Abstract
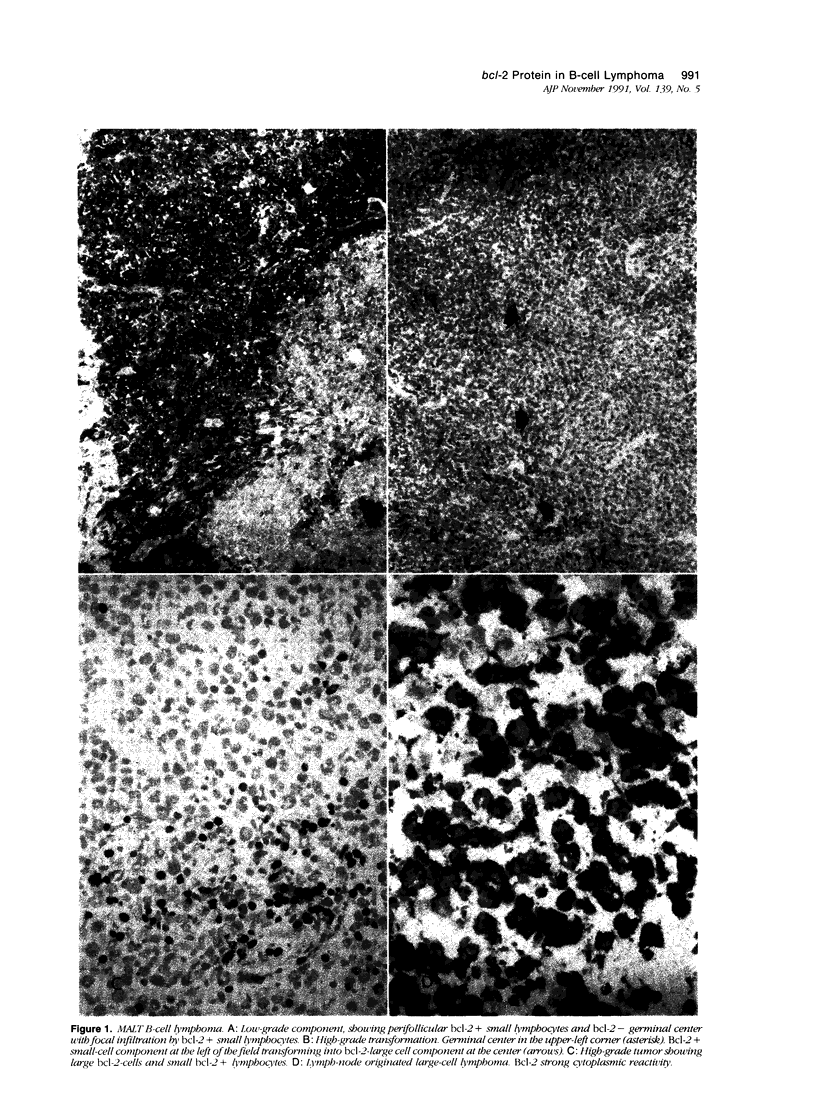
High-grade B-cell lymphomas, whether originated in a lymph node or in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), show similar morphologic traits, a fact that has fueled a long-running controversy about whether they represent different entities. They differ, however, in that some high-grade MALT lymphomas show less aggressive clinical behavior, a focal low-grade component being identified in some of them. In a search for bcl-2 protein expression, we have found a significant difference between nodal (39/48) and MALT high-grade B-cell lymphoma (1/15) (P less than 0.01). Bcl-2 gene product is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein able to give a survival advantage to B-cell lines by blocking programmed cell death. This protein is usually expressed by memory or resting B cells, most activated B cells being bcl-2 negative, except in lymph-node-originated high-grade B-cell lymphomas, which appear to be mainly bcl-2 positive. Presence of bcl-2 protein in nodal large-cell lymphomas seems to be independent of a t(14;18) translocation, only being found in 19 to 28% of these lymphomas, although it constitutes a definite difference between both tumors, suggesting the existence of different molecular genetic characteristics and pathogenesis, and is possibly related to the more aggressive clinical behavior of nodal high-grade tumors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisenberg A. C., Wilkes B. M., Jacobson J. O. The bcl-2 gene is rearranged in many diffuse B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):969–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. J., Enterline H. T. Primary gastric lymphomas. A clinicopathologic study of 58 cases with long-term follow-up and literature review. Cancer. 1983 Feb 15;51(4):701–711. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830215)51:4<701::aid-cncr2820510425>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. K., Ng C. S., Isaacson P. G. Relationship between high-grade lymphoma and low-grade B-cell mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALToma) of the stomach. Am J Pathol. 1990 May;136(5):1153–1164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Levy Z., Nourse J., Cleary M. L. The bcl-2 candidate proto-oncogene product is a 24-kilodalton integral-membrane protein highly expressed in lymphoid cell lines and lymphomas carrying the t(14;18) translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):701–710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey M. M., Feller A. C., Kirchner T., Müller J., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Genomic analysis of T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin antigen receptor genes and breakpoint cluster regions in gastrointestinal lymphomas. Hum Pathol. 1990 Dec;21(12):1283–1287. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(06)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P. G., Spencer J., Finn T. Primary B-cell gastric lymphoma. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jan;17(1):72–82. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P. G., Spencer J., Wright D. H. Classifying primary gut lymphomas. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1148–1149. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90574-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P. G., Wotherspoon A. C., Diss T. C., Pan L. X. Bcl-2 expression in lymphomas. Lancet. 1991 Jan 19;337(8734):175–176. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90838-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., McDonnell T. J., Nunez G., Hockenbery D., Young R. Bcl-2: B cell life, death and neoplasia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;166:203–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75889-8_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Blick M. B., Pathak S., Trujillo J. M., Butler J. J., Katz R. L., McLaughlin P., Hagemeister F. B., Velasquez W. S., Goodacre A. The gene located at chromosome 18 band q21 is rearranged in uncultured diffuse lymphomas as well as follicular lymphomas. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):90–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre M. J., Isaacson P. G. Primary B-cell gastric lymphoma--a reassessment of its histogenesis. J Pathol. 1987 May;152(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit K., Koduru P. R., Hollis R., Filippa D., Jhanwar S. C., Clarkson B. C., Chaganti R. S. 18q21 rearrangement in diffuse large cell lymphoma: incidence and clinical significance. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jun;72(2):178–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan L., Diss T. C., Cunningham D., Isaacson P. G. The bcl-2 gene in primary B cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):7–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y., Bastard C., Duval C., Krajewski A., Turner G. E., Ross F. M., Clark H., Jones D. B. Bcl-2 protein expression in follicular lymphomas in absence of 14;18 translocation. Lancet. 1990 Dec 15;336(8729):1510–1511. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93216-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Gorham J., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. The t(14;18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1390–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.3929382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Warnke R. A., Sklar J., Cleary M. L. Molecular analysis of the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation in malignant lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1987 Nov 5;317(19):1185–1189. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198711053171904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Mayer M. G., Arnesen M. A., Aeppli D. P., Oken M. M., Frizzera G. bcl-2 and other genomic alterations in the prognosis of large-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1047–1054. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong D., Voetdijk B. M., Van Ommen G. J., Kluin-Nelemans J. C., Beverstock G. C., Kluin P. M. Translocation t(14;18) in B cell lymphomas as a cause for defective immunoglobulin production. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):613–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Krieken J. H., Otter R., Hermans J., van Groningen K., Spaander P. J., van de Sandt M. M., Keuning J. F., Kluin P. M. Malignant lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract and mesentery. A clinico-pathologic study of the significance of histologic classification. NHL Study Group of the Comprehensive Cancer Center West. Am J Pathol. 1989 Aug;135(2):281–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Krieken J. H., Raffeld M., Raghoebier S., Jaffe E. S., van Ommen G. J., Kluin P. M. Molecular genetics of gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: unusual prevalence and pattern of c-myc rearrangements in aggressive lymphomas. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):797–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]