Abstract
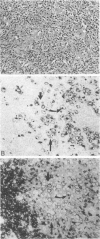
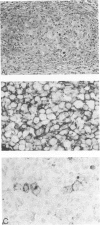
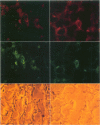
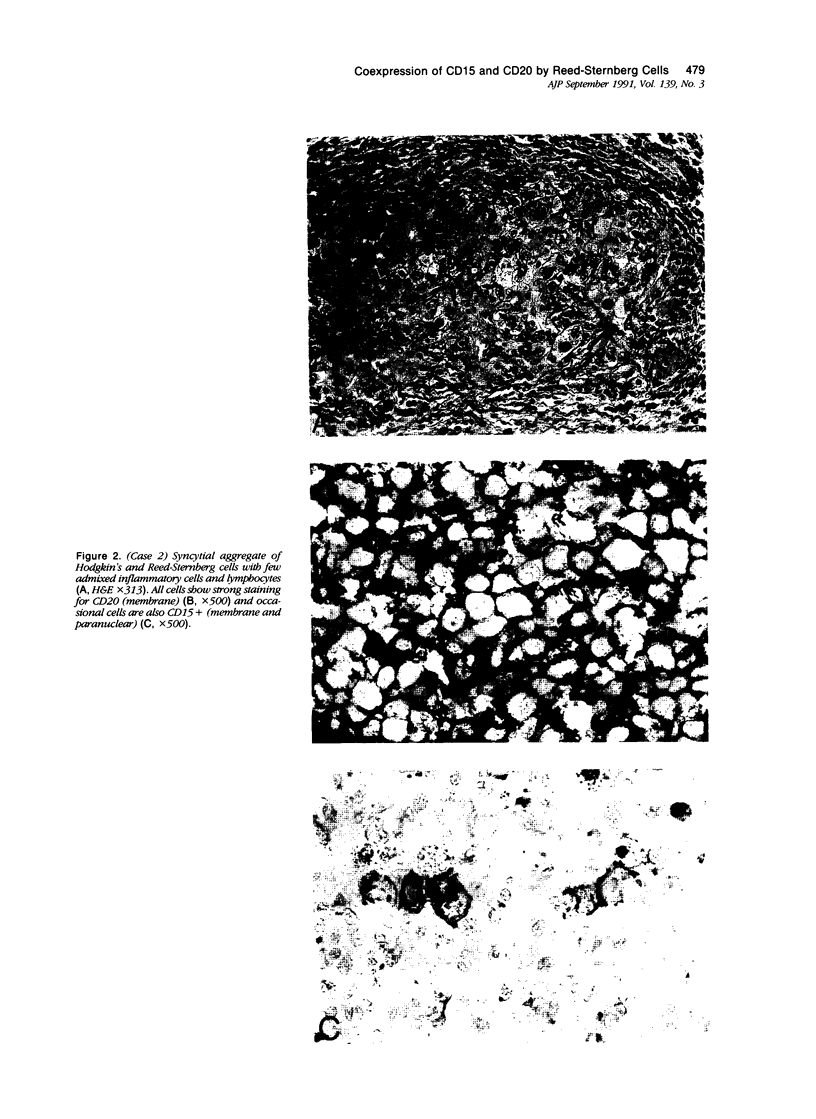
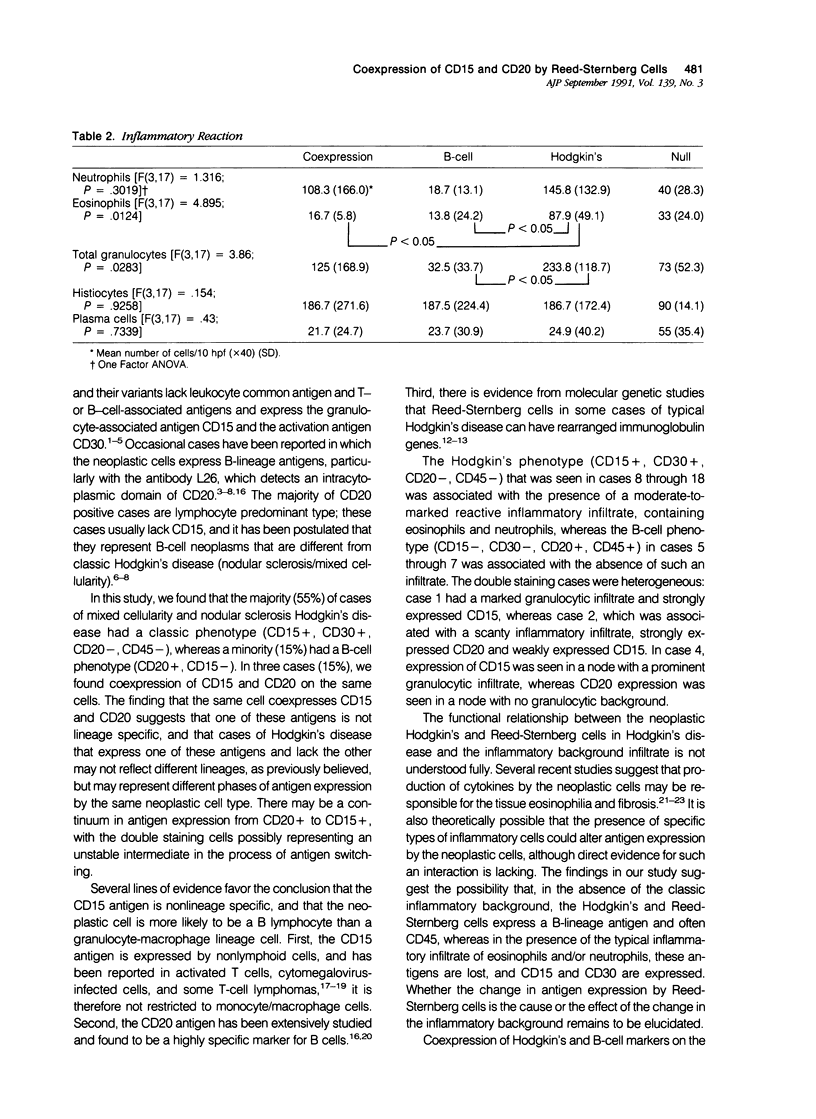
The immunophenotype of the Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease is heterogeneous among different cases; this heterogeneity has contributed to the continuing uncertainty regarding the normal counterpart of the Reed-Sternberg cell. In this study, the authors demonstrate coexpression of the B-cell marker, CD20, and the granulocyte associated antigen, CD15, by Reed-Sternberg cells in three of 20 cases of nodular sclerosis and mixed cellularity Hodgkin's disease using a double-labelling technique in one case and staining of serial sections in three cases. Additionally, the authors found that expression of CD20 occurred more often in tumors with a monomorphous proliferation of mononuclear and binucleate Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells, without numerous eosinophils or polymorphonuclear neutrophils. In contrast, expression of CD15 by Reed-Sternberg cells was associated with a greater granulocyte infiltrate. The presence or absence of fibrosis, plasma cells, and histiocytes did not correlate with antigen expression. These results suggest that there may be a continuum of antigen expression by Reed-Sternberg cells, with some cells expressing CD20, some CD15, and others expressing both antigens; cells coexpressing both CD15 and CD20 may represent an unstable intermediate in the process of antigen switching. The possibility that antigen expression by the neoplastic cells in a given case may modulate depending on the background infiltrate could explain the heterogeneity of immunophenotype among cases of Hodgkin's disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ezra J., Sheibani K., Swartz W., Stroup R., Traweek S. T., Kezirian J., Rappaport H. Relationship between eosinophil density and T-cell activation markers in lymph nodes of patients with Hodgkin's disease. Hum Pathol. 1989 Dec;20(12):1181–1185. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(89)80009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. W., Harris M., Smith A. P., Elsam K. J. Immunophenotypic study of lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin's disease. Histopathology. 1991 Jan;18(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecher M., Banks P. M. Hodgkin's disease variant of Richter's syndrome. Report of eight cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Mar;93(3):333–339. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.3.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey T. T., Cousar J. B., Mangum M., Williams M. E., Lee J. T., Greer J. P., Collins R. D. Monomorphic lymphomas arising in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Correlation of morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular genetic findings in 12 cases. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):81–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey T. T., Olson S. J., Cousar J. B., Collins R. D. Immunophenotypes of Reed-Sternberg cells: a study of 19 cases of Hodgkin's disease in plastic-embedded sections. Blood. 1989 Dec;74(8):2624–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittal S. M., Caverivière P., Schwarting R., Gerdes J., Al Saati T., Rigal-Huguet F., Stein H., Delsol G. Monoclonal antibodies in the diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease. The search for a rational panel. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Jan;12(1):9–21. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198801000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles F. B., Cartun R. W., Pastuszak W. T. Hodgkin's disease, lymphocyte-predominant type: immunoreactivity with B-cell antibodies. Mod Pathol. 1988 Jul;1(4):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Gatter K. C., Pulford K. A., Mason D. Y. An evaluation of the utility of anti-granulocyte and anti-leukocyte monoclonal antibodies in the diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jun;123(3):508–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., d'Ardenne A. J., Stansfeld A. G. Paraffin section immunohistochemistry. II. Hodgkin's disease and large cell anaplastic (Ki1) lymphoma. Histopathology. 1988 Aug;13(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1988.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanjan S. N., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. A monoclonal antibody (MMA) that identifies a differentiation antigen on human myelomonocytic cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):172–188. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansmann M. L., Fellbaum C., Hui P. K., Lennert K. Morphological and immunohistochemical investigation of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma combined with Hodgkin's disease. Histopathology. 1989 Jul;15(1):35–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1989.tb03039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansmann M. L., Stein H., Fellbaum C., Hui P. K., Parwaresch M. R., Lennert K. Nodular paragranuloma can transform into high-grade malignant lymphoma of B type. Hum Pathol. 1989 Dec;20(12):1169–1175. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(89)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S. The elusive Reed-Sternberg cell. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 23;320(8):529–531. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902233200813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Agnarsson B. A., Ellingsworth L. R., Newcom S. R. Immunohistochemical evidence of a role for transforming growth factor beta in the pathogenesis of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1209–1214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Muramoto L., Said J. Expression of T-cell antigens on Reed-Sternberg cells in a subset of patients with nodular sclerosing and mixed cellularity Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):345–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Comans-Bitter W. M., Cordell J. L., Verhoeven M. A., van Dongen J. J. Antibody L26 recognizes an intracellular epitope on the B-cell-associated CD20 antigen. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1215–1222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros L. J., Weiss L. M., Warnke R. A., Dorfman R. F. Utility of combining antigranulocyte with antileukocyte antibodies in differentiating Hodgkin's disease from non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer. 1988 Dec 15;62(12):2475–2481. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19881215)62:12<2475::aid-cncr2820621204>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Said J. W. Hodgkin's disease, lymphocyte predominance type, nodular--further evidence for a B cell derivation. L & H variants of Reed-Sternberg cells express L26, a pan B cell marker. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):211–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushin J. M., Riordan G. P., Heaton R. B., Sharpe R. W., Cotelingam J. D., Jaffe E. S. Cytomegalovirus-infected cells express Leu-M1 antigen. A potential source of diagnostic error. Am J Pathol. 1990 May;136(5):989–995. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M., Nansen L. Detection of interleukin-5 messenger RNA in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease with eosinophilia. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson M., Crush-Stanton S., Cossman J. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in Hodgkin's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 16;82(10):855–858. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.10.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundeen J. T., Cossman J., Jaffe E. S. Lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's disease nodular subtype with coexistent "large cell lymphoma". Histological progression or composite malignancy? Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Aug;12(8):599–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundeen J., Lipford E., Uppenkamp M., Sussman E., Wahl L., Raffeld M., Cossman J. Rearranged antigen receptor genes in Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):96–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Strickler J. G., Hu E., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in Hodgkin's disease. Hum Pathol. 1986 Oct;17(10):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek R., Burke J. S., Knowles D. M., 2nd Leu-M1 antigen expression in T-cell neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1985 Dec;121(3):374–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Schned A., Cotelingam J. D., Jaffe E. S. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia with coexistent Hodgkin's disease. Implications for the origin of the Reed-Sternberg cell. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Jan;15(1):33–42. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199101000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]