Abstract
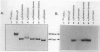
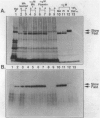
We tested the hypothesis that human plasma alpha 2 macroglobulin (alpha 2M) is a latent binding glycoprotein for human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Human recombinant 125I-TNF-alpha was incubated for 2 hours (37 degrees C) with purified native alpha 2M and with alpha 2M that was modified by reaction with methylamine or various proteinases. 125I-TNF-alpha/alpha 2M complexes were detected by nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis after autoradiography or by liquid chromatography on Superose-6. 125I-TNF-alpha bound strongly but noncovalently to alpha 2M-plasmin and alpha 2M-methylamine. There was minimal binding of 125I-TNF-alpha to native alpha 2M, alpha 2M-trypsin, or alpha 2M-thrombin. A 10(6) molar excess of porcine heparin did not reduce the binding of 125I-TNF-alpha to alpha 2M-methylamine or alpha 2M-plasmin. alpha 2M-plasmin or alpha 2M-methylamine added to human plasma or serum preferentially bound 125I-TNF-alpha in the presence of native alpha 2M. 125I-TNF-alpha also bound to 'fast' alpha-macroglobulins in methylamine-reacted human, rat, mouse, swine, equine, and bovine plasma. However, TNF-alpha, preincubated with either alpha 2M-plasmin or alpha 2M-methylamine, remained a potent necrogen for cultured L929 cells. Purified 125I-TNF-alpha/alpha 2M-plasmin complex injected intravenously in CD-1 mice rapidly cleared from the circulation, unless the alpha 2M-receptor pathway was blocked by coinjection of excess alpha 2M-trypsin. These findings demonstrate that alpha 2M is a latent plasmin-activated binding glycoprotein for TNF-alpha and that TNF-alpha/alpha 2M-plasmin complexes can be removed from the circulation by the alpha 2M-receptor pathway. This suggests that alpha 2M may be an important regulator of the activity and distribution of TNF-alpha in vivo.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Luger T. A. Identification of alpha 2-macroglobulin as a cytokine binding plasma protein. Binding of interleukin-1 beta to "F" alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5818–5825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. p-Nitrophenyl-p'-guanidinobenzoate HCl: a new active site titrant for trypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielpour D., Sporn M. B. Differential inhibition of transforming growth factor beta 1 and beta 2 activity by alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6973–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. A., Saksela O., Harpel P., Rifkin D. B. Alpha 2-macroglobulin is a binding protein for basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. B., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Binding and internalization of 125I-alpha 2-macroglobulin by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3454–3459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. R., Rosenberg M. R., Ney K. A., Michalopoulos G., Pizzo S. V. Binding of alpha 2-macroglobulin to hepatocytes: mechanism of in vivo clearance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):795–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick D. A., Gifford G. E. Comparison of in vitro cell cytotoxic assays for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Balber A. E., Hubbard W. J., Pizzo S. V. Ligand binding, conformational change and plasma elimination of human, mouse and rat alpha-macroglobulin proteinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):99–105. doi: 10.1042/bj2090099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Reynolds J. A., Pizzo S. V. Physical properties of human alpha 2-macroglobulin following reaction with methylamine and trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 10;705(3):306–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Alpha2-plasmin inhibitor and alpha2-macroglobulin-plasmin complexes in plasma. Quantitation by an enzyme-linked differential antibody immunosorbent assay. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):46–55. doi: 10.1172/JCI110253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin-enzyme interactions. Evidence for proteolytic modification of the subunit chain structure. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):508–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Deuel T. F. Human platelet-derived growth factor: radioimmunoassay and discovery of a specific plasma-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):383–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Deuel T. F. Specific covalent binding of platelet-derived growth factor to human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):342–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. S., O'Grady P., Huang J. S. Human transforming growth factor beta.alpha 2-macroglobulin complex is a latent form of transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1535–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Nielsen M. L. Analysis of macrophage surface receptors. I. Binding of alpha-macroglobulin . protease complexes to rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7323–7328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelker H. C., Oppenheim J. D., Stone-Wolff D., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Aggarwal B. B., Stevenson H. C., Vilcek J. Characterization of human tumor necrosis factor produced by peripheral blood monocytes and its separation from lymphotoxin. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):69–73. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo P. H., Stach R. W. Interaction of nerve growth factor with murine alpha-macroglobulin. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Mar;22(3):247–261. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarre J., Hayes M. A., Wollenberg G. K., Hussaini I., Hall S. W., Gonias S. L. An alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor-dependent mechanism for the plasma clearance of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in mice. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI114998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarre J., Wollenberg G. K., Gauldie J., Hayes M. A. Alpha 2-macroglobulin and serum preferentially counteract the mitoinhibitory effect of transforming growth factor-beta 2 in rat hepatocytes. Lab Invest. 1990 May;62(5):545–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Hirano T., Nagasawa S., Kishimoto T. Identification of alpha 2-macroglobulin as a carrier protein for IL-6. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):148–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. V. Synthesis in vitro by mononuclear phagocytes from various tissues of normal and BCG-injected rabbits. Br J Cancer. 1981 Sep;44(3):418–424. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey T. A., Falcone D. J., Brayton C. F., Agarwal L. A., Welt F. G., Weksler B. B. Transforming growth factor-beta activity is potentiated by heparin via dissociation of the transforming growth factor-beta/alpha 2-macroglobulin inactive complex. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):441–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor-McCourt M. D., Wakefield L. M. Latent transforming growth factor-beta in serum. A specific complex with alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14090–14099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Anundi H., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Nerve growth factor binds to serum alpha-2-macroglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91683-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. A human inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1511–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van Den Berghe H. Demonstration of an alpha2-macroglobulin receptor in human fibroblasts, absent in tumor-derived cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5155–5160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. Functional modifications of alpha 2-macroglobulin by primary amines. I. Characterization of alpha 2 M after derivatization by methylamine and by factor XIII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9016–9022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]