Abstract
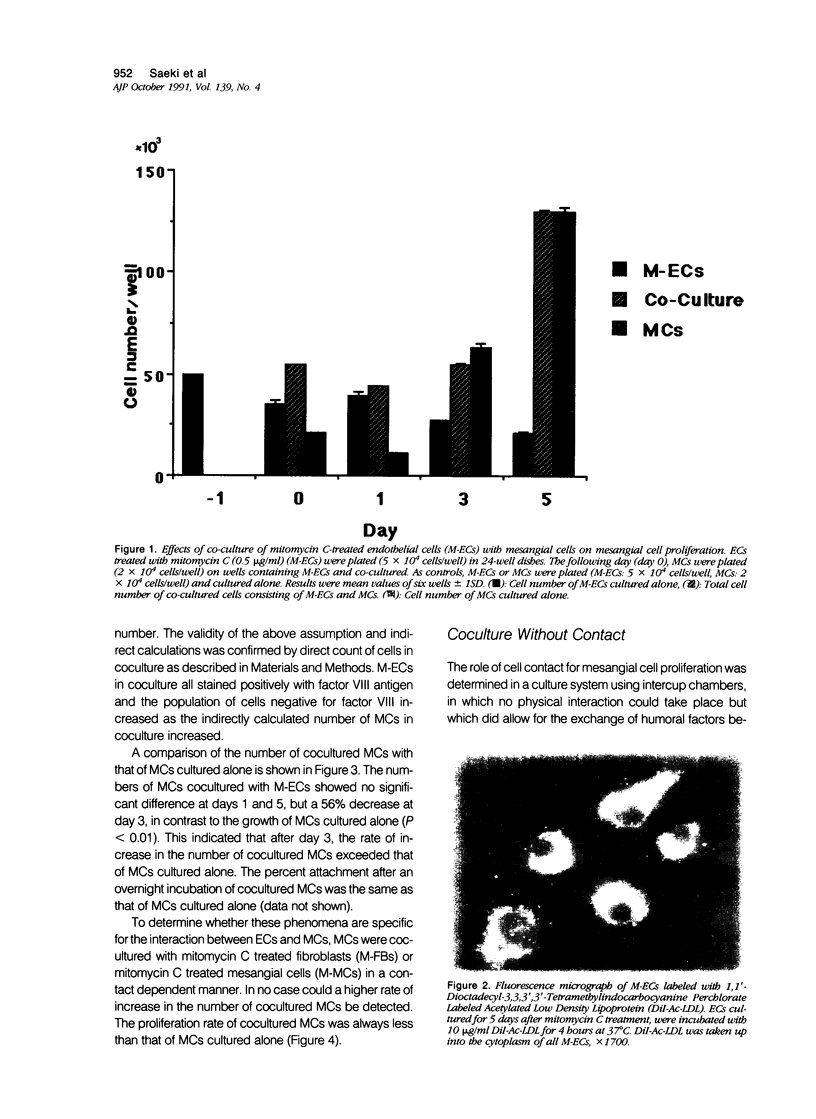
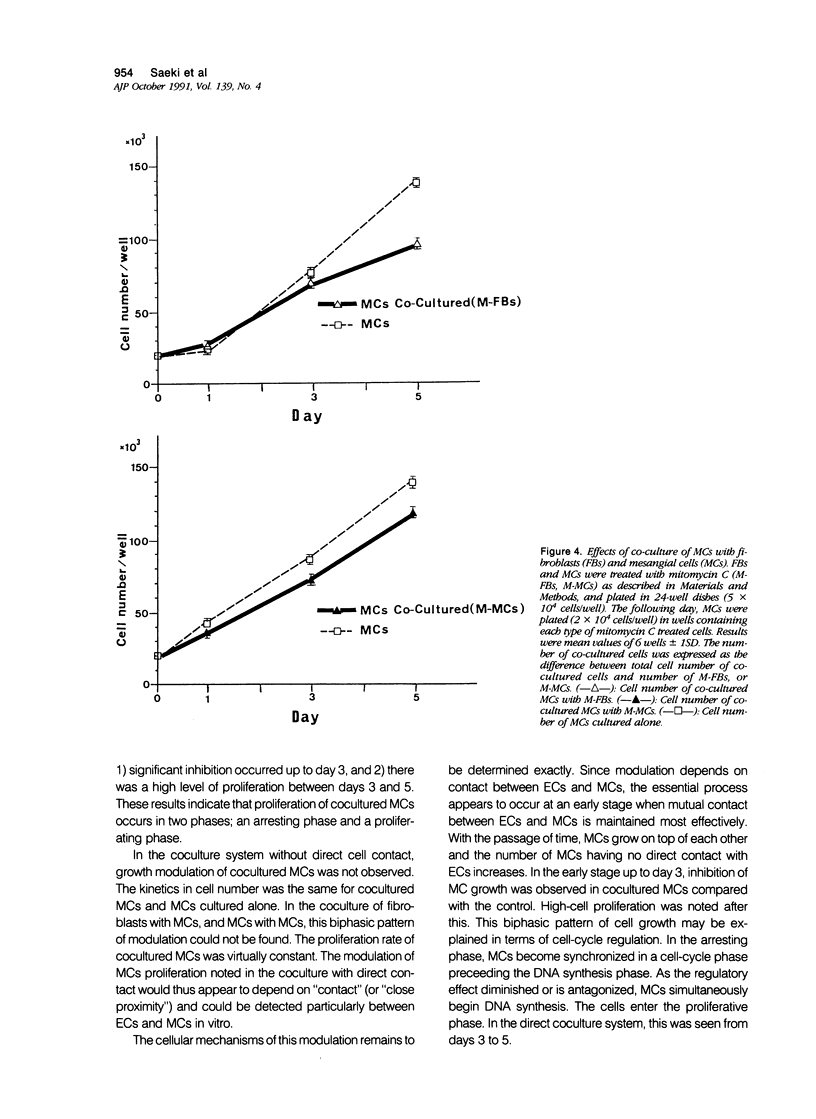
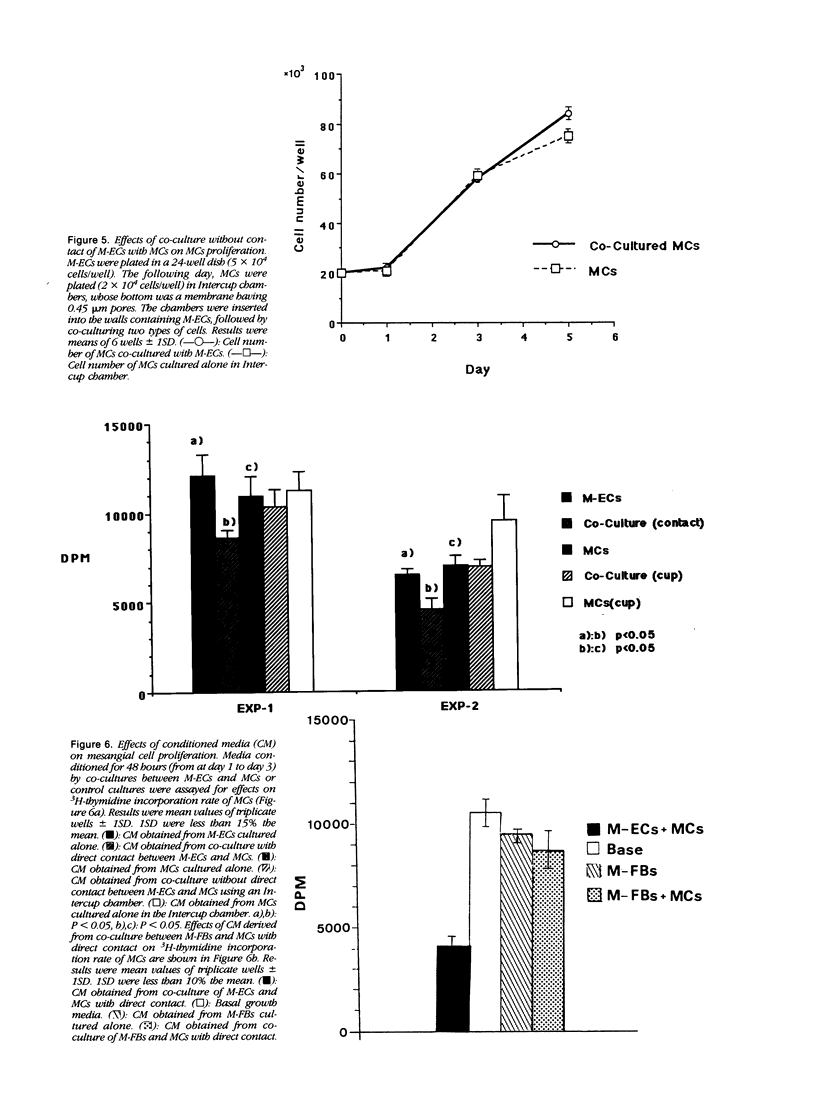
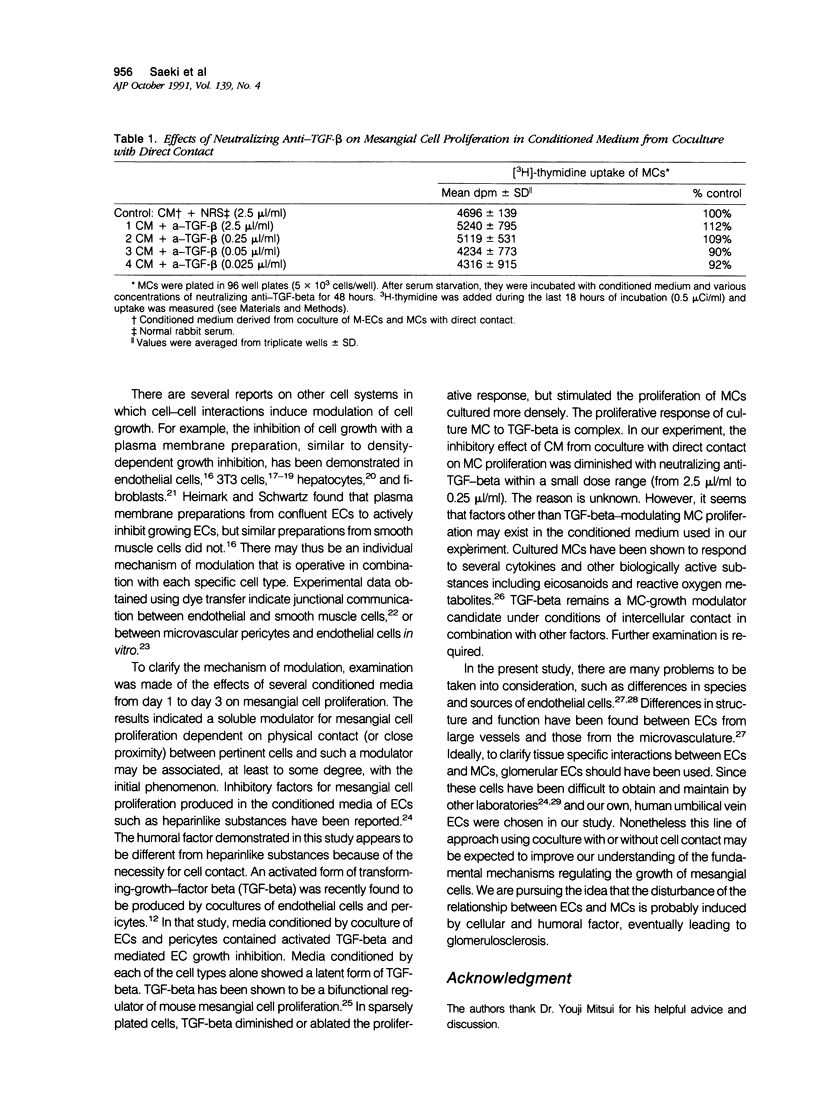
The effects of direct cell contact between endothelial (ECs) and mesangial cells (MCs) on MCs proliferation were examined in a coculture system in vitro. Mitomycin C treated ECs (M-ECs) were plated on culture dishes and MCs were cocultured with these M-ECs. Cell number was measured at the end of days 1, 3, and 5. In the coculture system with direct contact, the growth of cocultured MCs was modulated as follows: 1) the growth of MCs was inhibited up to day 3, and 2) a high level of proliferation was observed between days 3 and 5. This biphasic pattern of growth could not be detected in coculture of fibroblasts with MCs. In coculture without direct contact, using intercup chambers, the kinetics in cell proliferation between cocultured MCs and MCs alone were essentially the same. Conditioned media derived from cocultures up to day 3 in a contact-dependent manner inhibited the 3H-thymidine uptake of MCs. From these results, it would thus appear that MCs proliferation is regulated by intercellular contact with ECs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonelli-Orlidge A., Saunders K. B., Smith S. R., D'Amore P. A. An activated form of transforming growth factor beta is produced by cocultures of endothelial cells and pericytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular endothelial cells secrete a heparinlike inhibitor and a peptide stimulator of mesangial cell proliferation. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):493–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Ganz P., Diehl P. S. Reversible microcarrier-mediated junctional communication between endothelial and smooth muscle cell monolayers: an in vitro model of vascular cell interactions. Lab Invest. 1985 Dec;53(6):710–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Schwartz S. M. The role of membrane-membrane interactions in the regulation of endothelial cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1934–1940. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jozaki K., Marucha P. T., Despins A. W., Kreutzer D. L. An in vitro model of cell migration: evaluation of vascular endothelial cell migration. Anal Biochem. 1990 Oct;190(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara Y., Ashihara Y. Colorimetry of angiotensin-I converting enzyme activity in serum. Clin Chem. 1981 Nov;27(11):1922–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo E. W., Gotlieb A. I. Endothelial stimulation of intimal cell proliferation in a porcine aortic organ culture. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):497–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. M., Carson M. P., Haudenschild C. C. Junctional transfer of small molecules in cultured bovine brain microvascular endothelial cells and pericytes. Microvasc Res. 1987 Sep;34(2):184–199. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(87)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau D. C., Wong K. L., Tough S. C. Regional differences in the replication rate of cultured rat microvascular endothelium from retroperitoneal and epididymal fat pads. Metabolism. 1987 Jul;36(7):631–636. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Sterzel R. B. Stimulation of rat mesangial cell proliferation by macrophage interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2830–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Sterzel R. B. Cell culture approaches to the analysis of glomerular inflammation. Kidney Int. 1986 Aug;30(2):246–254. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Striker L. J., Elliot S., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L., Striker G. E. Glomerular epithelial, mesangial, and endothelial cell lines from transgenic mice. Kidney Int. 1988 Mar;33(3):677–684. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Striker L. J., Stauffer J. W., Doi T., Agodoa L. Y., Striker G. E. Transforming growth factor-beta. Murine glomerular receptors and responses of isolated glomerular cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1160–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI113996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka T., Narita I., Shimizu F., Oite T. Production by cultured human monocytes of mesangial cell proliferation factor(s) differing from interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):182–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Oite T., Kihara I., Yamamoto T., Hara M., Naka A., Ohno S. Culture of isolated glomeruli from normal and nephritic rabbits. I. Characterization of outgrowing cells. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1980 Nov;30(6):917–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1980.tb03280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Yoshimoto K., Nakayama Y., Tomita Y., Ichihara A. Reciprocal modulation of growth and differentiated functions of mature rat hepatocytes in primary culture by cell--cell contact and cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7229–7233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlidge A., D'Amore P. A. Inhibition of capillary endothelial cell growth by pericytes and smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1455–1462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):420–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterzel R. B., Lovett D. H., Foellmer H. G., Perfetto M., Biemesderfer D., Kashgarian M. Mesangial cell hillocks. Nodular foci of exaggerated growth of cells and matrix in prolonged culture. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Glomerular cell culture. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz M., Chowdary D., Lipman R., Shimotakahara S., Veiro D., Walker V., Verdine G. L. Reaction of DNA with chemically or enzymatically activated mitomycin C: isolation and structure of the major covalent adduct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6702–6706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Peterson S. W., Matiuck N. V., Fox C. F. Purified plasma membranes inhibit polypeptide growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in subconfluent 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1129–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittenberger B., Glaser L. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in cultures of 3T3 cells by isolated surface membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2251–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittenberger B., Raben D., Lieberman M. A., Glaser L. Inhibition of growth of 3T3 cells by extract of surface membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5457–5461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieser R. J., Oesch F. Contact inhibition of growth of human diploid fibroblasts by immobilized plasma membrane glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):361–367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]