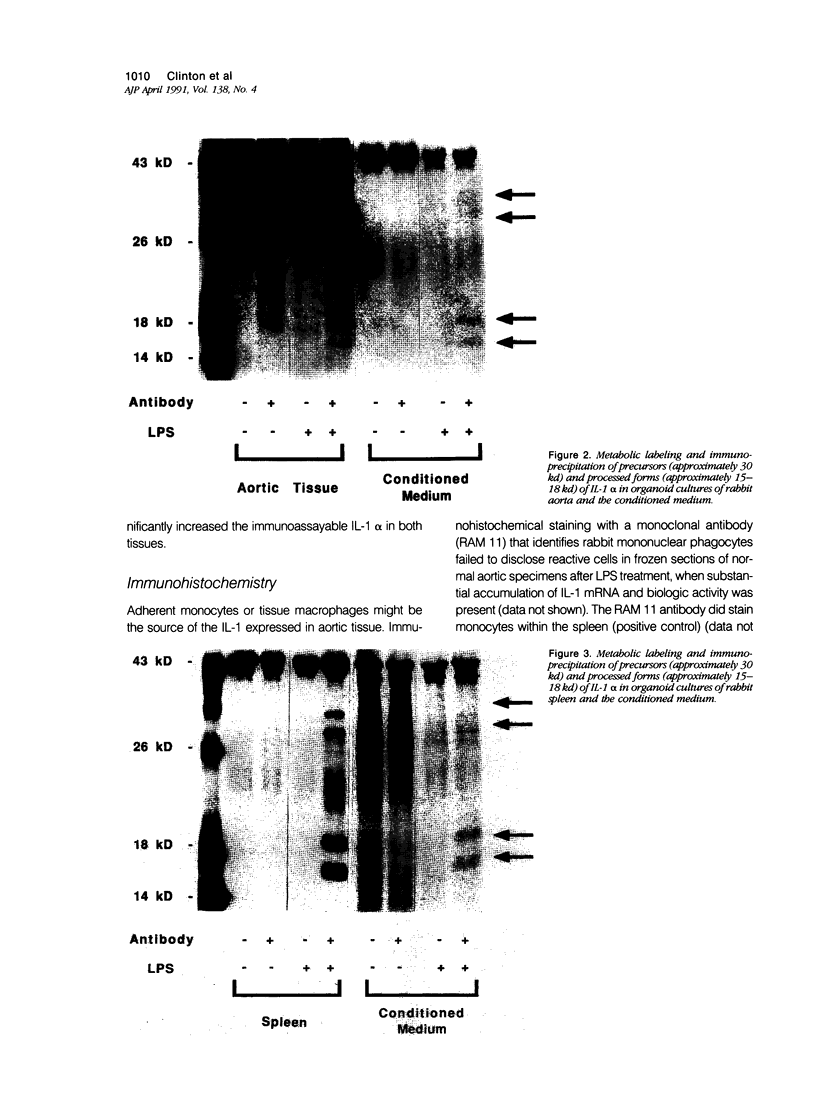
Cultured human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells express interleukin-1 (IL-1) genes when exposed to bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and a variety of inflammatory mediators. Local production of IL-1 may contribute to the pathogenesis of various vascular diseases. Therefore the ability of intact vascular tissue to accumulate IL-1 mRNA and synthesize de novo biologically active IL-1 protein was examined. Escherichia coli LPS (10 micrograms/kg) was administered intravenously to adult rabbits and total RNA was isolated from aortic tissue at various times after LPS injection. In saline-injected rabbits, RNA extracted from the thoracic aorta contained little or no IL-1 message detected by Northern analysis using IL-1 alpha and beta cDNA probes cloned from an LPS-stimulated rabbit splenic macrophage library. Lipopolysaccharide treatment promptly induced transient accumulation of mRNA for IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta within the aorta (maximal 1-hour after injection). Short-term organoid cultures of rabbit aorta exposed to LPS in vitro synthesized immunoprecipitable IL-1 alpha protein. Extracts of aortic tissue excised 1.5 to 3.0 hours after intravenous LPS administration contained immunoreactive and biologically active IL-1 alpha. Anti-rabbit IL-1 alpha antibody neutralized the biologic activity (more than 90%). Microscopic and immunohistochemical studies did not disclose adherent or infiltrating macrophages in rabbit aorta at the time of maximal IL-1 mRNA accumulation after LPS administration (1.5 hours), indicating that intrinsic vascular wall cells rather than mononuclear phagocytes probably account for the IL-1 activity induced by LPS. In addition, aortic tissue from rabbits fed an atherogenic diet showed an enhanced ability to accumulate IL-1 alpha and beta mRNA and produce immunodetectable protein in response to LPS administration. These studies demonstrate inducible IL-1 gene expression in rabbit vascular tissue in vivo and support a local role for this cytokine in vascular pathophysiology.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley D., Cohen R. A., Levinsky N. G. Interleukin 1 inhibits contraction of vascular smooth muscle. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):331–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI113879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Schleef R. R., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of the fibrinolytic system of cultured human vascular endothelium by interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):587–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI112613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursten S. L., Locksley R. M., Ryan J. L., Lovett D. H. Acylation of monocyte and glomerular mesangial cell proteins. Myristyl acylation of the interleukin 1 precursors. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1479–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI113755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Clark B. D., Wingfield P., Schmeissner U., Losberger C., Dinarello C. A., Shaw A. R. Rabbit IL-1. Cloning, expression, biologic properties, and transcription during endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Breviario F., Erroi A., Bussolino F., Mussoni L., Gramse M., Pintucci G., Casali B., Dinarello C. A., Van Damme J. Modulation of endothelial cell functions by different molecular species of interleukin 1. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):695–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demczuk S., Baumberger C., Mach B., Dayer J. M. Expression of human IL 1 alpha and beta messenger RNAs and IL 1 activity in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987;3(5):255–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Clark B. D., Puren A. J., Savage N., Rosoff P. M. The interleukin 1 receptor. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):49–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Measurement of immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta from human mononuclear cells: optimization of recovery, intrasubject consistency, and comparison with interleukin-1 alpha and tumor necrosis factor. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Dec;49(3):424–438. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Membrane interleukin 1 induction on human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2317–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Friedman G. B., Salomon R. N. Cytokines as modulators of cell proliferation in fibrotic diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1114–1117. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Ordovas J. M., Auger K. R., Robbins A. H., Birinyi L. K., Dinarello C. A. Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor induce interleukin-1 gene expression in adult human vascular endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):179–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Ordovas J. M., Birinyi L. K., Auger K. R., Dinarello C. A. Inducible interleukin-1 gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1432–1438. doi: 10.1172/JCI112732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Salomon R. N., Payne D. D., Schoen F. J., Pober J. S. Functions of vascular wall cells related to development of transplantation-associated coronary arteriosclerosis. Transplant Proc. 1989 Aug;21(4):3677–3684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Warner S. J., Friedman G. B. Interleukin 1: a mitogen for human vascular smooth muscle cells that induces the release of growth-inhibitory prostanoids. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):487–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI113346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisi P. J., Chu C. W., Koch G. A., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Dinarello C. A. Development and use of a radioimmunoassay for human interleukin-1 beta. Lymphokine Res. 1987 Summer;6(3):229–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Flad H. D., Dürrbaum I., Musehold J., Fetting R., Ulmer A. J., Herzbeck H., Brandt E. Detection of interleukin 1 with human dermal fibroblasts. Immunobiology. 1989 Jun;179(2-3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Cybulsky M. I., Colditz I. G., Chan M. K., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation in gram-negative infection: endotoxin, interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and neutrophils. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Hajjar K. A., Silverstein R. L., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1595–1600. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orencole S. F., Dinarello C. A. Characterization of a subclone (D10S) of the D10.G4.1 helper T-cell line which proliferates to attomolar concentrations of interleukin-1 in the absence of mitogens. Cytokine. 1989 Nov;1(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(89)91044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Dower S. K., Ross R. Interleukin-1 mitogenic activity for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells is due to PDGF-AA. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.2783498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Masuda J., Raines E. W., Gown A. M., Katsuda S., Sasahara M., Malden L. T., Masuko H., Sato H. Localization of PDGF-B protein in macrophages in all phases of atherogenesis. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1009–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2343305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp E. A., Cameron P. M., Ranawat C. S., Schmidt J. A., Bayne E. K. Specific bioactivities of monocyte-derived interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta are similar to each other on cultured murine thymocytes and on cultured human connective tissue cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):836–839. doi: 10.1172/JCI112649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Bank I., Nawroth P. P., Cassimeris J., Kisiel W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Dinarello C., Chess L., Jaffe E. A. Self-regulation of procoagulant events on the endothelial cell surface. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1223–1235. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Rosenfeld M., Ross R., Gown A. M. Immunocytochemical analysis of cellular components in atherosclerotic lesions. Use of monoclonal antibodies with the Watanabe and fat-fed rabbit. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):601–613. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C. R., Vetto R. M., Burger D. R. Expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) and interleukin 1 by subcultured human endothelial cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jun;93(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner S. J., Auger K. R., Libby P. Human interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1 gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1316–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner S. J., Auger K. R., Libby P. Interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1. II. Recombinant human interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1 production by adult human vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1911–1917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner S. J., Libby P. Human vascular smooth muscle cells. Target for and source of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):100–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]