Abstract
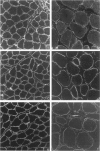
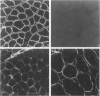
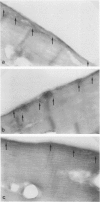
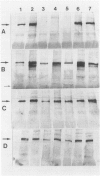
A protein of Mr 400 K and slightly lower Mr than Xp21 dystrophin was detected in skeletal muscle from patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy by three antibodies raised against the midrod and C-terminal portions of chicken dystrophin, and by antibodies to dystrophin-related protein. Immunocytochemistry showed continuous sarcolemmal staining of Duchenne muscle with these antibodies. Subcellular localization to the inner face of the plasma membrane of Duchenne muscle was demonstrated by immunoelectron microscopy using the model of a Duchenne patient deleted for most of the dystrophin gene. Other antibodies were specific for Xp21 dystrophin. In conclusion, a dystrophin homologue that may be identical to the previously described dystrophin-related protein (DRP)1 is expressed in Duchenne muscle with intracellular distribution similar to Xp21 dystrophin in normal muscle.
Full text
PDF


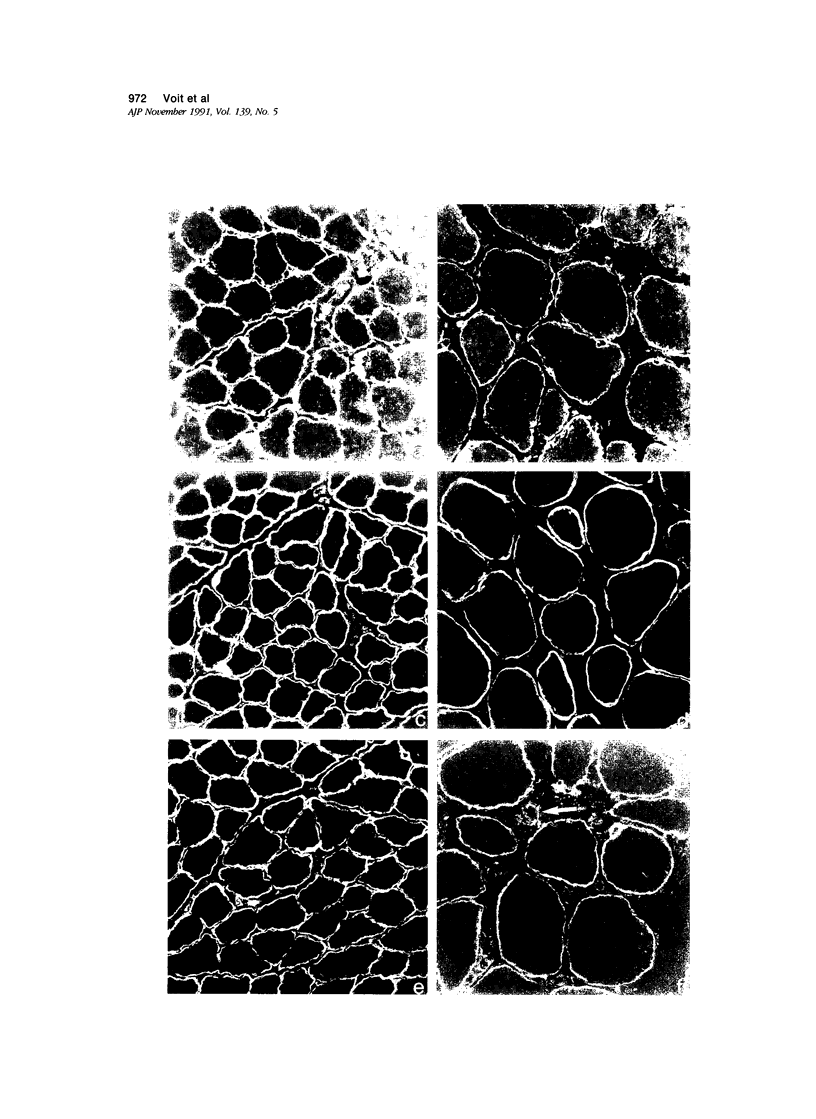
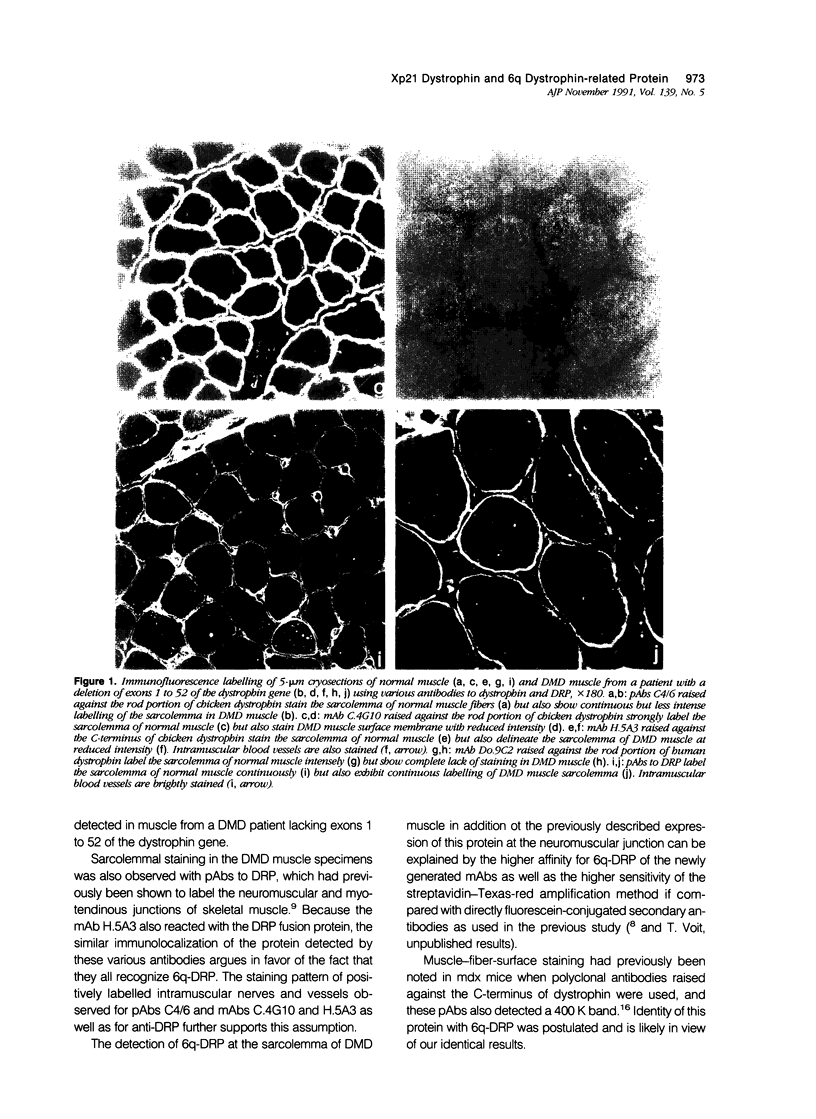

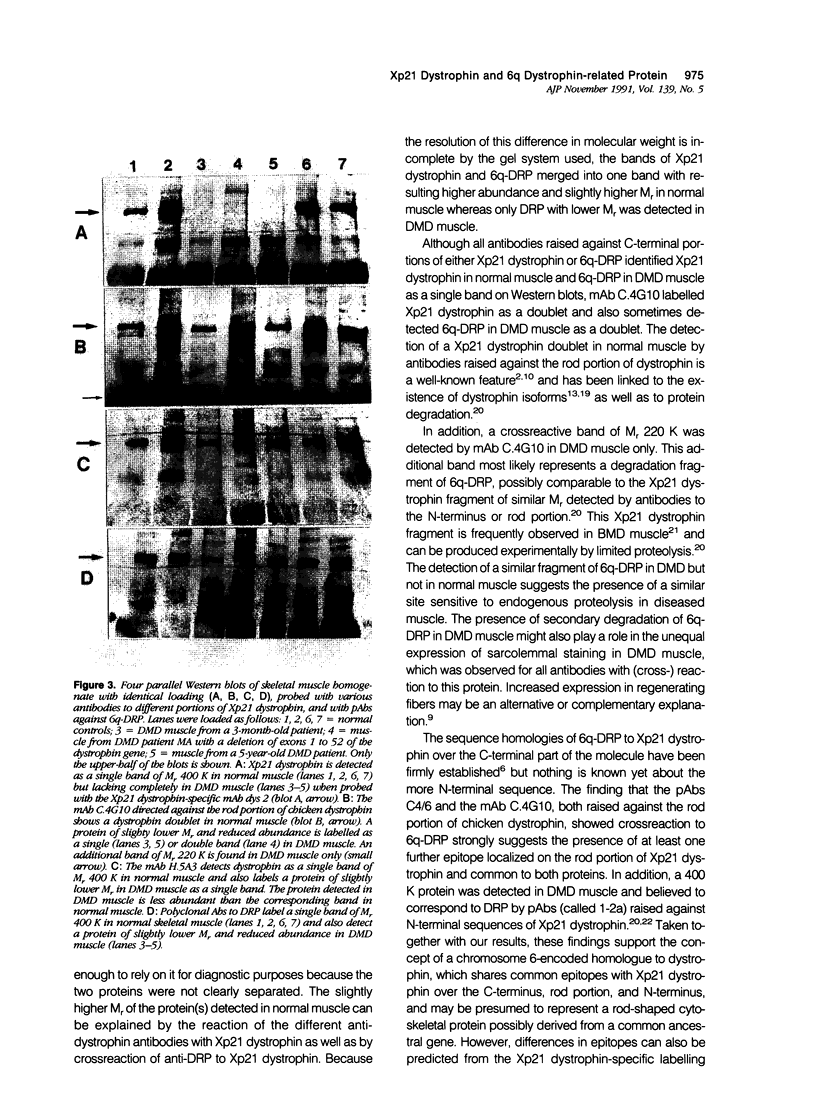

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cullen M. J., Walsh J., Nicholson L. V., Harris J. B. Ultrastructural localization of dystrophin in human muscle by using gold immunolabelling. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 May 22;240(1297):197–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. D., Critchley D. R. alpha-Actinins and the DMD protein contain spectrin-like repeats. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):159–160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr Protein sequence of DMD gene is related to actin-binding domain of alpha-actinin. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):1–1. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Beggs A. H., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M., Angelini C. Cross-reactive protein in Duchenne muscle. Lancet. 1989 Nov 18;2(8673):1211–1212. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91812-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Hudecki M. S., Rosenberg P. A., Pollina C. M., Kunkel L. M. Cell and fiber-type distribution of dystrophin. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Kunkel L. M., Angelini C., Clarke A., Johnson M., Harris J. B. Improved diagnosis of Becker muscular dystrophy by dystrophin testing. Neurology. 1989 Aug;39(8):1011–1017. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.8.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khurana T. S., Hoffman E. P., Kunkel L. M. Identification of a chromosome 6-encoded dystrophin-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16717–16720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Detailed analysis of the repeat domain of dystrophin reveals four potential hinge segments that may confer flexibility. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4560–4566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love D. R., Hill D. F., Dickson G., Spurr N. K., Byth B. C., Marsden R. F., Walsh F. S., Edwards Y. H., Davies K. E. An autosomal transcript in skeletal muscle with homology to dystrophin. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):55–58. doi: 10.1038/339055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love D. R., Morris G. E., Ellis J. M., Fairbrother U., Marsden R. F., Bloomfield J. F., Edwards Y. H., Slater C. P., Parry D. J., Davies K. E. Tissue distribution of the dystrophin-related gene product and expression in the mdx and dy mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3243–3247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. V., Davison K., Falkous G., Harwood C., O'Donnell E., Slater C. R., Harris J. B. Dystrophin in skeletal muscle. I. Western blot analysis using a monoclonal antibody. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Dec;94(1-3):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons F., Augier N., Léger J. O., Robert A., Tomé F. M., Fardeau M., Voit T., Nicholson L. V., Mornet D., Léger J. J. A homologue of dystrophin is expressed at the neuromuscular junctions of normal individuals and DMD patients, and of normal and mdx mice. Immunological evidence. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80468-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Immunochemistry on ultrathin frozen sections. Histochem J. 1980 Jul;12(4):381–403. doi: 10.1007/BF01011956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit T., Patel K., Dunn M. J., Dubowitz V., Strong P. N. Distribution of dystrophin, nebulin and Ricinus communis I (RCA-I)-binding glycoprotein in tissues of normal and mdx mice. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Feb;89(2-3):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit T., Stuettgen P., Cremer M., Goebel H. H. Dystrophin as a diagnostic marker in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Correlation of immunofluorescence and western blot. Neuropediatrics. 1991 Aug;22(3):152–162. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins S. C., Hoffman E. P., Slayter H. S., Kunkel L. M. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of dystrophin in myofibres. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):863–866. doi: 10.1038/333863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]