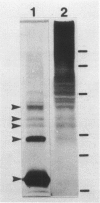
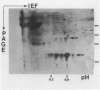
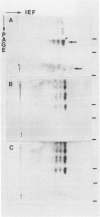
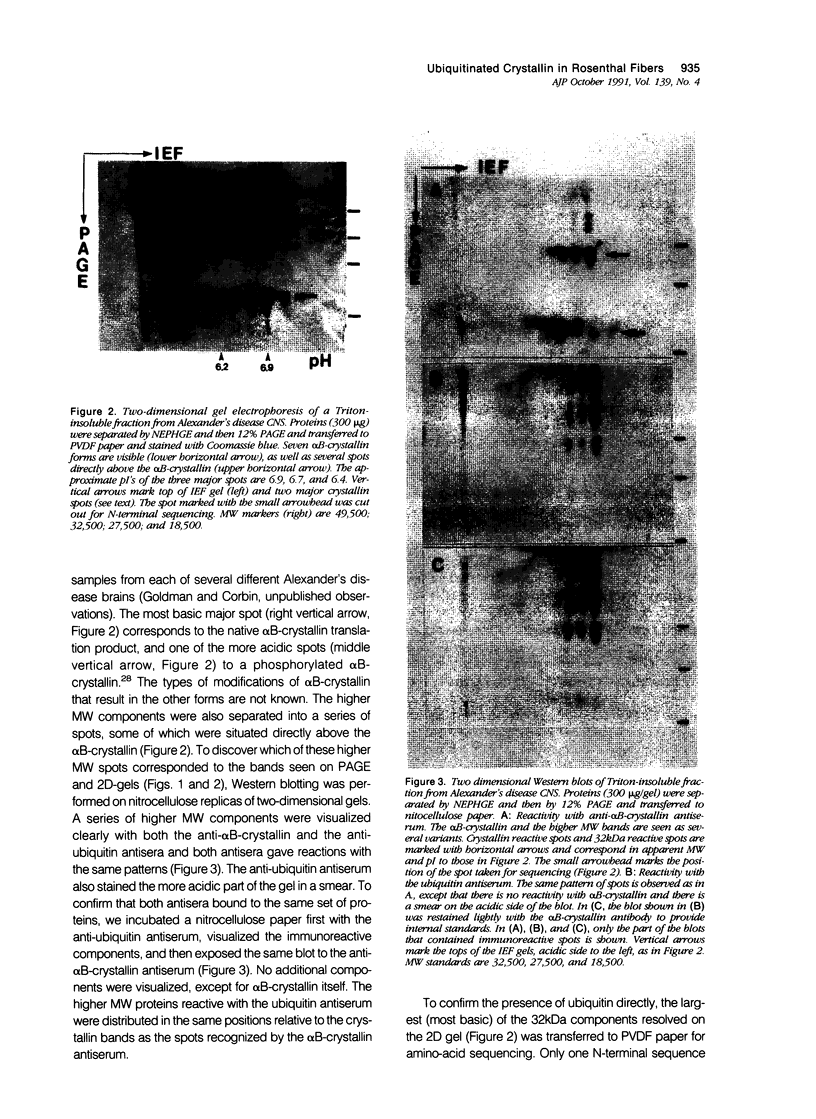
Abstract
The vertebrate lens protein, alpha B-crystallin, is a major component of Rosenthal fibers (RFs) inclusion in astrocytes in Alexander's disease. Antibodies to ubiquitin bind to RFs, but it is not known whether the ubiquitin associated with RFs is bound to a specific protein or proteins, and if so, what the identity of the conjugates is. The authors have analyzed the proteins of RFs from Alexander's disease and have found mono- and polyubiquitinated conjugates of alpha B-crystallin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball E., Karlik C. C., Beall C. J., Saville D. L., Sparrow J. C., Bullard B., Fyrberg E. A. Arthrin, a myofibrillar protein of insect flight muscle, is an actin-ubiquitin conjugate. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H. Lens proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;12(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238209105849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrett D., Becker L. E. Alexander's disease. A disease of astrocytes. Brain. 1985 Jun;108(Pt 2):367–385. doi: 10.1093/brain/108.2.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Norton W. T. Bulk preparation of CNS cytoskeleton and the separation of individual neurofilament proteins by gel filtration: dye-binding characteristics and amino acid compositions. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1252–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinda A. K., Sarkar C., Roy S. Rosenthal fibres: an immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and immunoelectron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;79(4):456–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00308723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Corbin E. Isolation of a major protein component of Rosenthal fibers. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):569–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon R. M., Rubinstein L. J., Freeman J. M., Mathieson G. Light and electron microscopic observations on Rosenthal fibers in Alexander's disease and in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Oct;29(4):524–551. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197010000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoenders H. J., Bloemendal H. The N-terminus of the lens protein alpha-crystallin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 19;147(1):183–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki T., Kume-Iwaki A., Goldman J. E. Cellular distribution of alpha B-crystallin in non-lenticular tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Jan;38(1):31–39. doi: 10.1177/38.1.2294148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki T., Kume-Iwaki A., Liem R. K., Goldman J. E. Alpha B-crystallin is expressed in non-lenticular tissues and accumulates in Alexander's disease brain. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahngen J. H., Haas A. L., Ciechanover A., Blondin J., Eisenhauer D., Taylor A. The eye lens has an active ubiquitin-protein conjugation system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13760–13767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. B., Bettica A. On-grid immunogold labeling of glial intermediate filaments in epoxy-embedded tissue. Am J Anat. 1989 Jun-Jul;185(2-3):335–341. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001850228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T. E., Gawinowicz M. A., Barzilai A., Kandel E. R., Sweatt J. D. Sequencing of proteins from two-dimensional gels by using in situ digestion and transfer of peptides to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes: application to proteins associated with sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7008–7012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Park Y. D., Yen S. H., Ksiezak-Reding H., Goldman J. E., Dickson D. W. A study of infantile motor neuron disease with neurofilament and ubiquitin immunocytochemistry. Neuropediatrics. 1989 May;20(2):107–111. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Blanchard A., Morrell K., Lennox G., Reynolds L., Billett M., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament inclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as Rosenthal fibres in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol. 1988 May;155(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., McDermott H., Landon M., Mayer R. J., Wilkinson K. D. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase (PGP 9.5) is selectively present in ubiquitinated inclusion bodies characteristic of human neurodegenerative diseases. J Pathol. 1990 Jun;161(2):153–160. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Morrell K., Lennox G., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Rosenthal fibres are based on the ubiquitination of glial filaments. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Jan-Feb;15(1):45–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetto V., Abdul-Karim F. W., Perry G., Tabaton M., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Selective presence of ubiquitin in intracellular inclusions. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):505–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetto V., Perry G., Tabaton M., Mulvihill P., Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L. Ubiquitin is associated with abnormal cytoplasmic filaments characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4501–4505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A., Siegel N. R., Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A. Degradation of proteins with acetylated amino termini by the ubiquitin system. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1480–1483. doi: 10.1126/science.2544030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo J., Ihara Y. Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1641–1644. doi: 10.1126/science.3029875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B. E., Davie J. R. Structure of polyubiquitinated histone H2A. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):964–968. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N. Multiple Sklerose mit Rosenthalschen Fasern. Acta Neuropathol. 1965 Oct 4;5(1):61–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00689163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Ubiquitin-mediated pathways for intracellular proteolysis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M., Bond M. W., Gallatin W. M., St John T., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Cell surface molecule associated with lymphocyte homing is a ubiquitinated branched-chain glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):823–829. doi: 10.1126/science.3003913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomokane N., Iwaki T., Tateishi J., Iwaki A., Goldman J. E. Rosenthal fibers share epitopes with alpha B-crystallin, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and ubiquitin, but not with vimentin. Immunoelectron microscopy with colloidal gold. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):875–885. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]