Abstract
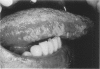
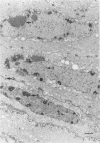
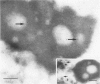
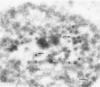
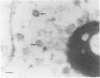
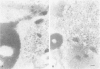
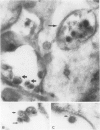
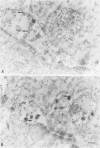
The authors investigated the life cycle of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in keratinocytes of oral hairy leukoplakia by combining immunohistochemistry. DNA in situ hybridization, and lectin histochemistry with electron microscopy. Diffuse-staining components of the EBV early antigen complex (EA-D), EBV 150-kd capsid antigen (VCA), EBV membrane antigen (gp350/220), and double-stranded DNA were labeled with monoclonal antibodies. An EBV-DNA probe was used to locate EBV DNA. Wheat-germ agglutinin (WGA) was employed to distinguish Golgi-associated compartments. The authors found EBV proteins and EBV DNA only in keratinocytes with apparent viral assembly. In situ hybridization showed EBV DNA in free corelike material and in electron-dense cores of mature nucleocapsids. Monoclonal antibodies to nonspecific double-stranded DNA attached to the same structures and to marginated chromatin. Components of EA-D were dispersed throughout the nuclei but accumulated near condensed chromatin and in 'punched-out' regions of the chromatin. Epstein-Barr virus 150-kd capsid antigen was found only in the nuclei, where it appeared preferentially on mature nucleocapsids. As yet unexplained arrays of intranuclear particles that remained unlabeled with all EBV-specific probes reacted intensely with an antiserum against common papillomavirus antigen. Gp350/220 was detectable in various cellular membrane compartments and was highly concentrated on EBV envelopes in peripheral Golgi-associated secretory vesicles. It was less abundant on the extracellular EBV, indicating that viral membrane antigen partly dissociates from the mature virus. Combined lectin-binding histochemistry and electron microscopy demonstrated for the first time that EBV is processed in the Golgi apparatus, which eventually releases the virus by fusion with the plasma membrane. These results provide insight into the biologic events that occur during complete EBV replication in vivo.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Barr S., Timbury M. C. The fine structure of cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):103–119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belton C. M., Eversole L. R. Oral hairy leukoplakia: ultrastructural features. J Oral Pathol. 1986 Oct;15(9):493–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1986.tb00665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoni G., Nguyen Q. V., Humphreys R. E., Sairenji T. Intracellular synthesis of Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen gp350/220. Inhibitory effect of monensin on its expression. Intervirology. 1989;30(2):61–73. doi: 10.1159/000150077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birx D. L., Redfield R. R., Tosato G. Defective regulation of Epstein-Barr virus infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or AIDS-related disorders. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 3;314(14):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604033141403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral G. A., Schaffer P. A. Electron microscope studies of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):727–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.727-737.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. K., Sears J. F. Preparation of infectious cell-free herpes-type virus associated with Marek's disease. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.258-261.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maubeuge J., Ledoux M., Feremans W., Zissis G., Goens J., Andre J., Gourdain J. M., Menu R., De Wit S., Cran S. Oral "hairy" leucoplakia in an African AIDS patient. J Cutan Pathol. 1986 Jun;13(3):235–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb01650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Souza Y. G., Greenspan D., Felton J. R., Hartzog G. A., Hammer M., Greenspan J. S. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in the epithelial cells of oral hairy leukoplakia by in situ hybridization of tissue sections. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 8;320(23):1559–1560. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906083202315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desgranges C., Bornkamm G. W., Zeng Y., Wang P. C., Zhu J. S., Shang M., De-Thé G. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral DNA internal repeats in the nasopharyngeal mucosa of Chinese with IgA/EBV-specific antibodies. Int J Cancer. 1982 Jan 15;29(1):87–91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A., ACHONG B. G., BARR Y. M. VIRUS PARTICLES IN CULTURED LYMPHOBLASTS FROM BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA. Lancet. 1964 Mar 28;1(7335):702–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eversole L. R., Jacobsen P., Stone C. E., Freckleton V. Oral condyloma planus (hairy leukoplakia) among homosexual men: a clinicopathologic study of thirty-six cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1986 Mar;61(3):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(86)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eversole L. R., Stone C. E., Beckman A. M. Detection of EBV and HPV DNA sequences in oral "hairy" leukoplakia by in situ hybridization. J Med Virol. 1988 Nov;26(3):271–277. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficarra G., Barone R., Gaglioti D., Milo D., Riccardi R., Romagnoli P., Zorn M. Oral hairy leukoplakia among HIV-positive intravenous drug abusers: a clinicopathologic and ultrastructural study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988 Apr;65(4):421–426. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(88)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Kocks C., L'Age-Stehr J., Reupke H. Comparative immunoelectron microscopy with monoclonal antibodies on yellow fever virus-infected cells: pre-embedding labelling versus immunocryoultramicrotomy. J Virol Methods. 1985 Mar;10(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan W. D., Ackerman G. A. Adsorption of horseradish peroxidase, ovomucoid and anti-immunoglobulin to colloidal gold for the indirect detection of concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin and goat anti-human immunoglobulin G on cell surfaces at the electron microscopic level: a new method, theory and application. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Nov;25(11):1187–1200. doi: 10.1177/25.11.21217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan D., Greenspan J. S., Conant M., Petersen V., Silverman S., Jr, de Souza Y. Oral "hairy" leucoplakia in male homosexuals: evidence of association with both papillomavirus and a herpes-group virus. Lancet. 1984 Oct 13;2(8407):831–834. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90872-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Greenspan D., Lennette E. T., Abrams D. I., Conant M. A., Petersen V., Freese U. K. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus within the epithelial cells of oral "hairy" leukoplakia, an AIDS-associated lesion. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1564–1571. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Rabanus J. P., Petersen V., Greenspan D. Fine structure of EBV-infected keratinocytes in oral hairy leukoplakia. J Oral Pathol Med. 1989 Dec;18(10):565–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1989.tb01553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A., Young B. D., Griffin B. E. Random association of Epstein-Barr virus genomes with host cell metaphase chromosomes in Burkitt's lymphoma-derived cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):328–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanas R. J., Abrams A. M., Jensen J. L., Wuerker R. B., Handlers J. P. Oral hairy leukoplakia: ultrastructural observations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988 Mar;65(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(88)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmig W., Mensing H., Seyfarth K., Schaeg G., Jänner M., Nasemann T. Orale "hairy" Leukoplakie--Frühsymptom bei HTLV-III/LAV-Infektion. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1986 Sep 12;111(37):1394–1397. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1068640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton G. P., James W. D., Redfield R. R., Brown C., Rodman O. G. Oral hairy leukoplakia. A distinctive marker of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III) infection. Arch Dermatol. 1987 May;123(5):624–628. doi: 10.1001/archderm.123.5.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löning T., Henke R. P., Reichart P., Becker J. In situ hybridization to detect Epstein-Barr virus DNA in oral tissues of HIV-infected patients. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;412(2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00716184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Heller M., Petti L., O'Shiro E., Kieff E. Persistence of the entire Epstein-Barr virus genome integrated into human lymphocyte DNA. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1322–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6095452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. J., Smith A. R., Barker R. N., Epstein M. A. A structural investigation of the Epstein-Barr (EB) virus membrane antigen glycoprotein, gp340. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):397–404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. G., Achong B. G., Epstein M. A. Unusual intranuclear tubular structures associated with the maturation of Herpesvirus saimiri in monkey kidney cell cultures. Br J Cancer. 1973 Jun;27(6):434–440. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motz M., Deby G., Wolf H. Truncated versions of the two major Epstein-Barr viral glycoproteins (gp250/350) are secreted by recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Gene. 1987;58(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motz M., Fan J., Seibl R., Jilg W., Wolf H. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus 138-kDa early protein in Escherichia coli for the use as antigen in diagnostic tests. Gene. 1986;42(3):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazerian K., Lee L. F., Witter R. L., Burmester B. R. Ultrastructural studies of a herpesvirus of turkeys antigenically related to Marek's disease virus. Virology. 1971 Feb;43(2):442–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii S. Electron microscopic observations on FL cells infected with herpes simplex virus. I. Viral forms. Biken J. 1971 Jun;14(2):177–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Orr T. W. Antibody-dependent lymphocyte cytotoxicity against cells expressing Epstein-Barr virus antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):485–488. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Yao Q. Y., Wallace L. E. The Epstein-Barr virus as a model of virus-host interactions. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jan;41(1):75–79. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sairenji T., Bertoni G., Medveczky M. M., Medveczky P. G., Nguyen Q. V., Humphreys R. E. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) release from P3HR-1 and B95-8 cell lines by monoclonal antibodies to EBV membrane antigen gp350/220. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2614–2621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2614-2621.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Brunschwig J. P., McCombs R. M., Benyesh-Melnick M. Electron microscopic studies of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):444–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibl R., Wolf H. Mapping of Epstein-Barr virus proteins on the genome by translation of hybrid-selected RNA from induced P3HR1 cells and induced Raji cells. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro I. M., Volsky D. J. Infection of normal human epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1225–1228. doi: 10.1126/science.6298935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Lemon S. M., Pagano J. S. A second site for Epstein-Barr virus shedding: the uterine cervix. Lancet. 1986 Nov 15;2(8516):1122–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackpole C. W. Herpes-type virus of the frog renal adenocarcinoma. I. Virus development in tumor transplants maintained at low temperature. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):75–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.75-93.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Geilinger K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Ekblom P., Laurila P. Subcellular compartmentalization of saccharide moieties in cultured normal and malignant cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):429–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Kwong A., Frenkel N. Site-specific cleavage/packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA and the selective maturation of nucleocapsids containing full-length viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang Y., Silberklang M., Morgan A., Munshi S., Lenny A. B., Ellis R. W., Kieff E. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus gp350/220 gene in rodent and primate cells. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1796–1807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1796-1807.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Haus M., Wilmes E. Persistence of Epstein-Barr virus in the parotid gland. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):795–798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.795-798.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Clark D., Sixbey J. W., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human pharyngeal epithelia. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):240–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. L., Langford A., Becker J., Rabanus J. P., Pohle H. D., Reichart P., Gelderblom H. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical findings in oral hairy leukoplakia. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;412(6):533–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00844289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Labban N., Rindum J., Nielsen H., Pindborg J. J. Crystalline inclusions in epithelial cells of hairy leukoplakia: a new ultrastructural finding. Scand J Dent Res. 1988 Aug;96(4):353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1988.tb01567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]