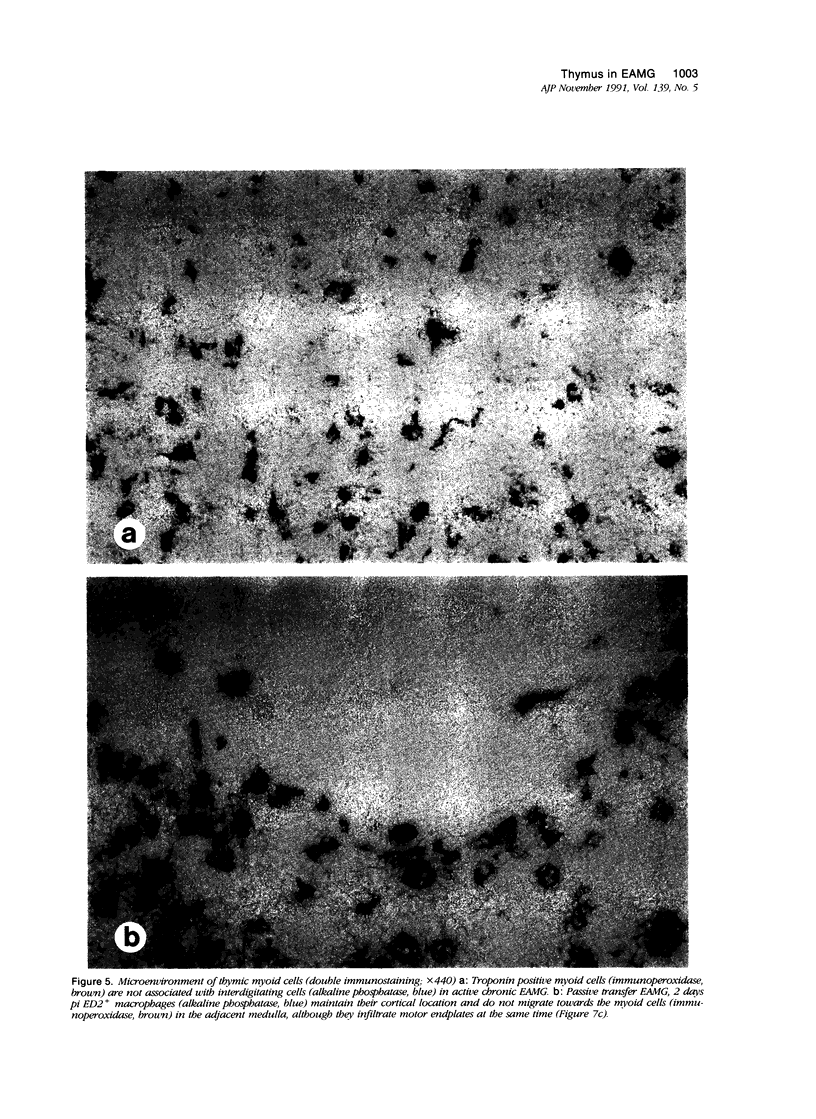
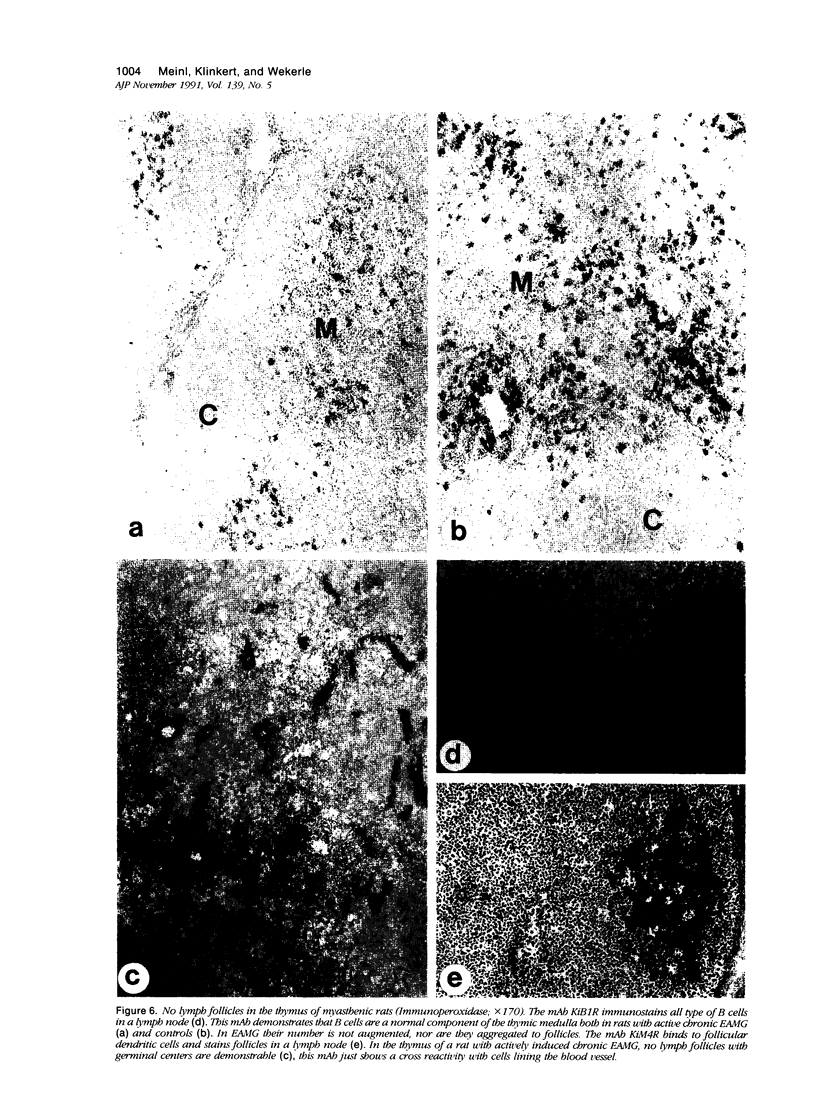
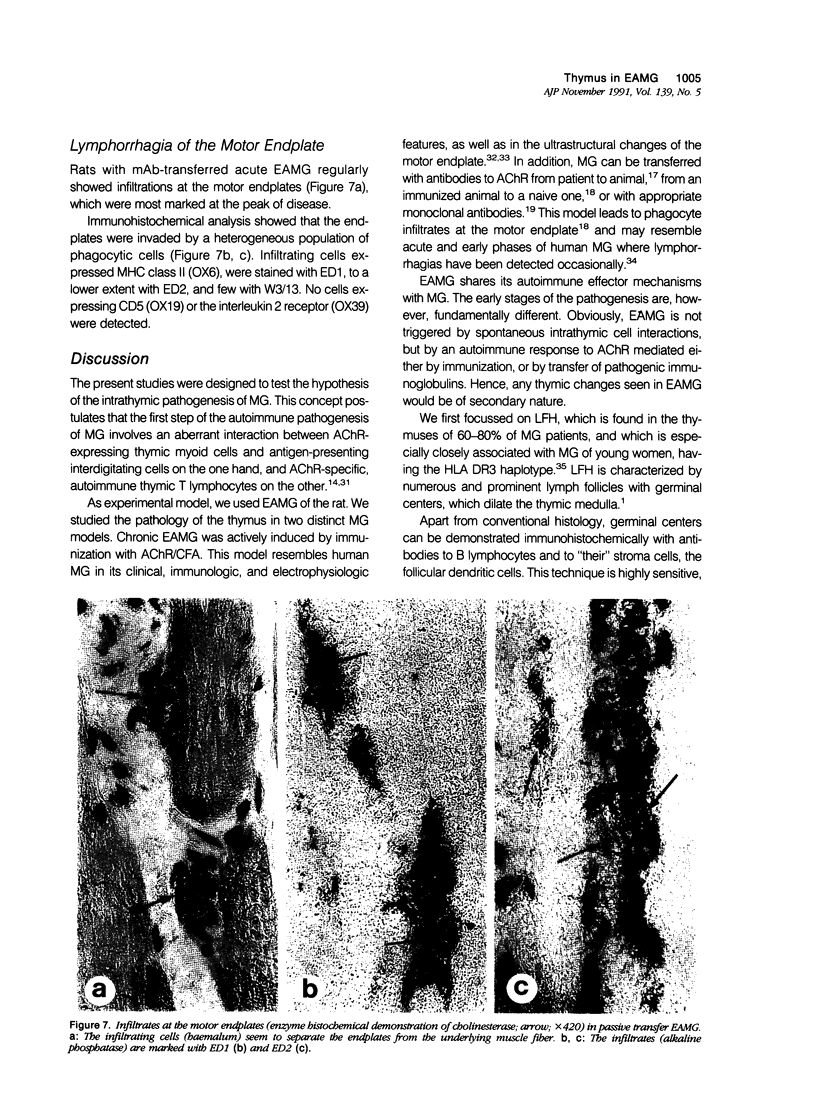
Abstract
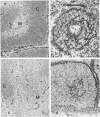
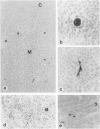
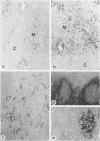
In human myasthenia gravis (MG) formation of autoantibodies against acetylcholine receptor (AChR) is commonly associated with thymic changes termed lymphofollicular hyperplasia (LFH). To learn whether the thymic lesions of human MG are primary changes in the autoimmune pathogenesis, or rather secondary events caused by peripheral autoimmunization, the authors compared the pathologic changes of MG thymuses with the thymuses of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis (EAMG). EAMG was induced either actively by immunization with AChR, or transferred passively with monoclonal antibodies (mAb) binding to AChR. The clinical diagnosis of EAMG was confirmed by electromyography. Germinal centers, which are typical for human MG thymuses, were not detectable in the thymus of EAMG rats. Scattered B cells were seen as normal components of the thymic medulla. In EAMG their number was not augmented, nor were they accumulated focally. The perivascular spaces (PVS) were not distended and the amount of reticulin was not increased. Thymic myoid cells were identified in EAMG as well as in control thymuses; their cellular microenvironment was inconspicuous. Both in normal and in EAMG thymuses, a subpopulation of myoid cells expressed the main immunogenic region of the AChR. Heavily affected rats showed a severe cortical involution, but no specific changes of the medulla. The fact that none of the thymic lesions characteristic for human MG was found in EAMG is compatible with the concept that the thymic changes in MG are primary events in the autoimmune pathogenesis of this disease.
Full text
PDF




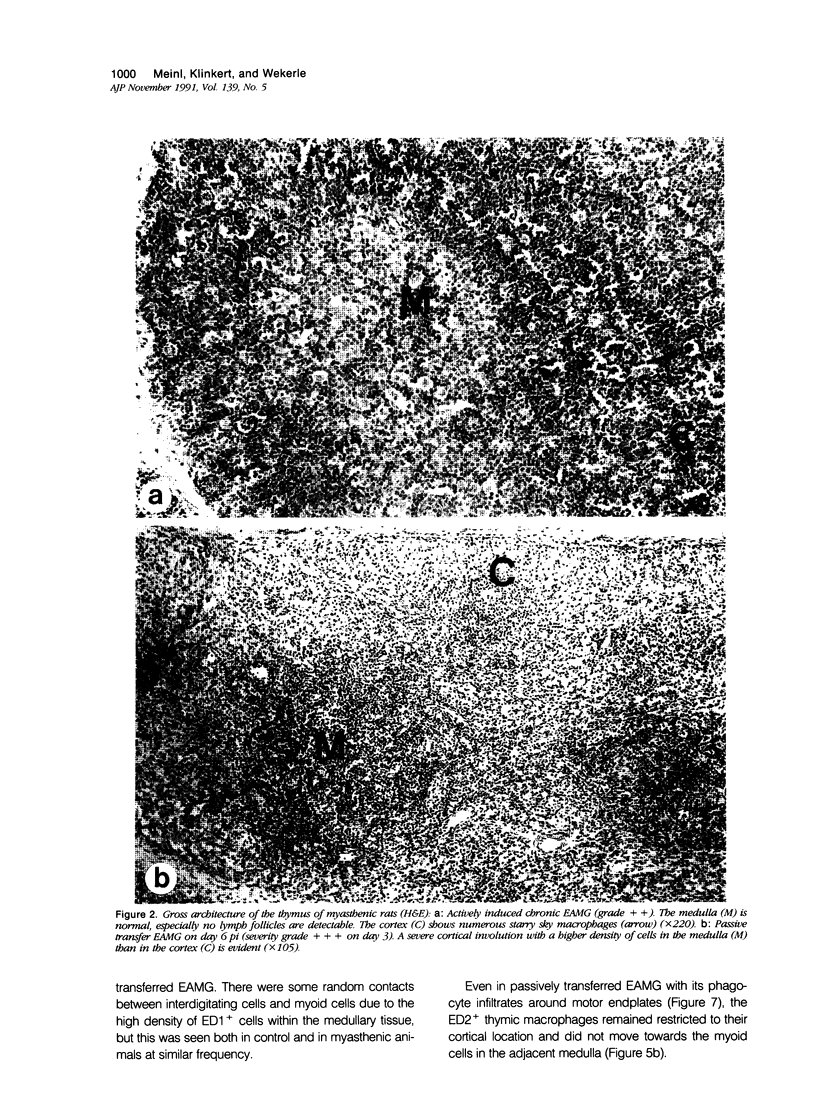
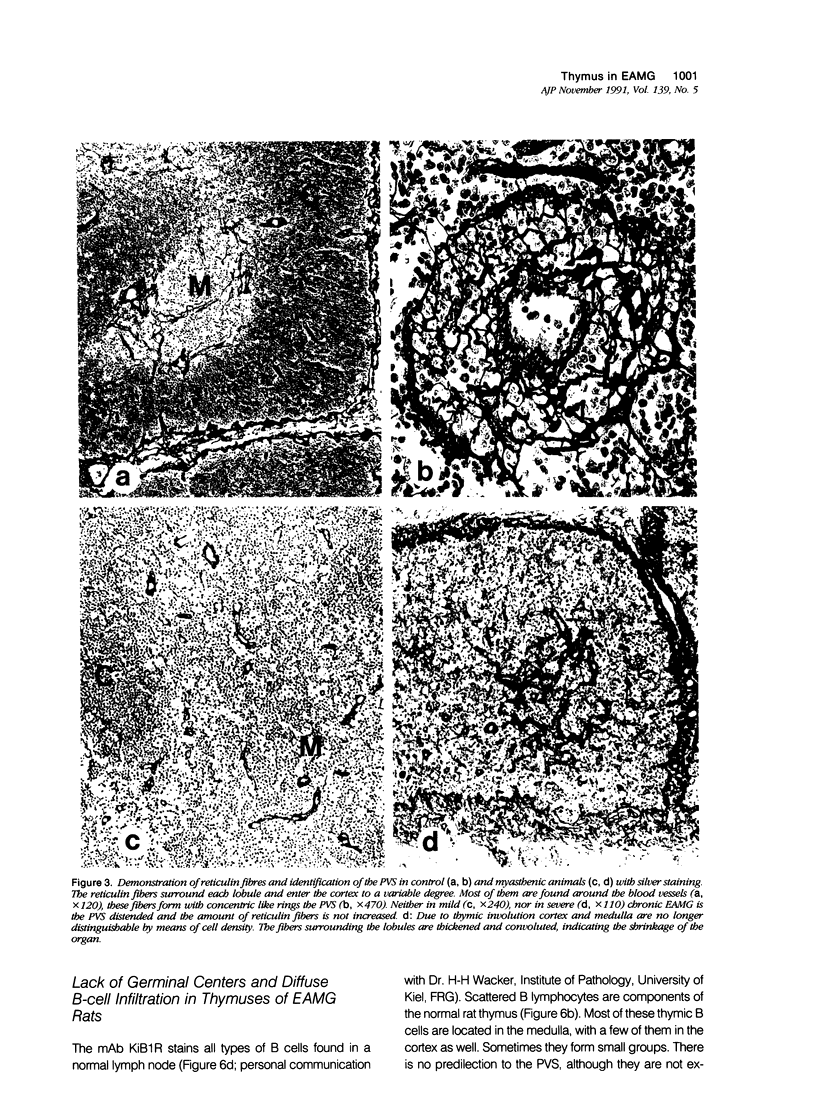
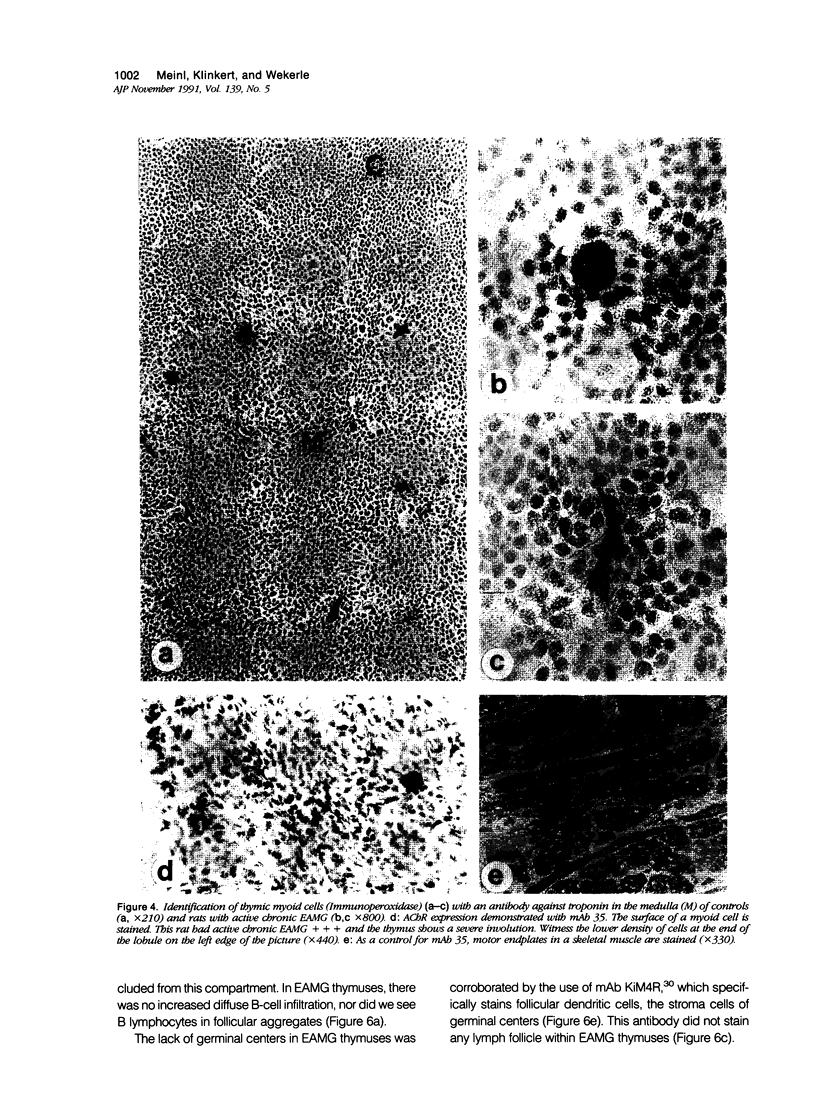



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brüggemann M., Teale C., Clark M., Bindon C., Waldmann H. A matched set of rat/mouse chimeric antibodies. Identification and biological properties of rat H chain constant regions mu, gamma 1, gamma 2a, gamma 2b, gamma 2c, epsilon, and alpha. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3145–3150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castleman B. The pathology of the thymus gland in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jan 26;135(1):496–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb45497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston D. A., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J., Batchelor J. R. Clinical, pathological, HLA antigen and immunological evidence for disease heterogeneity in myasthenia gravis. Brain. 1980 Sep;103(3):579–601. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J., Weissman I. L. Thymic cytotoxic T lymphocytes are primed in vivo to minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):436–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Hashimoto J., Monden Y., Ito T., Nakahara K., Kawashima Y. Specific activation of lymphocytes against acetylcholine receptor in the thymus in myasthenia gravis. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):887–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastkemper N. A., Wubbena A. S., Gimbrère F. J., de Graaff A., Nieuwenhuis P. Germinal centres and the B-cell system. V. Presence of germinal centre-precursor cells among lymphocytes of the thoracic duct in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;219(2):281–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00210148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Whittingham S. Experimental autoimmune thymitis. An animal model of human myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1966 Aug 6;2(7458):315–318. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92599-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner T., Schalke B., Melms A., von Kügelgen T., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Immunohistological patterns of non-neoplastic changes in the thymus in Myasthenia gravis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1986;52(3):237–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02889966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner T., Schalke B., Melms A., von Kügelgen T., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Immunohistological patterns of non-neoplastic changes in the thymus in Myasthenia gravis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1986;52(3):237–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02889966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner T., Tzartos S., Hoppe F., Schalke B., Wekerle H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Acetylcholine receptor-related antigenic determinants in tumor-free thymuses and thymic epithelial tumors. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):268–280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyewski B. A., Fathman C. G., Kaplan H. S. Intrathymic presentation of circulating non-major histocompatibility complex antigens. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):196–199. doi: 10.1038/308196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert E. H., Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A. End-plate potentials in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:300–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Lindstrom J. M., Seybold M. E. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis: cellular and humoral immune responses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:283–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Lindstrom J. M., Seybold M. E. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia: A model of myasthenia gravis in rats and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1365–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. I., Zweiman B., Lisak R. P. Immunopathogenesis and treatment of myasthenia gravis. J Clin Immunol. 1987 May;7(3):187–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00915723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Engel A. G., Seybold M. E., Lennon V. A., Lambert E. H. Pathological mechanisms in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. II. Passive transfer of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in rats with anti-acetylcholine recepotr antibodies. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):739–753. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Tzartos S. Production and assay of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):432–460. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Shelton D., Fujii Y. Myasthenia gravis. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:233–284. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60847-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Holoshitz J., Eisenstein S., Reshef T., Rappaport S., Chemke J., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Effector T lymphocyte line cells migrate to the thymus and persist there. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):262–264. doi: 10.1038/300262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom-Davis J., Willcox N., Schluep M., Harcourt G., Vincent A., Mossman S., Wray D., Burges J. Immunological heterogeneity and cellular mechanisms in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;505:12–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb51279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palestro G., Tridente G., Botto Micca F., Novero D., Valente G., Godio L. Immunohistochemical and enzyme histochemical contributions to the problem concerning the role of the thymus in the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1983;44(2):173–186. doi: 10.1007/BF02890168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Lindstrom J. Autoimmune response to acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviola E., Karnovsky M. J. Evidence for a blood-thymus barrier using electron-opaque tracers. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):466–498. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino W., Berrih S. Thymic extracellular matrix in myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1984 Jul 7;2(8393):45–46. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluep M., Willcox N., Vincent A., Dhoot G. K., Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptors in human thymic myoid cells in situ: an immunohistological study. Ann Neurol. 1987 Aug;22(2):212–222. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seybold M. E., Lambert E. H., Lennon V. A., Lindstrom J. M. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia: clinical, neurophysiologic, and pharmacologic aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyka K. V., Brachman D. B., Pestronk A., Kao I. Myasthenia gravis: passive transfer from man to mouse. Science. 1975 Oct 24;190(4212):397–399. doi: 10.1126/science.1179220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Hochschwender S., Vasquez P., Lindstrom J. Passive transfer of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by monoclonal antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the acetylcholine receptor. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Jun;15(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Swanson L. W., Lindstrom J. Characteristics of monoclonal antibodies to denatured Torpedo and to native calf acetylcholine receptors: species, subunit and region specificity. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Jan;10(3):235–253. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J., Newton P., Beck N. Acetylcholine receptor antibody and clinical response to thymectomy in myasthenia gravis. Neurology. 1983 Oct;33(10):1276–1282. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.10.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker H. H., Radzun H. J., Mielke V., Parwaresch M. R. Selective recognition of rat follicular dendritic cells (dendritic reticulum cells) by a new monoclonal antibody Ki-M4R in vitro and in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Jan;41(1):70–77. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Hohlfeld R., Ketelsen U. P., Kalden J. R., Kalies I. Thymic myogenesis, T-lymphocytes and the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;377:455–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb33753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Ketelsen U. P. Intrathymic pathogenesis and dual genetic control of myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):678–680. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Ketelsen U. P., Zurn A. D., Fulpius B. W. Intrathymic pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis: transient expression of acetylcholine receptors on thymus-derived myogenic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):579–582. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. The thymus in myasthenia gravis. Curr Top Pathol. 1986;75:179–206. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-82480-7_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle T. H., paterson B., Ketelsen U., Feldman M. Striated muscle fibres differentiate in monolayer cultures of adult thymus reticulum. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):493–494. doi: 10.1038/256493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geld H. W., Strauss A. J. Myasthenia gravis. Immunological relationship between striated muscle and thymus. Lancet. 1966 Jan 8;1(7428):57–60. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]