Abstract
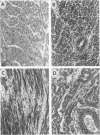
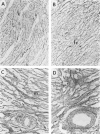
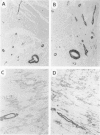
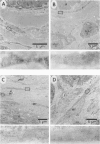
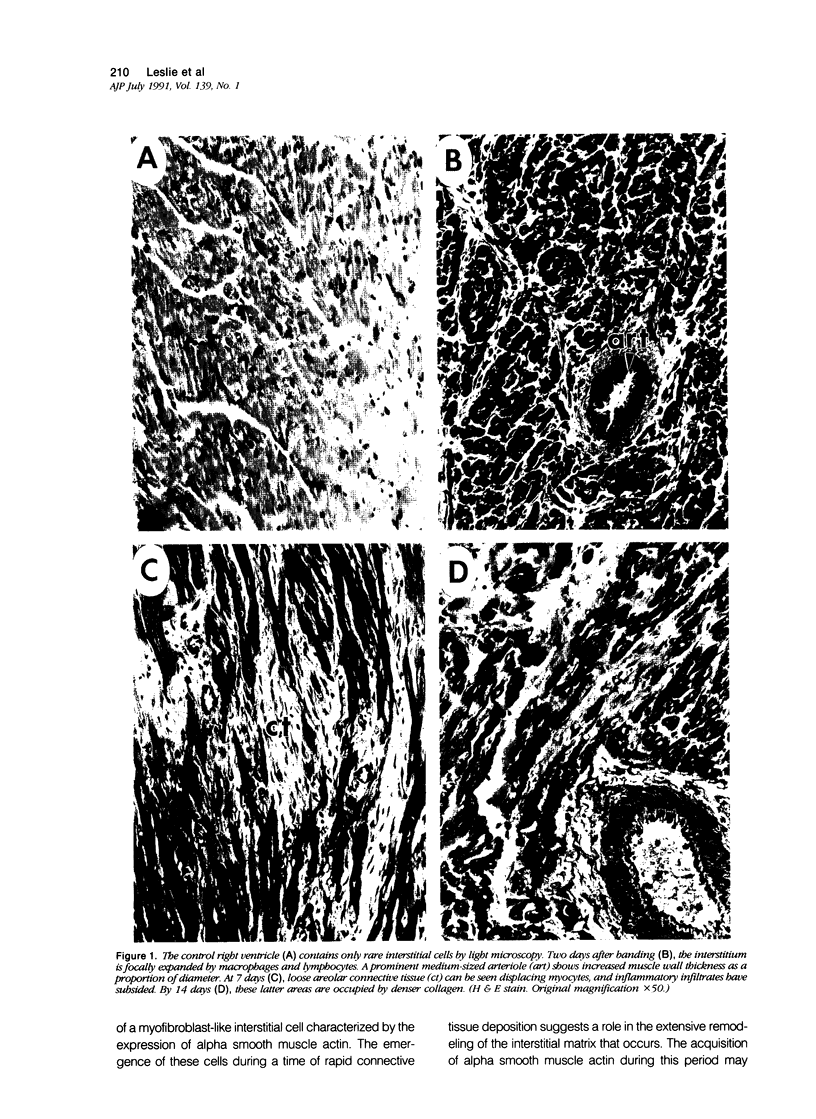
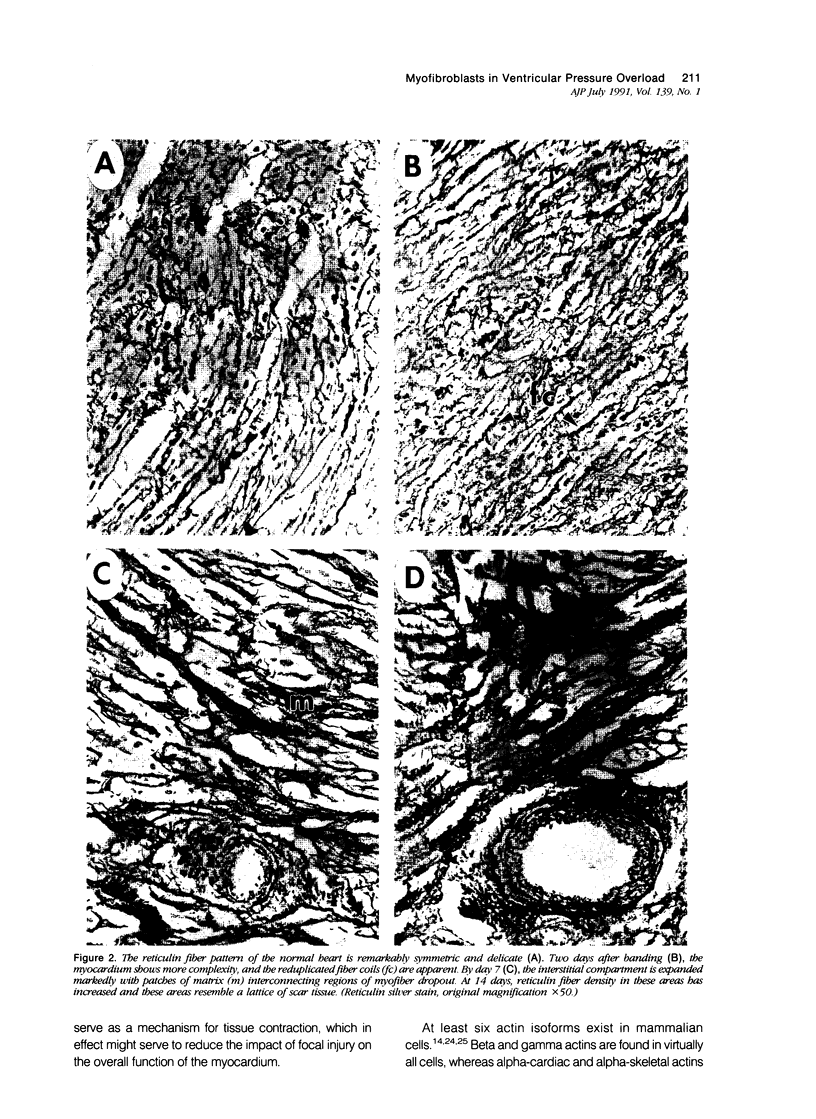
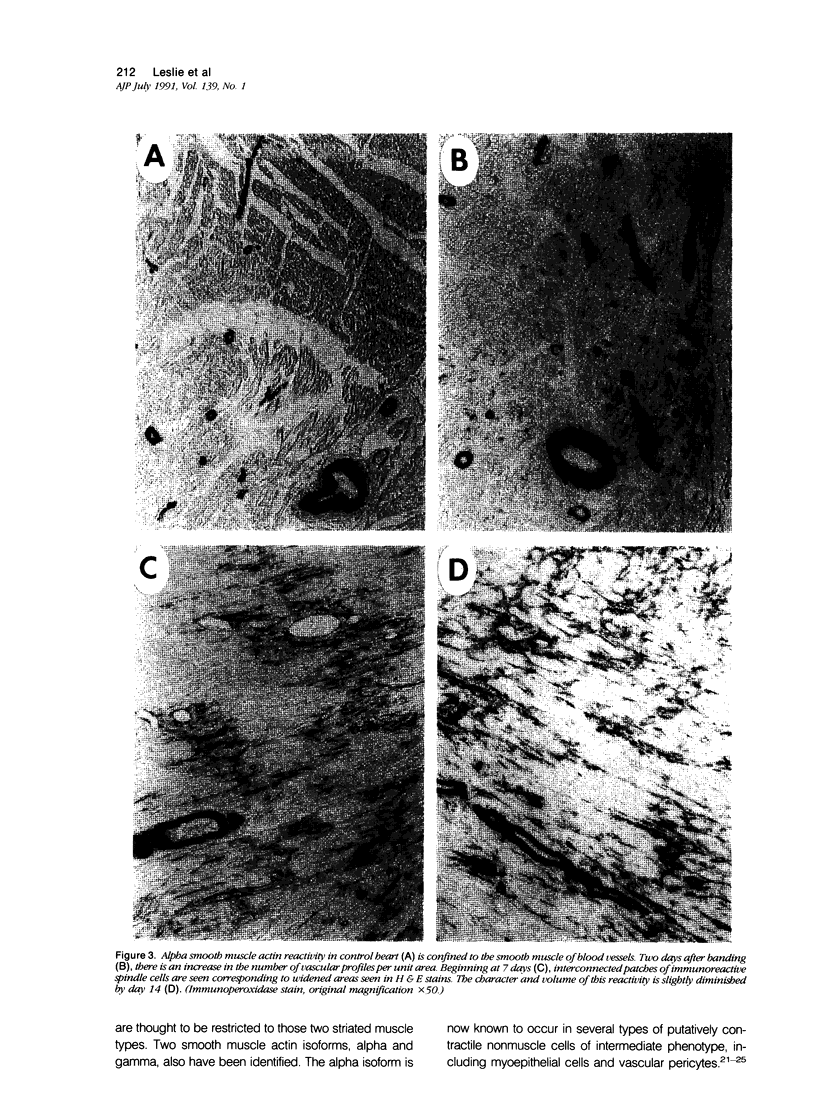
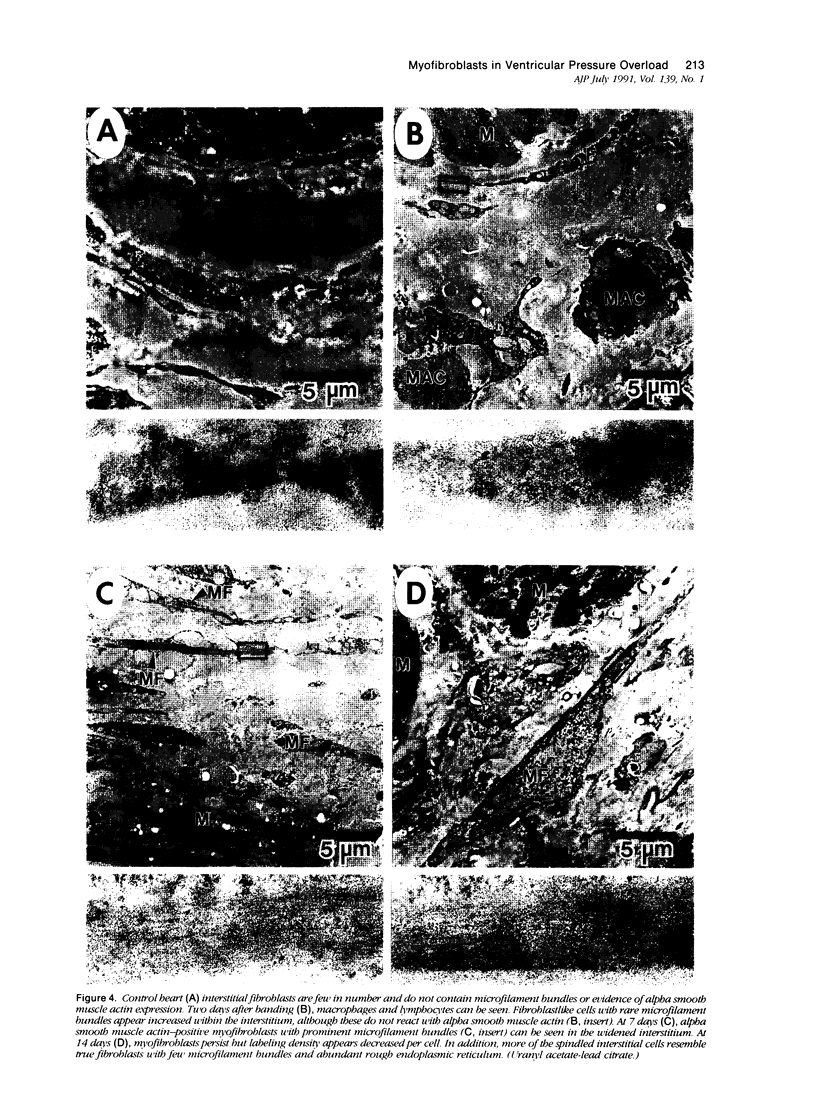
A number of changes occur in contractile proteins and mechanical performance of the heart within 2 weeks of right ventricular pressure overload in 8- to 12-week-old rabbits. These changes are accompanied by increases in collagen concentration and the ratio of type I to type III collagen. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the evolution of these connective tissue changes morphologically and to characterize the interstitial cells that might be responsible. The myocardium is infiltrated by mononuclear inflammatory cells 2 days after banding, accompanied by focal myocyte necrosis. By 7 days, the inflammatory infiltrates subside and the damaged myocytes seen at 2 days are replaced by new collagen and a population of spindle-shaped cells, with ultrastructural features of myofibroblasts. A significant proportion of these cells contain alpha smooth muscle actin by immunohistochemical analysis. At 14 days, there is a large increase in stainable collagen with complex remodeling and reduplication of the collagen fiber network of the interstitium. Alpha smooth muscle actin-containing myofibroblasts persist, but their immunoreactivity appears reduced compared with day 7. The authors hypothesize that the interstitial fibroblasts that acquire smooth-muscle-like features in this model play a critical role in the heart's response to severe and sudden mechanical stress and are at least partly responsible for the changes in connective tissue that occur as a result of pressure overload in this model.
Full text
PDF


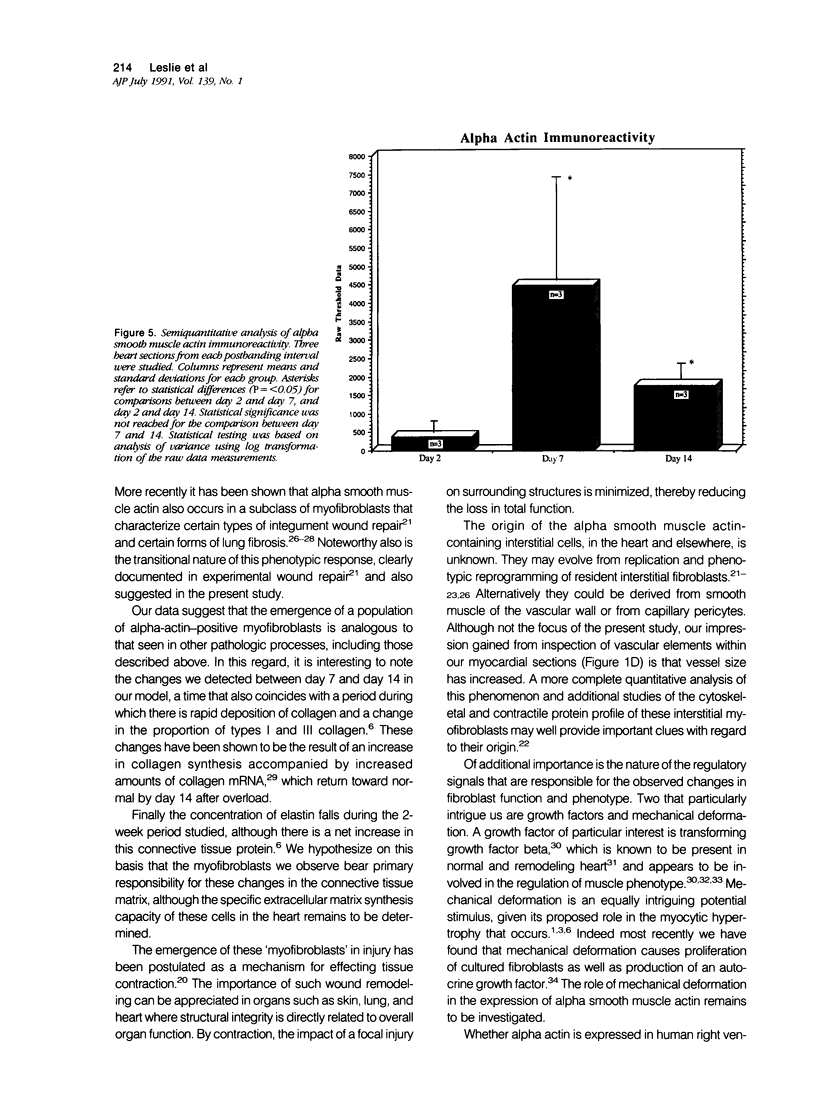


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert N. R., Hamrell B. B., Halpern W. Mechanical and biochemical correlates of cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 1974 Aug;35(2):suppl II–II:82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G., 4th Cardiocyte adaptation to chronically altered load. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:501–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor S. M., Robinson T. F. Comparative connective tissue structure-function relationships in biologic pumps. Lab Invest. 1988 Feb;58(2):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast: a key cell for wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;54:183–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H., Sweets H. H. A Simple Method for the Silver Impregnation of Reticulum. Am J Pathol. 1936 Jul;12(4):545–552.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamrell B. B., Alpert N. R. The mechanical characteristics of hypertrophied rabbit cardiac muscle in the absence of congestive heart failure: the contractile and series elastic elements. Circ Res. 1977 Jan;40(1):20–25. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. The use of antiavidin antibody and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex in immunoperoxidase technics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jun;75(6):816–821. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie K., King T. E., Jr, Low R. Smooth muscle actin is expressed by air space fibroblast-like cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 1991 Mar;99(3 Suppl):47S–48S. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.3_supplement.47s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litten R. Z., 3rd, Martin B. J., Low R. B., Alpert N. R. Altered myosin isozyme patterns from pressure-overloaded and thyrotoxic hypertrophied rabbit hearts. Circ Res. 1982 Jun;50(6):856–864. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Stirewalt W. S., Hultgren P., Low E. S., Starcher B. Changes in collagen and elastin in rabbit right-ventricular pressure overload. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):709–713. doi: 10.1042/bj2630709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Reynolds S., Low R., Leslie K., Adler K., Gabbiani G., Skalli O. Alpha-smooth muscle actin in parenchymal cells of bleomycin-injured rat lung. Lab Invest. 1989 May;60(5):643–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan H. E., Gordon E. E., Kira Y., Chua H. L., Russo L. A., Peterson C. J., McDermott P. J., Watson P. A. Biochemical mechanisms of cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:533–543. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai R., Low R. B., Stirewalt W. S., Alpert N. R., Litten R. Z. Efficiency and capacity of protein synthesis are increased in pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):H325–H328. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.2.H325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K., Geisterfer A. A., Yang Y. W., Komoriya A. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced growth inhibition and cellular hypertrophy in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):771–780. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Roberts A. B., Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Sporn M. B., Dawid I. B. Mesoderm induction in amphibians: the role of TGF-beta 2-like factors. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):783–785. doi: 10.1126/science.3422517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Garavito M. Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 May;29(5):663–671. doi: 10.1177/29.5.6166664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Pelte M. F., Peclet M. C., Gabbiani G., Gugliotta P., Bussolati G., Ravazzola M., Orci L. Alpha-smooth muscle actin, a differentiation marker of smooth muscle cells, is present in microfilamentous bundles of pericytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Mar;37(3):315–321. doi: 10.1177/37.3.2918221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Schürch W., Seemayer T., Lagacé R., Montandon D., Pittet B., Gabbiani G. Myofibroblasts from diverse pathologic settings are heterogeneous in their content of actin isoforms and intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):275–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Bazoberry F., Speir E. H., Casscells W., Ferrans V. J., Flanders K. C., Kondaiah P., Geiser A. G., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta-1 in acute myocardial infarction in rats. Growth Factors. 1988;1(1):91–99. doi: 10.3109/08977198809000251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin typing on total cellular extracts: a highly sensitive protein-chemical procedure able to distinguish different actins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):595–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. T. Cardiac interstitium in health and disease: the fibrillar collagen network. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Jun;13(7):1637–1652. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90360-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. T., Janicki J. S., Shroff S. G., Pick R., Chen R. M., Bashey R. I. Collagen remodeling of the pressure-overloaded, hypertrophied nonhuman primate myocardium. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):757–765. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]