Abstract
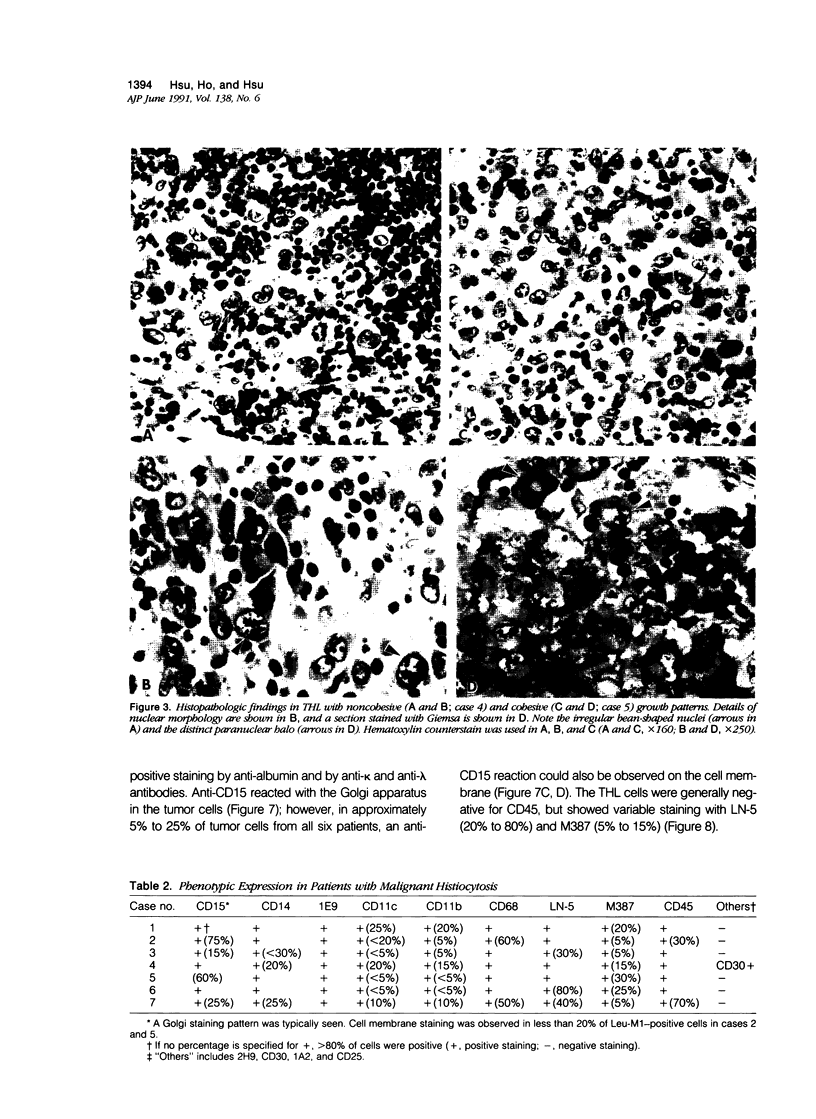
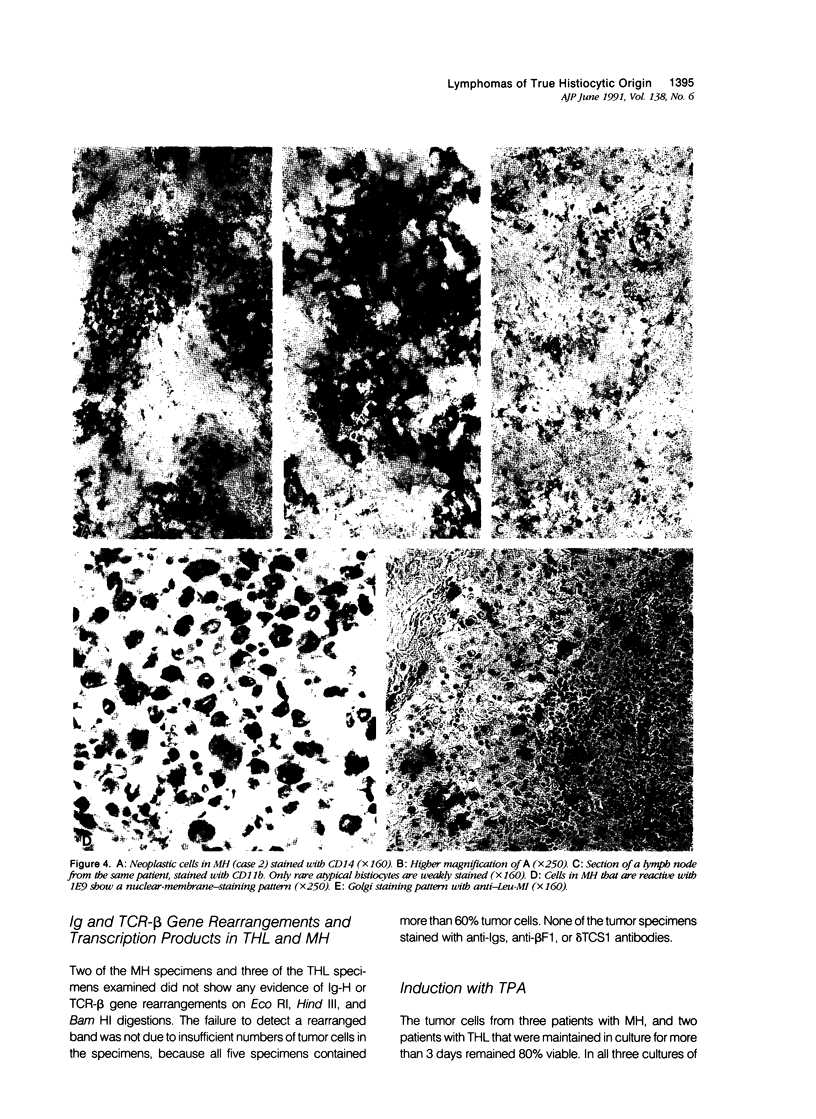
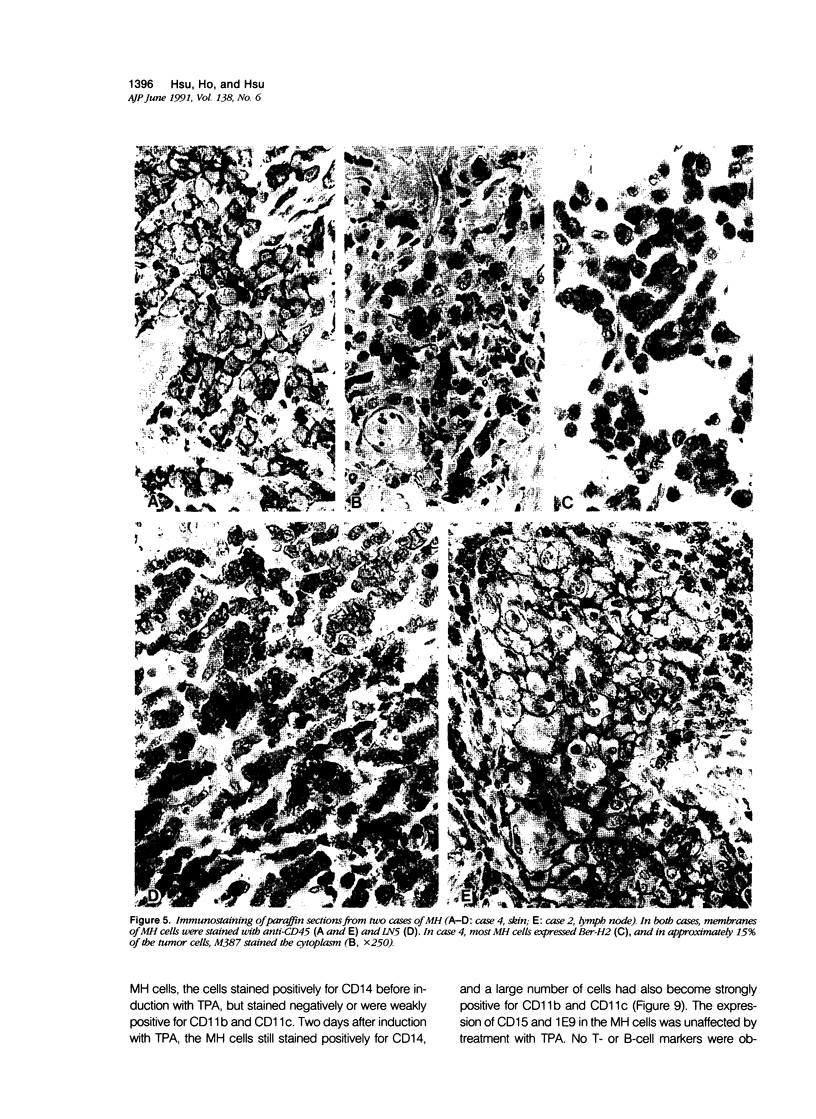
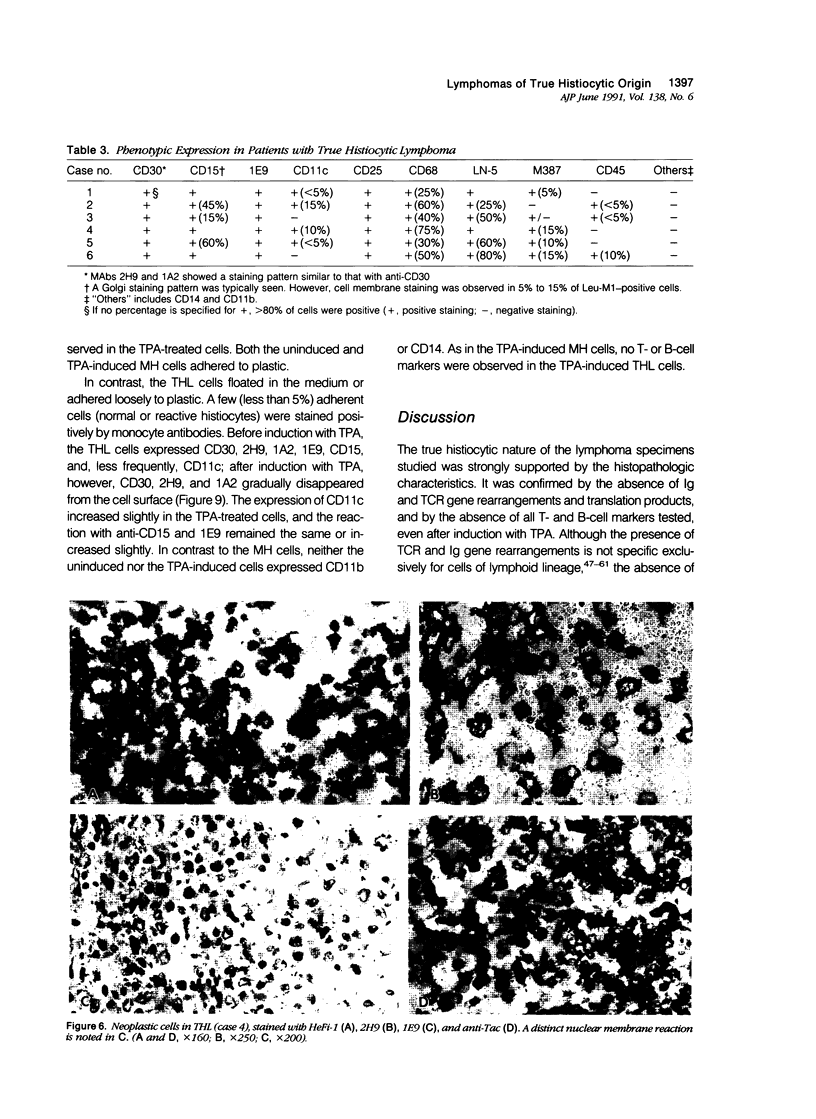
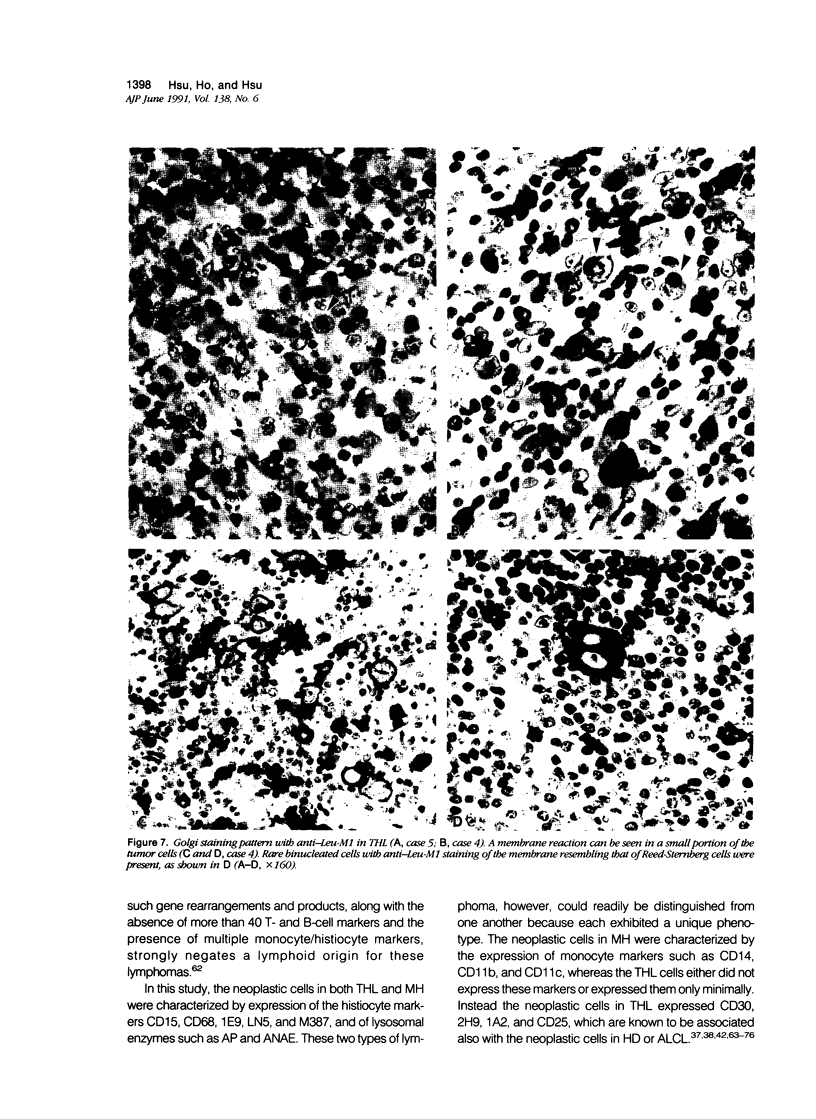
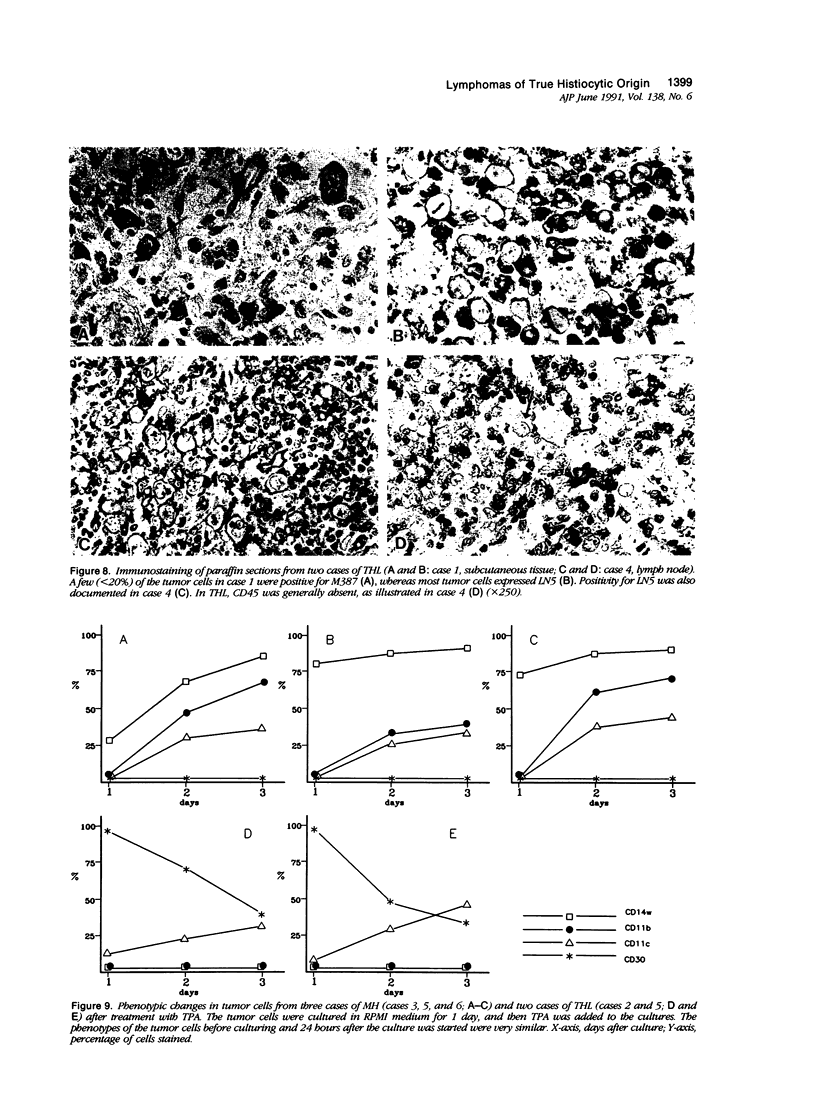
The authors determined the phenotypes of neoplastic cells in true histiocytic lymphoma and malignant histiocytosis by using a large panel of monoclonal antibodies and enzyme histochemistry procedures. Although the phenotypes overlapped slightly, the authors noted a distinct pattern in these tumors. The tumor cells of malignant histiocytosis generally expressed the monocyte markers CD11b, CD11c, CD14, and CD45, especially after induction with phorbol ester. In contrast, the tumor cells of true histiocytic lymphoma exhibited a marker expression very similar to that of Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. These cells expressed markers CD30, 2H9, and 1A2, but rarely expressed CD11b, CD11c, CD14, or CD45. Regardless of their cytologic features, the tumor cells from both types of histiocytic lymphoma exhibited diffuse nonspecific esterase and acid phosphatase activities, and they expressed histiocyte markers CD15, CD68, LN5, 1E9, and M387 to varying degrees. The tumor cells from both lymphomas did not exhibit T- or B-cell markers, T-cell receptor or immunoglobulin gene rearrangements, or gene translation products, even when they were induced with phorbol ester. The phenotypic expression in these two histiocytic malignancies suggests that they are derived from different types of histiocytes, or from histiocytes in different stages of maturation or differentiation, or from histiocytes that have distinct mechanisms of tumorigenic transformation. The expression of circulating monocyte markers in malignant histiocytosis suggests that this tumor originates in monocytes or free histiocytes, whereas the phenotype of true histiocytic lymphoma is compatible with an origin in fixed histiocytes, which generally are devoid of the monocyte markers CD11b and CD14.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnarsson B. A., Kadin M. E. Ki-1 positive large cell lymphoma. A morphologic and immunologic study of 19 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Apr;12(4):264–274. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198804000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen R., Brugger W., Löhr G. W., Bross K. J. Human macrophages can express the Hodgkin's cell-associated antigen Ki-1 (CD30). Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azar H. A., Jaffe E. S., Berard C. W., Callihan T. R., Braylan R. R., Cossman J., Triche T. J. Diffuse large cell lymphomas (reticulum cell sarcomas, histiocytic lymphomas). Correlation of morphologic features with functional markers. Cancer. 1980 Sep 15;46(6):1428–1441. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800915)46:6<1428::aid-cncr2820460624>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band H., Hochstenbach F., McLean J., Hata S., Krangel M. S., Brenner M. B. Immunochemical proof that a novel rearranging gene encodes the T cell receptor delta subunit. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):682–684. doi: 10.1126/science.3672118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoopat L., Turner R. R., Stathopoulos E., Meyer P. R., Taylor C. R., Marder R. J., Epstein A. L. Immunohistochemical characterization of two new monoclonal antibodies (LN-4, LN-5) reactive with human macrophage subsets and derived malignancies in B5-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1079–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Jones D. B., Flavell D. J., Fagerhol M. K. Mac 387 antibody and detection of formalin resistant myelomonocytic L1 antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Sep;41(9):963–970. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.9.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braylan R. C., Jaffe E. S., Berard C. W. Malignant lymphomas: current classification and new observations. Pathol Annu. 1975;10:213–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Scheft H., Warnke R. A., Jones N., Strominger J. L. Characterization and expression of the human alpha beta T cell receptor by using a framework monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1502–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouet J. C., Preud'Homme J. L., Flandrin G., Chelloul N., Seligmann M. Membrane markers in "histiocytic" lymphomas (reticulum cell sarcomas). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):631–633. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns B. F., Cripps C., Dardick I. A case of a Ki-1 large cell anaplastic lymphoma with ultrastructural features. Hum Pathol. 1989 Apr;20(4):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos L., Guyotat D., Larese A., Mazet L., Bourgeot J. P., Ehrsam A., Fiere D. Expression of CD 19 antigen on acute monoblastic leukemia cells at diagnosis and after TPA-induced differentiation. Leuk Res. 1988;12(5):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. K., Ng C. S., Hui P. K., Leung T. W., Lo E. S., Lau W. H., McGuire L. J. Anaplastic large cell Ki-1 lymphoma. Delineation of two morphological types. Histopathology. 1989 Jul;15(1):11–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1989.tb03038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. C., Greaves M. F. Acute leukaemia with mixed lymphoid and myeloid phenotype. Br J Haematol. 1984 Sep;58(1):203–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb06075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G. Y., Minden M. D., Toyonaga B., Mak T. W., McCulloch E. A. T cell receptor and immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in acute myeloblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):414–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G. Y., Minden M. D., Toyonaga B., Mak T. W., McCulloch E. A. T cell receptor and immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in acute myeloblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):414–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriu-Bona A., Burmester G. R., Waters S. J., Winchester R. J. Human mononuclear phagocyte differentiation antigens. I. Patterns of antigenic expression on the surface of human monocytes and macrophages defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. L., Kaplan H. S. Biology of the human malignant lymphomas. I. Establishment in continuous cell culture and heterotransplantation of diffuse histiocytic lymphomas. Cancer. 1974 Dec;34(6):1851–1872. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197412)34:6<1851::aid-cncr2820340602>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller A. C., Sterry W. Large cell anaplastic lymphoma of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1989 Nov;121(5):593–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1989.tb08191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippa D. A., Lieberman P. H., Erlandson R. A., Koziner B., Siegal F. P., Turnbull A., Zimring A., Good R. A. A study of malignant lymphomas using light and ultramicroscopic, cytochemical and immunologic technics: correlation with clinical features. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer P., Nacheva E., Mason D. Y., Sherrington P. D., Hoyle C., Hayhoe F. G., Karpas A. A Ki-1 (CD30)-positive human cell line (Karpas 299) established from a high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, showing a 2;5 translocation and rearrangement of the T-cell receptor beta-chain gene. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontenay M., Flandrin G., Baurman H., Loiseau P., Valensi F., Daniel M. T., Sigaux F. T cell receptor delta gene rearrangements occur predominantly in immature myeloid leukemias exhibiting lineage promiscuity. Leukemia. 1990 Feb;4(2):100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa F., Taniguchi S., Oguchi M., Komura J., Takiuchi H., Shirakawa S. True histiocytic lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 1980 Aug;116(8):915–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhartz H. H., Bartram C. R., Raghavachar A., Schmetzer H., Clemm C., Wilmanns W., Thiel E. Spontaneous Epstein-Barr virus transformed B-cell line sharing the identical immunoglobulin gene rearrangement with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):684–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Chan L. C., Furley A. J., Watt S. M., Molgaard H. V. Lineage promiscuity in hemopoietic differentiation and leukemia. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesser H., Tkachuk D., Reis M. D., Mak T. W. Gene rearrangements and translocations in lymphoproliferative diseases. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1402–1415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanjan S. N., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. A monoclonal antibody (MMA) that identifies a differentiation antigen on human myelomonocytic cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):172–188. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Longo D. L., Cossman J., Bolen J. B., Hsu S. M., Israel M., Fisher R. I. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody that binds Reed-Sternberg cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4231–4236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho F. C., Todd D. Malignant histiocytosis: report of five Chinese patients. Cancer. 1978 Nov;42(5):2450–2460. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197811)42:5<2450::aid-cncr2820420547>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Hsu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin by cells of Hodgkin's neoplastic cell lines HDLM-1 and KM-H2. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):735–745. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Cossman J., Jaffe E. S. Lymphocyte subsets in normal human lymphoid tissues. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;80(1):21–30. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Aberrant expression of T cell and B cell markers in myelocyte/monocyte/histiocyte-derived lymphoma and leukemia cells. Is the infrequent expression of T/B cell markers sufficient to establish a lymphoid origin for Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg cells? Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):203–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Lymphocyte functional antigens stabilize agglutination between Reed-Sternberg cells and T cells, but are not responsible for homotypic binding of Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):563–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Phenotypes and phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human histiocytic lymphoma cell lines (U-937 and SU-DHL-1) and Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):223–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Huang L. C., Hsu P. L., Ge Z. H., Ho Y. S., Cuttita F., Mulshine J. Biochemical and ultrastructural study of Leu M1 antigen in Reed-Sternberg cells: comparison with granulocytes and interdigitating reticulum cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Aug;77(2):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of B-lymphocytes. 1. Identification with monoclonal antibodies in normal lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of T lymphocytes in thymus and peripheral lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1985 Oct;121(1):69–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Krupen K., Lachman L. B. Heterogeneity of interleukin 1 production in cultured Reed-Sternberg cell lines HDLM-1, HDLM-1d, and KM-H2. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):33–38. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M. Phenotypic expression of cells of stationary elements in human lymphoid tissues. A histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Hematol Pathol. 1987;1(1):45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Xie S. S., Hsu P. L. Cultured Reed-Sternberg cells HDLM-1 and KM-H2 can be induced to become histiocytelike cells. H-RS cells are not derived from lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):353–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhao X., Hsu P. L., Lok M. S. Extracellular matrix does not induce the proliferation, but promotes the differentiation, of Hodgkin's cell line HDLM-1. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):9–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn D., Meister P. Malignant histiocytosis: morphologic and cytochemical findings. Cancer. 1978 Sep;42(3):1341–1349. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197809)42:3<1341::aid-cncr2820420345>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S., Braylan R. C., Nanba K., Frank M. M., Berard C. W. Functional markers: a new perspective on malignant lymphomas. Cancer Treat Rep. 1977 Sep;61(6):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Sako D., Berliner N., Franklin W., Woda B., Borowitz M., Ireland K., Schweid A., Herzog P., Lange B. Childhood Ki-1 lymphoma presenting with skin lesions and peripheral lymphadenopathy. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1042–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Tourneau A., Audouin J., Diebold J. Ultrastructural study of 4 cases of Ki-1 positive large anaplastic cell malignant lymphoma. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;413(3):215–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00718613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone R., Lo Coco F., De Rossi G., Diverio D., Frontani M., Spadea A., Testi A. M., Cordone I., Mandelli F. Immunoglobulin heavy chain and T-cell receptor beta chain gene rearrangements in acute non lymphoid leukemia. Haematologica. 1990 Mar-Apr;75(2):125–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Harrison G., Jr Histochemical and immunohistochemical study of diffuse large-cell lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Nov;70(5):721–732. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm J. S., Barron D. R., Williams M. E., Swerdlow S. H. Ki-1-positive cutaneous large cell lymphoma of T cell type: report of an indolent subtype. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Feb;20(2 Pt 2):342–348. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden M. D., Mak T. W. The structure of the T cell antigen receptor genes in normal and malignant T cells. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):327–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirchandani I., Shah I., Palutke M., Varadachari C., Tabaczka P., Franklin R., Bishop C. True histiocytic lymphoma. A report of four cases. Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;52(10):1911–1918. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831115)52:10<1911::aid-cncr2820521023>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R., Smith S. D., Hecht B. K., Christy V., Mellentin J. D., Warnke R., Cleary M. L. Lack of involvement of the c-fms and N-myc genes by chromosomal translocation t(2;5)(p23;q35) common to malignancies with features of so-called malignant histiocytosis. Blood. 1989 Jun;73(8):2155–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morra E., Rosso R., Lazzarino M., Paulli M., Cespa M., Orlandi E., Magrini U., Bernasconi C. Adult Ki-1-positive large cell anaplastic lymphoma presenting with skin lesions. Acta Haematol. 1989;81(1):51–55. doi: 10.1159/000205401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor N. T., Stein H., Gatter K. C., Wainscoat J. S., Crick J., Al Saati T., Falini B., Delsol G., Mason D. Y. Genotypic analysis of large cell lymphomas which express the Ki-1 antigen. Histopathology. 1987 Jul;11(7):733–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyashiki J. H., Ohyashiki K., Toyama K., Kimura N., Minowada J., Kinniburgh A. J., Sandberg A. A. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement and its expression in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Feb;37(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyashiki J. H., Ohyashiki K., Toyama K., Kimura N., Minowada J., Kinniburgh A. J., Sandberg A. A. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement and its expression in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Feb;37(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pileri S., Mazza P., Zinzani P. L., Poggi S., Poletti G., Falini B., Tura S. Ki-1 lymphoma and Hodgkin's disease. Haematologica. 1989 May-Jun;74(3):333–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H., Dahl G. V., Melvin S., Williams D. L., Peiper S., Mirro J., Murphy S. B., Stass S. Acute leukaemia with mixed lymphoid and myeloid phenotype. Br J Haematol. 1984 Jan;56(1):121–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosso R., Paulli M., Magrini U., Kindl S., Boveri E., Volpato G., Poggi S., Baglioni P., Pileri S. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, CD30/Ki-1 positive, expressing the CD15/Leu-M1 antigen. Immunohistochemical and morphological relationships to Hodgkin's disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1990;416(3):229–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01678982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab U., Stein H., Gerdes J., Lemke H., Kirchner H., Schaadt M., Diehl V. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):65–67. doi: 10.1038/299065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Gerdes J., Dürkop H., Falini B., Pileri S., Stein H. BER-H2: a new anti-Ki-1 (CD30) monoclonal antibody directed at a formol-resistant epitope. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1678–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Stein H., Wang C. Y. The monoclonal antibodies alpha S-HCL 1 (alpha Leu-14) and alpha S-HCL 3 (alpha Leu-M5) allow the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):974–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwonzen M., Kuehn N., Vetten B., Diehl V., Pfreundschuh M. Phenotyping of acute myelomonocytic (AMMOL) and monocytic leukemia (AMOL): association of T-cell-related antigens and skin-infiltration in AMOL. Leuk Res. 1989;13(10):893–898. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(89)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Jensen J. P., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and expression in diffuse histiocytic lymphomas reveal cellular lineage, molecular defects, and sites of chromosomal translocation. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):391–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundeen J., Lipford E., Uppenkamp M., Sussman E., Wahl L., Raffeld M., Cossman J. Rearranged antigen receptor genes in Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):96–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., 3rd, Van Agthoven A., Schlossman S. F., Terhorst C. Structural analysis of differentiation antigens Mo1 and Mo2 on human monocytes. Hybridoma. 1982;1(3):329–337. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traweek S. T., Ben-Ezra J., Braziel R. M., Winberg C. D. The in-vitro response of CD2-positive acute myelogenous leukemia to proliferation and differentiation inducing agents. Leuk Res. 1990;14(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs R. R., Sheibani K., Sebek B. A., Savage R. A. Malignant histiocytosis. Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical characterization. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Jan;104(1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadachari C., Palutke M., Climie A. R., Weise R. W., Chason J. L. Immunoblastic sarcoma (histiocytic lymphoma) of the brain with B cell markers. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1978 Dec;49(6):887–892. doi: 10.3171/jns.1978.49.6.0887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnke R. A., Kim H., Dorfman R. F. Malignant histiocytosis (histiocytic medullary reticulosis). I. Clinicopatholigic study of 29 cases. Cancer. 1975 Jan;35(1):215–230. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197501)35:1<215::aid-cncr2820350127>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Picker L. J., Copenhaver C. M., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Large-cell hematolymphoid neoplasms of uncertain lineage. Hum Pathol. 1988 Aug;19(8):967–973. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A., Hirsch J. G., Humphrey J. H., Spector W. G., Langevoort H. L. The mononuclear phagocyte system: a new classification of macrophages, monocytes, and their precursor cells. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(6):845–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P., te Velde J., Jansen J., Ruiter D. J., Spaander P. J., Cornelisse C. J., Meijer C. J. Malignant lymphoma of true histiocytic origin: histiocytic sarcoma. A morphological, ultrastructural, immunological, cytochemical and clinical study of 10 cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1981;391(3):249–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00709158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P., van Oostveen J. W., Stel H. V., van der Kwast T. H., Melief C. J., Meijer C. J. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of large-cell lymphomas, formerly classified as true histiocytic lymphoma: identification of an unusual group of tumors. Leuk Res. 1990;14(4):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]