Abstract
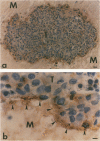
Using an antibody probe specific for the class of fibronectins that contain the oncofetal domain, it was shown that oncofetal fibronectin (onfFN) is present wherever trophoblasts make contact with extraplacental extracellular matrix (ECM). In normal human implantation sites, onfFN was localized to a highly specific region-the ECM connecting extravilous trophoblasts and trophoblastic cell columns to the uterine decidua. This same zone of onfFN was present in an analogous location in extrauterine gestations. Like these in vivo extravillous trophoblasts, isolated cytotrophoblasts in primary culture synthesized and secreted onfFN as they underwent differentiation. Furthermore, when cocultured with an ECM gel, cytotrophoblast aggregates deposited onfFN at cell-ECM contact sites, resembling early implanting trophoblasts in vivo. In the presence of cyclic AMP agonists, onfFN synthesis was inhibited markedly. It is concluded from these results that onfFN is a trophoblast protein that, under cAMP regulation, could mediate implantation and placental-uterine attachment throughout gestation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Earl U., Estlin C., Bulmer J. N. Fibronectin and laminin in the early human placenta. Placenta. 1990 May-Jun;11(3):223–231. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80268-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman M. A., Kliman H. J., Caltabiano S., Strauss J. F., 3rd 8-Bromo-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate stimulates the endocrine activity of human cytotrophoblasts in culture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Nov;63(5):1211–1217. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-5-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTIG A. T., ROCK J., ADAMS E. C. A description of 34 human ova within the first 17 days of development. Am J Anat. 1956 May;98(3):435–493. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000980306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Akiyama S. K., Komoriya A., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of an alternatively spliced site in human plasma fibronectin that mediates cell type-specific adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2637–2647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Komoriya A., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of two distinct regions of the type III connecting segment of human plasma fibronectin that promote cell type-specific adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6886–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao L. C., Caltabiano S., Wu S., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Kliman H. J. The human villous cytotrophoblast: interactions with extracellular matrix proteins, endocrine function, and cytoplasmic differentiation in the absence of syncytium formation. Dev Biol. 1988 Dec;130(2):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Feinberg R. F., Haimowitz J. E. Human trophoblast-endometrial interactions in an in vitro suspension culture system. Placenta. 1990 Jul-Aug;11(4):349–367. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Feinberg R. F. Human trophoblast-extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions in vitro: ECM thickness modulates morphology and proteolytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3057–3061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Nestler J. E., Sermasi E., Sanger J. M., Strauss J. F., 3rd Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placentae. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1567–1582. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Kennedy S. P., Madri J. A. Alternative splicing of endothelial cell fibronectin mRNA in the IIICS region. Functional significance. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1509–1524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loridon-Rosa B., Vielh P., Matsuura H., Clausen H., Cuadrado C., Burtin P. Distribution of oncofetal fibronectin in human mammary tumors: immunofluorescence study on histological sections. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1608–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura H., Greene T., Hakomori S. An alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminylation at the threonine residue of a defined peptide sequence creates the oncofetal peptide epitope in human fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10472–10476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura H., Takio K., Titani K., Greene T., Levery S. B., Salyan M. E., Hakomori S. The oncofetal structure of human fibronectin defined by monoclonal antibody FDC-6. Unique structural requirement for the antigenic specificity provided by a glycosylhexapeptide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3314–3322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulloa-Aguirre A., August A. M., Golos T. G., Kao L. C., Sakuragi N., Kliman H. J., Strauss J. F., 3rd 8-Bromo-adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate regulates expression of chorionic gonadotropin and fibronectin in human cytotrophoblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 May;64(5):1002–1009. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-5-1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartio T., Laitinen L., Närvänen O., Cutolo M., Thornell L. E., Zardi L., Virtanen I. Differential expression of the ED sequence-containing form of cellular fibronectin in embryonic and adult human tissues. J Cell Sci. 1987 Nov;88(Pt 4):419–430. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Isemura M., Yamaguchi Y., Munakata H., Hayashi N., Kyogoku M. Immunohistochemical localization of fibronectin in the human placentas at their different stages of maturation. Histochemistry. 1987;86(6):579–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00489550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]