Abstract
The Lewy body is an intraneuronal inclusion body that is one of the histologic hallmarks of Parkinson's disease, a degenerative disease of the brain. Ultrastructural analysis has shown that the Lewy body is composed of straight 7-20 nm filaments and amorphous elements. Previous light microscopic, immunocytochemical studies have suggested the presence of neurofilament, microtubule, ubiquitin, and paired helical filament-related epitopes in Lewy bodies. Yet the biochemical composition of the Lewy body remains incompletely elucidated. The ultrastructural and immunocytochemical similarities and differences between the Lewy body and the neurofibrillary tangle of Alzheimer's disease raise questions as to their relation to each other and possible shared mechanisms of formation. In this study the authors examine whether ultrastructural immunocytochemical analysis of Lewy bodies confirms the light microscopic data, whether the structures and epitopes of Lewy bodies share with Alzheimer's disease neurofibrillary tangles the property of insolubility in sodium dodecyl sulfate, and speculate about the subunit composition of Lewy body filaments.
Full text
PDF



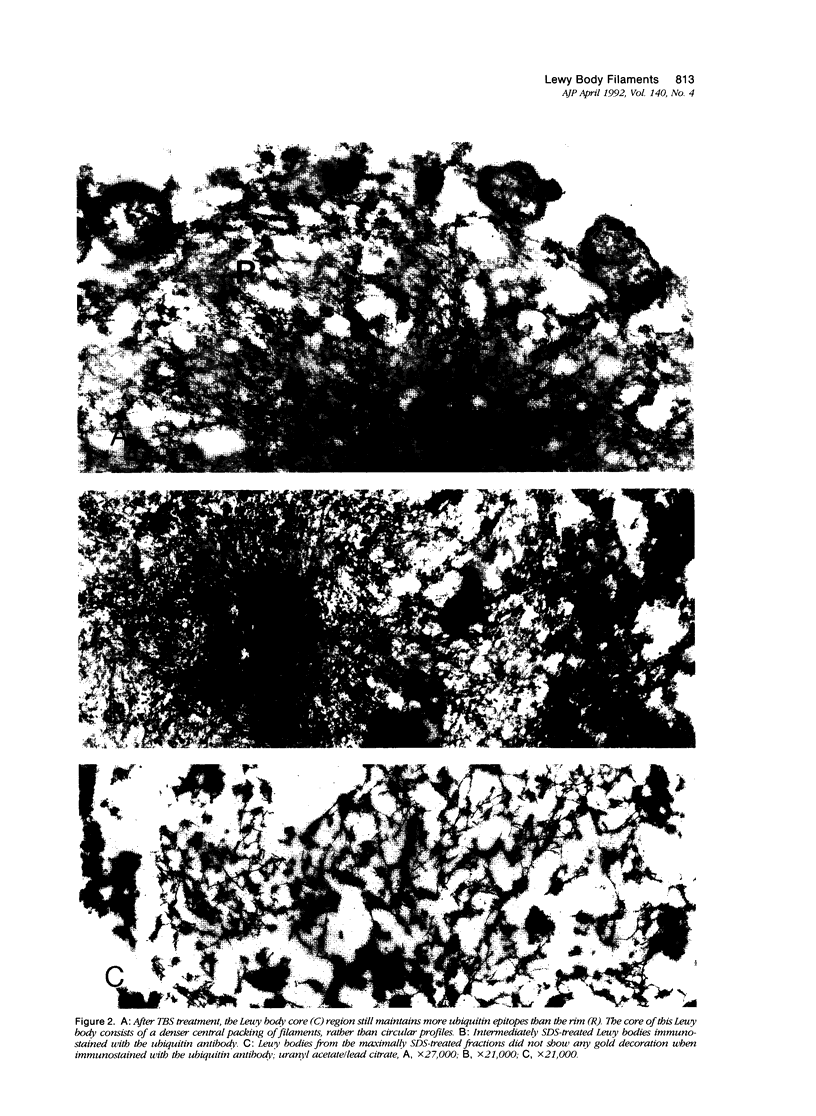

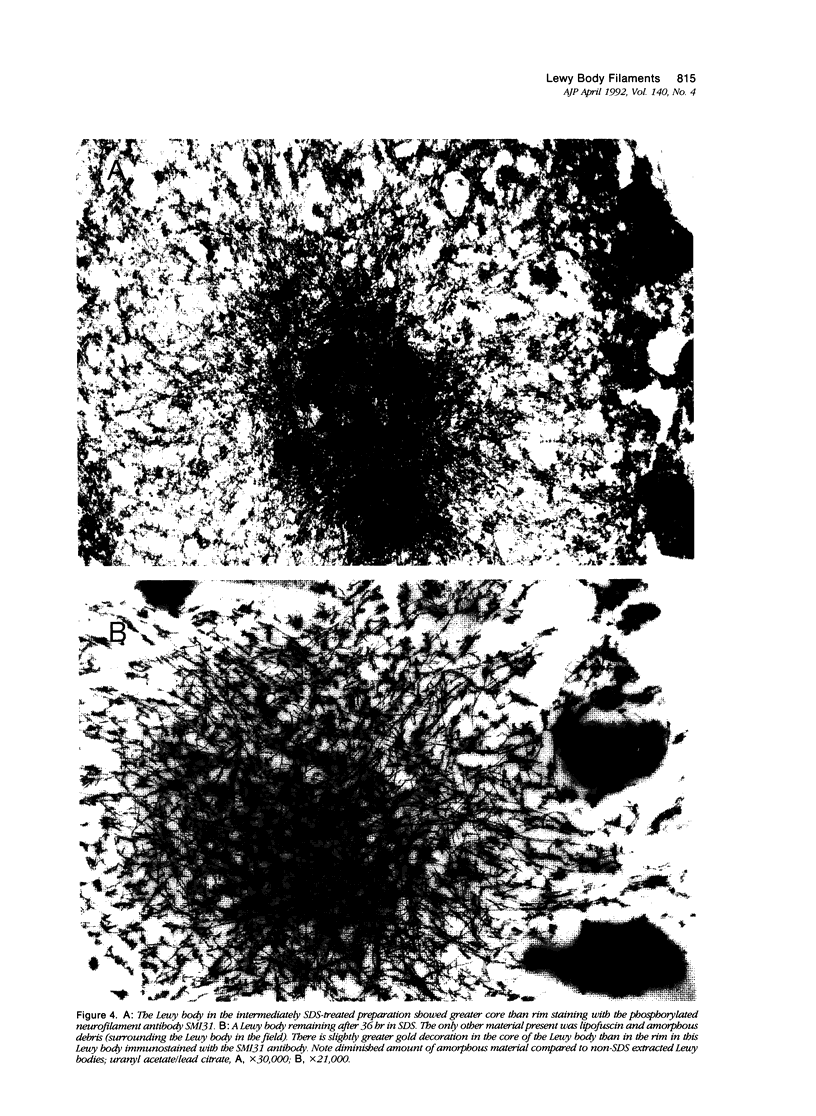
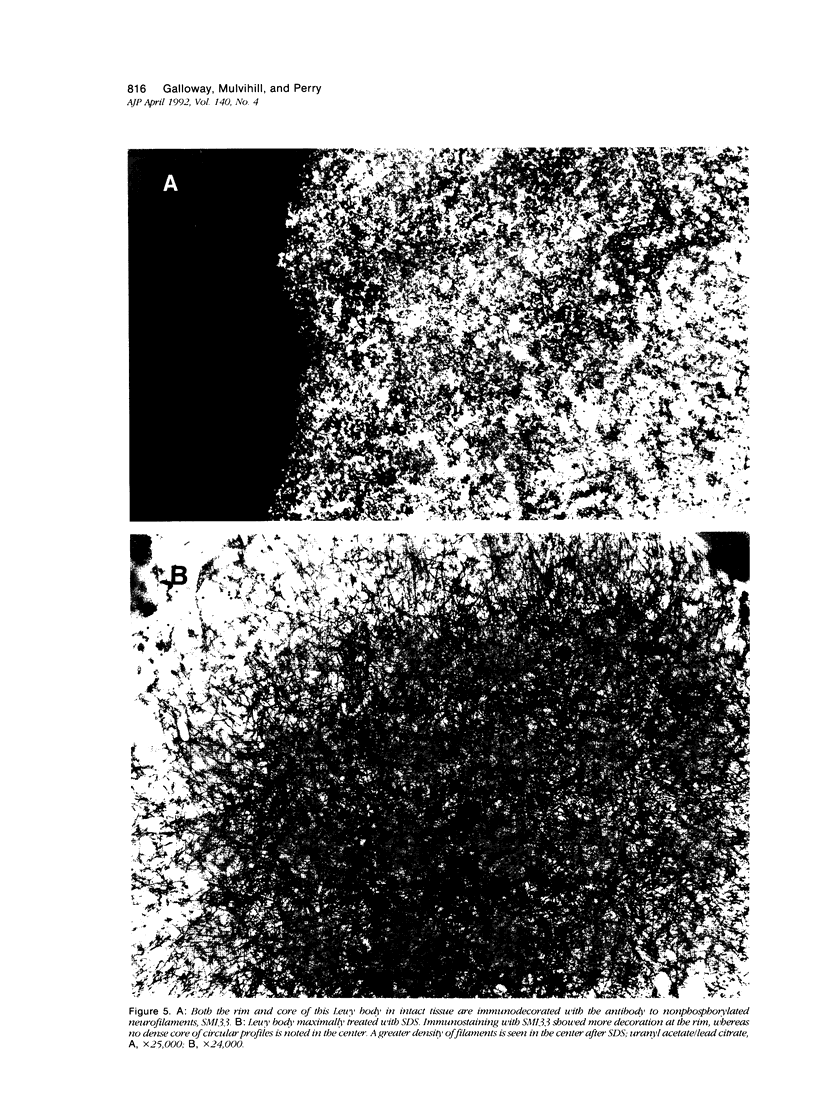

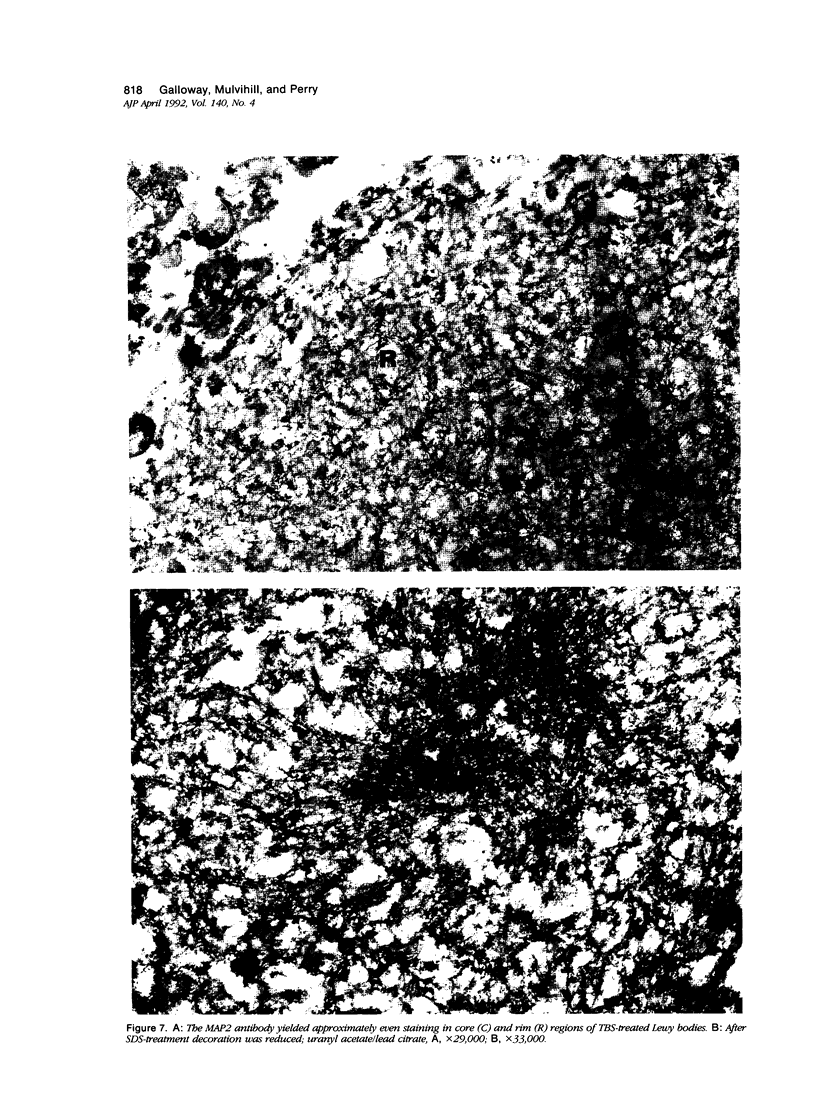
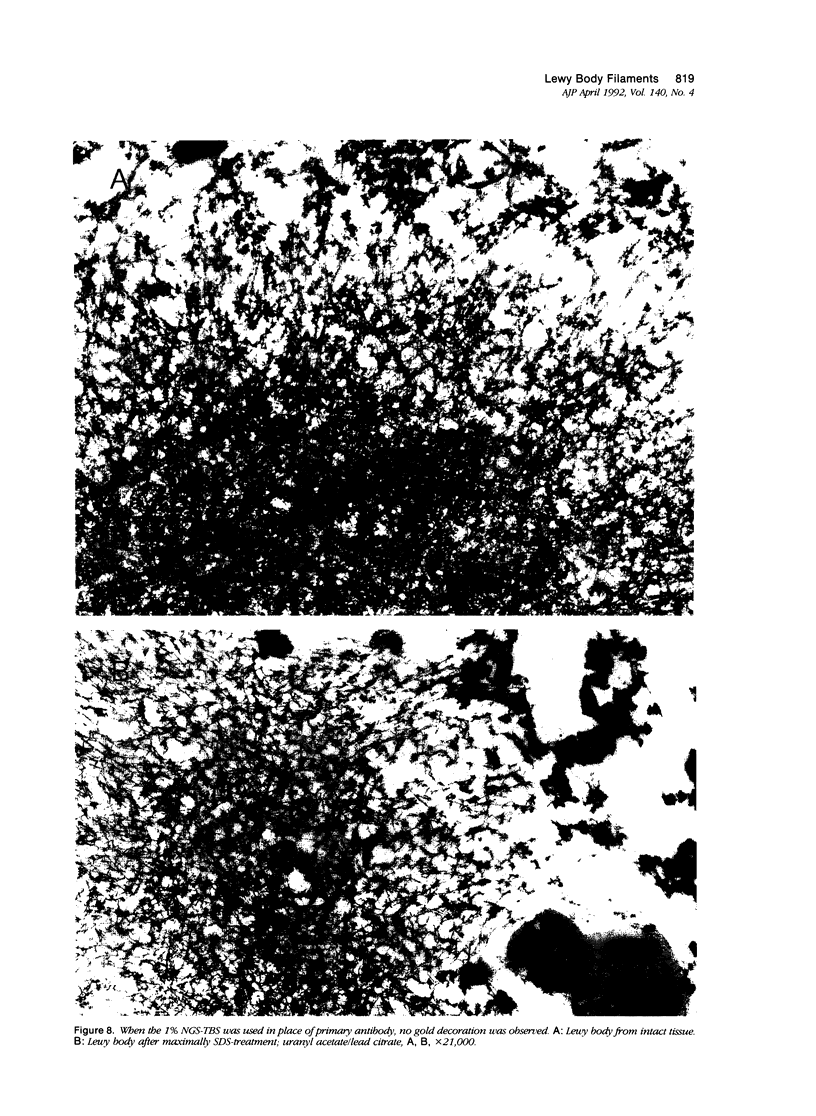



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forno L. S., Sternberger L. A., Sternberger N. H., Strefling A. M., Swanson K., Eng L. F. Reaction of Lewy bodies with antibodies to phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated neurofilaments. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Mar 14;64(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENFIELD J. G., BOSANQUET F. D. The brain-stem lesions in Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1953 Nov;16(4):213–226. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.16.4.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G. Antigenic characteristics of neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 31;91(2):148–153. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Bergeron C., Perry G. The presence of tau distinguishes Lewy bodies of diffuse Lewy body disease from those of idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90651-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
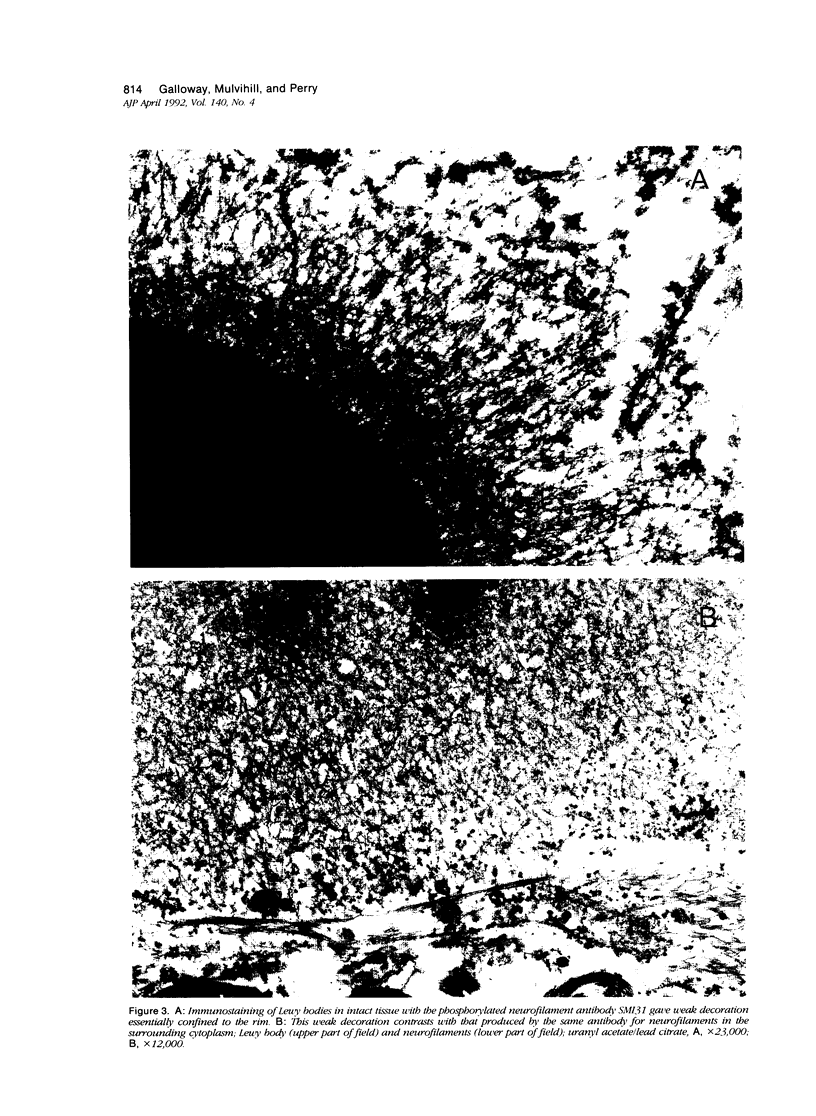
- Galloway P. G., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Perry G. Lewy bodies contain epitopes both shared and distinct from Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;47(6):654–663. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Mulvihill P., Siedlak S., Mijares M., Kawai M., Padget H., Kim R., Perry G. Immunochemical demonstration of tropomyosin in the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):291–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Perry G., Gambetti P. Hirano body filaments contain actin and actin-associated proteins. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 Mar;46(2):185–199. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198703000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E. The association of actin with Hirano bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1983 Mar;42(2):146–152. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198303000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Yen S. H., Chiu F. C., Peress N. S. Lewy bodies of Parkinson's disease contain neurofilament antigens. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1082–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.6308771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Quinlan M., Tung Y. C., Zaidi M. S., Wisniewski H. M. Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):6084–6089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Bright P. M. The immunochemical detection and quantitation of intracellular ubiquitin-protein conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12464–12473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):727–730. doi: 10.1038/304727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J., Anderton B. H., Gibb W. R., Lees A. J., Wells F. R., Marsden C. D. Neuronal filaments in Alzheimer's, Pick's, and Parkinson's diseases. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 22;313(8):520–521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508223130817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Duffy L. K., Dowling M. M., Abraham C., McCluskey A., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7941–7945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Duffy L. K., Dowling M. M., Abraham C., McCluskey A., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7941–7945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Joachim C. L., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4044–4048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Dickson D. W., Davies P., Yen S. H. Recognition of tau epitopes by anti-neurofilament antibodies that bind to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3410–3414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Yen S. H. Two monoclonal antibodies recognize Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles, neurofilament, and microtubule-associated proteins. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):455–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetto V., Perry G., Tabaton M., Mulvihill P., Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L. Ubiquitin is associated with abnormal cytoplasmic filaments characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4501–4505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. C., Brion J. P., Calvert R., Chin T. K., Eagles P. A., Downes M. J., Flament-Durand J., Haugh M., Kahn J., Probst A. Alzheimer's paired helical filaments share epitopes with neurofilament side arms. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo J., Ihara Y. Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1641–1644. doi: 10.1126/science.3029875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Friedman R., Shaw G., Chau V. Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3033–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Kawai M., Tabaton M., Onorato M., Mulvihill P., Richey P., Morandi A., Connolly J. A., Gambetti P. Neuropil threads of Alzheimer's disease show a marked alteration of the normal cytoskeleton. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1748–1755. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01748.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Mulvihill P., Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K. Immunochemical properties of ubiquitin conjugates in the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem. 1989 May;52(5):1523–1528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Mulvihill P., Manetto V., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Immunocytochemical properties of Alzheimer straight filaments. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3736–3738. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03736.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Rizzuto N., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Paired helical filaments from Alzheimer disease patients contain cytoskeletal components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Selkoe D. J., Block B. R., Stewart D., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Electron microscopic localization of Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangle components recognized by an antiserum to paired helical filaments. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Mar;45(2):161–168. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198603000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Stewart D., Friedman R., Manetto V., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Filaments of Pick's bodies contain altered cytoskeletal elements. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jun;127(3):559–568. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock N. J., Mirra S. S., Binder L. I., Hansen L. A., Wood J. G. Filamentous aggregates in Pick's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Alzheimer's disease share antigenic determinants with microtubule-associated protein, tau. Lancet. 1986 Nov 22;2(8517):1211–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Wolman L. Ultrastructural observations in Parkinsonism. J Pathol. 1969 Sep;99(1):39–44. doi: 10.1002/path.1710990106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Ihara Y., Salazar F. J. Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.6120571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkman D. R., Hammon K. M., White C. L., 3rd Production and characterization of a monospecific antiserum (A128) to disaggregated Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 May;38(5):703–715. doi: 10.1177/38.5.2110208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., Ulrich J. Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4274–4276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaton M., Perry G., Autilio-Gambetti L., Manetto V., Gambetti P. Influence of neuronal location on antigenic properties of neurofibrillary tangles. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jun;23(6):604–610. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich J., Haugh M., Anderton B. H., Probst A., Lautenschlager C., His B. Alzheimer dementia and Pick's disease: neurofibrillary tangles and Pick bodies are associated with identical phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;73(3):240–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00686617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. P., Grundke-Iqbal I., Kascsak R. J., Iqbal K., Wisniewski H. M. Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles: monoclonal antibodies to inherent antigen(s). Acta Neuropathol. 1984;62(4):268–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00687608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Mirra S. S., Pollock N. J., Binder L. I. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4040–4043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Dickson D. W., Crowe A., Butler M., Shelanski M. L. Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles contain unique epitopes and epitopes in common with the heat-stable microtubule associated proteins tau and MAP2. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):81–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Gaskin F., Terry R. D. Immunocytochemical studies of neurofibrillary tangles. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jul;104(1):77–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Horoupian D. S., Terry R. D. Immunocytochemical comparison of neurofibrillary tangles in senile dementia of Alzheimer type, progressive supranuclear palsy, and postencephalitic parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 1983 Feb;13(2):172–175. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Jager W. A. Sphingomyelin in Lewy inclusion bodies in Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1969 Dec;21(6):615–619. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480180071006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]