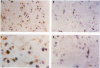
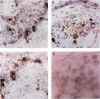
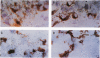
Abstract
A common feature of human melanoma is infiltration by monocytes at early stages of tumorigenesis. This infiltration may be highly significant since macrophages have the capacity to alter the behavior of tumor cells. The authors previously demonstrated that the predominant monocyte chemoattractant produced by tumor cells in vitro was monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1). The authors identify the expression of MCP-1 in pathologic specimens of both primary and metastatic human melanoma but not in normal skin. The finding that MCP-1 is produced by malignant melanoma suggests that specific genes are expressed in tumor cells that can induce the recruitment of monocytes in vivo.
Full text
PDF
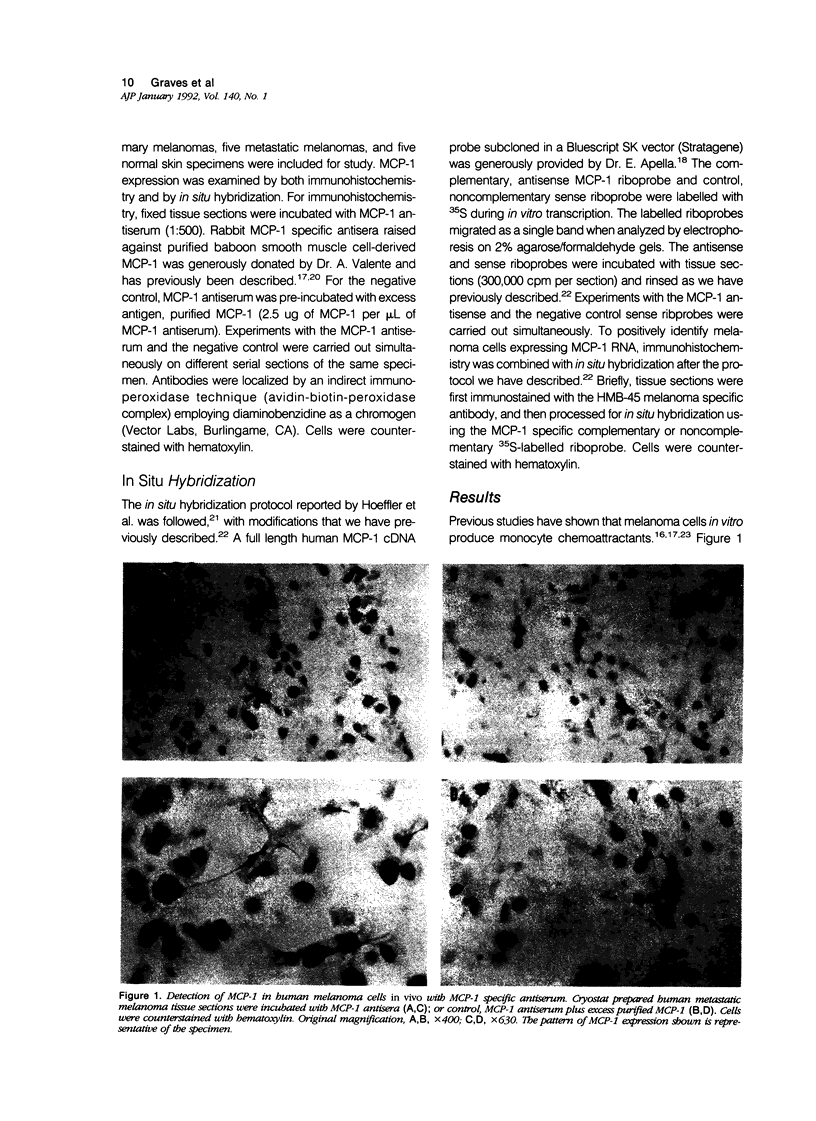
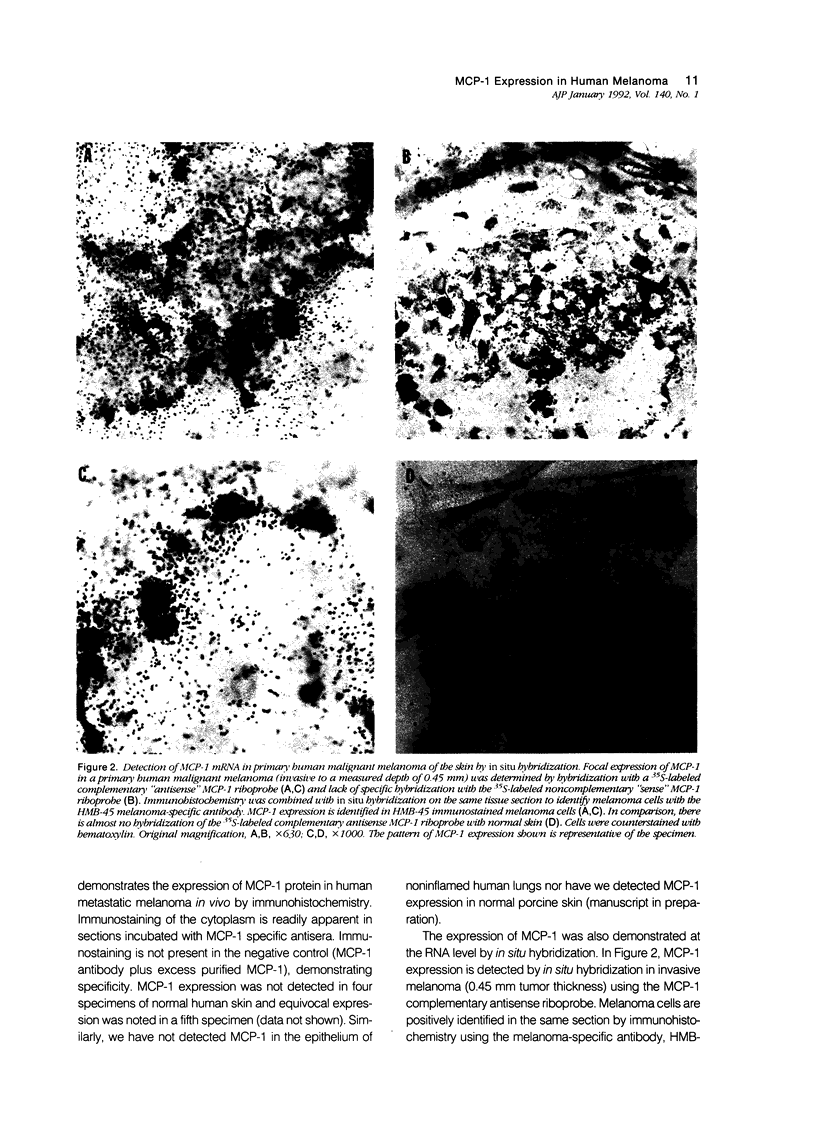
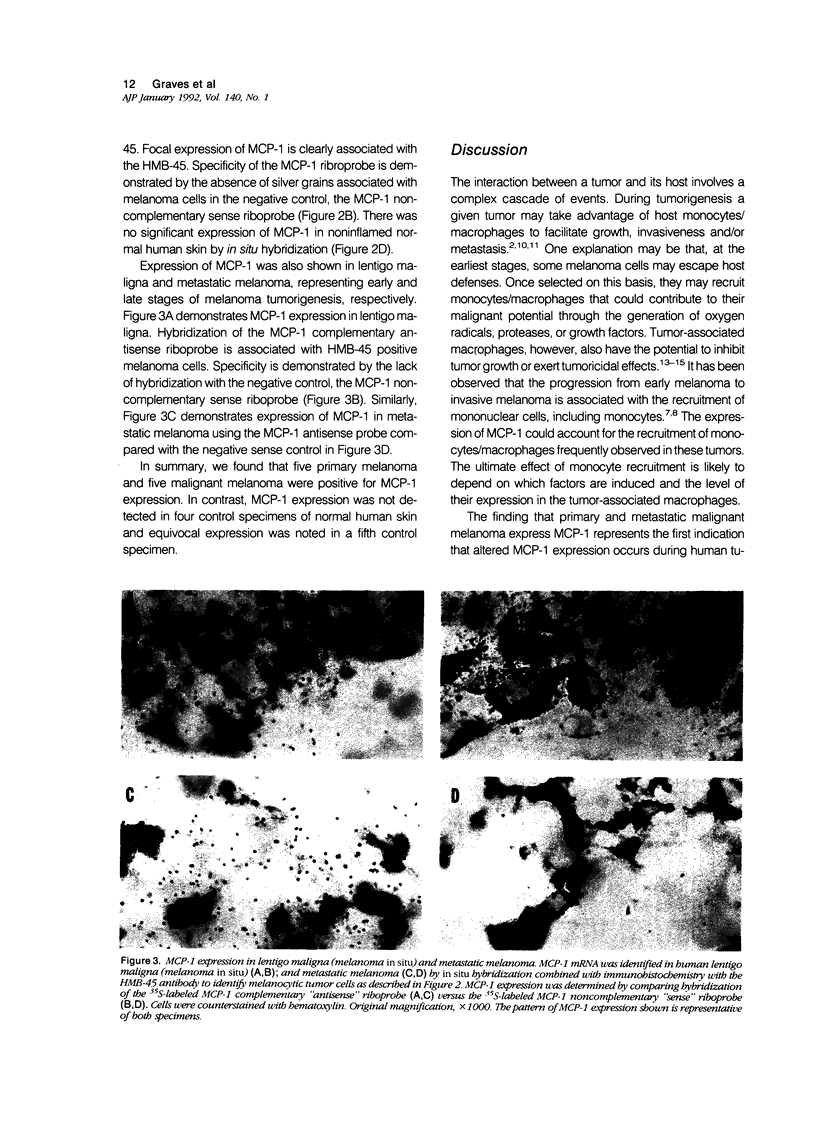


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Kiritsy C. P., Lynch S. E. Injury induces in vivo expression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor mRNAs in skin epithelial cells and PDGF mRNA in connective tissue fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benomar A., Ming W. J., Taraboletti G., Ghezzi P., Balotta C., Cianciolo G. J., Snyderman R., Doré J. F., Mantovani A. Chemotactic factor and P15E-related chemotaxis inhibitor in human melanoma cell lines with different macrophage content and tumorigenicity in nude mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2372–2379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzi B., Polentarutti N., Acero R., Balsari A., Boraschi D., Ghezzi P., Salmona M., Mantovani A. Regulation of the macrophage content of neoplasms by chemoattractants. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):210–212. doi: 10.1126/science.6828888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröcker E. B., Zwadlo G., Holzmann B., Macher E., Sorg C. Inflammatory cell infiltrates in human melanoma at different stages of tumor progression. Int J Cancer. 1988 Apr 15;41(4):562–567. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröcker E. B., Zwadlo G., Suter L., Brune M., Sorg C. Infiltration of primary and metastatic melanomas with macrophages of the 25F9-positive phenotype. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1987;25(2):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00199945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. H., Jr, Elder D. E., Guerry D., 4th, Epstein M. N., Greene M. H., Van Horn M. A study of tumor progression: the precursor lesions of superficial spreading and nodular melanoma. Hum Pathol. 1984 Dec;15(12):1147–1165. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing S. D., Berliner J. A., Valente A. J., Territo M. C., Navab M., Parhami F., Gerrity R., Schwartz C. J., Fogelman A. M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein induces monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5134–5138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit V. M., Green S., Sarma V., Holzman L. B., Wolf F. W., O'Rourke K., Ward P. A., Prochownik E. V., Marks R. M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induction of novel gene products in human endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale B. E., Zacharchuk C. M., Shin H. S. Mechanism of macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity: production of a soluble cytotoxic factor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2362–2367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Anti-angiogenesis: new concept for therapy of solid tumors. Ann Surg. 1972 Mar;175(3):409–416. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197203000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauci C. L., Alexander P. The macrophage content of some human tumours. Cancer Lett. 1975 Sep;1(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(75)94826-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. T., Jiang Y. L., Williamson M. J., Valente A. J. Identification of monocyte chemotactic activity produced by malignant cells. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2781291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler H., Childers H., Montminy M. R., Lechan R. M., Goodman R. H., Wolfe H. J. In situ hybridization methods for the detection of somatostatin mRNA in tissue sections using antisense RNA probes. Histochem J. 1986 Nov-Dec;18(11-12):597–604. doi: 10.1007/BF01675295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaizer L., Lala P. K. Post-mitotic age of monocuclear cells migrating into TA-3(St) solid tumors. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1977 May;10(3):279–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1977.tb00296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N. Production of an anti-tumour cytotoxin by human monocytes. Immunology. 1981 Sep;44(1):135–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride W. H. Phenotype and functions of intratumoral macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 5;865(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestor M. S., Cochran A. J. Identification and quantification of subsets of mononuclear inflammatory cells in melanocytic and other human tumors. Pigment Cell Res. 1987;1(1):22–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1987.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran P. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Unanue E. R. Activated macrophages induce vascular proliferation. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):804–806. doi: 10.1038/269804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Pober J. S. Interleukin-4 induces the synthesis and secretion of MCP-1/JE by human endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1315–1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., Gillespie G. Y., Pace J. L. Evidence for mononuclear phagocytes in solid neoplasms and appraisal of their nonspecific cytotoxic capabilities. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1980;10:143–166. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3677-8_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Decock B., Lenaerts J. P., Conings R., Bertini R., Mantovani A., Billiau A. Identification by sequence analysis of chemotactic factors for monocytes produced by normal and transformed cells stimulated with virus, double-stranded RNA or cytokine. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2367–2373. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. W., Gollahon K. A. Detection and quantitation of macrophage infiltration into primary human tumors with the use of cell-surface markers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Oct;59(4):1081–1087. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Lipton B. A., Rosenfeld M. E., Särkioja T., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in macrophage-rich areas of human and rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Yuhki N., Moore S. K., Appella E., Lerman M. I., Leonard E. J. Human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). Full-length cDNA cloning, expression in mitogen-stimulated blood mononuclear leukocytes, and sequence similarity to mouse competence gene JE. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]