Abstract
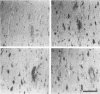
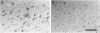
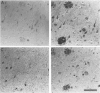
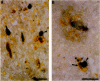
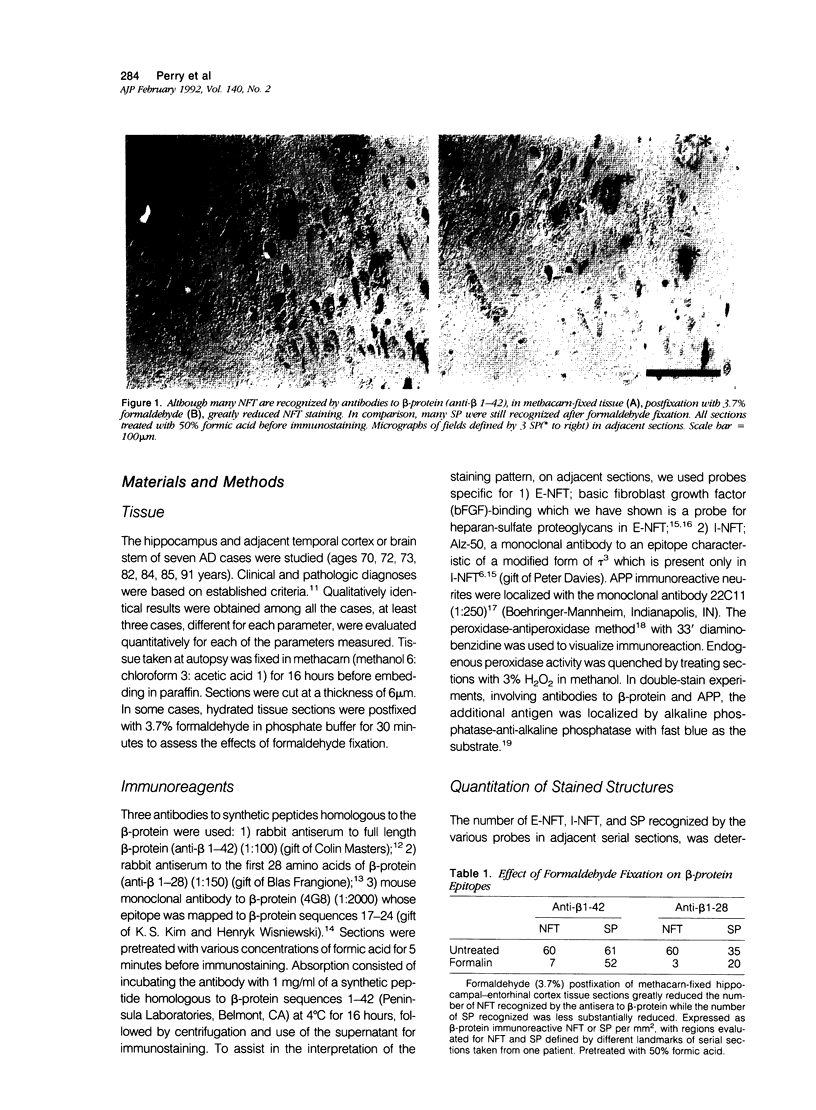
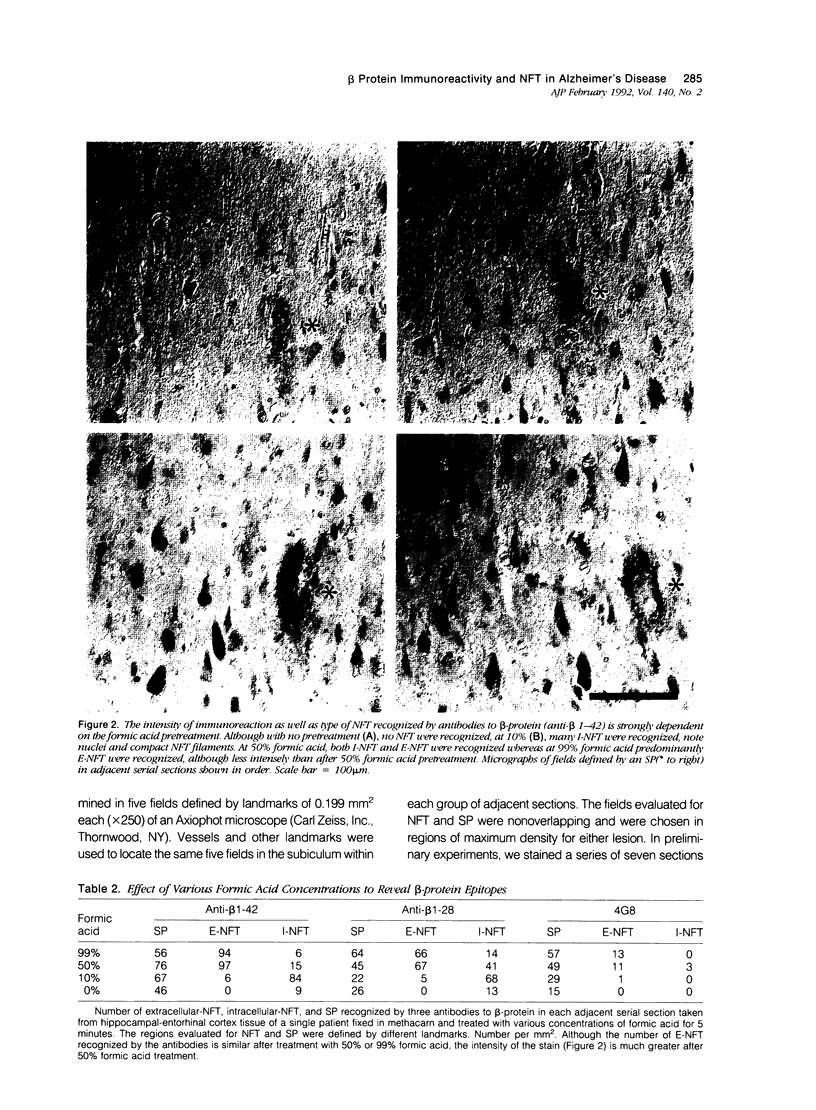
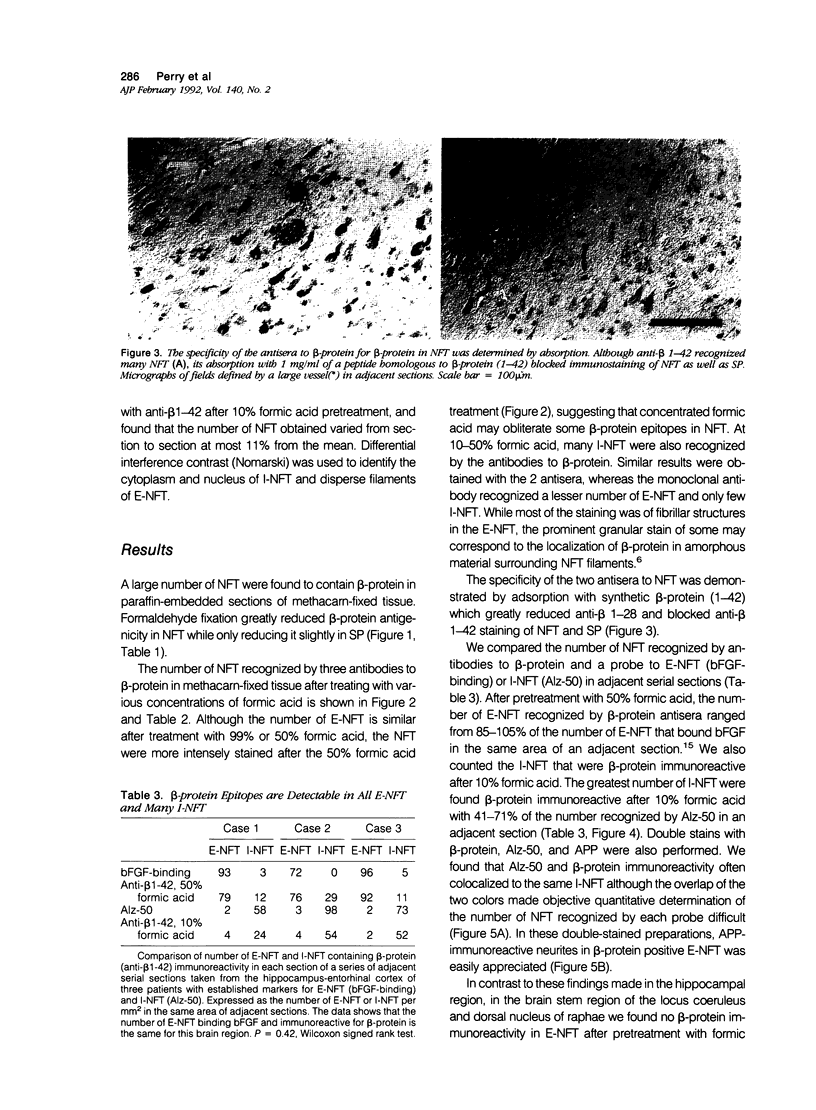
The presence of dystrophic neurites in most extracellular neurofibrillary tangles (E-NFT) suggests a factor promoting neurite growth in E-NFT. Although the beta-protein detected in E-NFT may fill that role, reports that only 2-10% of E-NFT contain beta-protein whereas 80-100% contain dystrophic neurites suggested that beta-protein does not play an important role. In this study, the authors used two antisera and one monoclonal antibody to beta-protein to establish the effects of tissue preparation and formic acid enhancement on the detection of beta-protein in E-NFT. We found that beta-protein epitopes in E-NFT are sensitive to formaldehyde fixation and are best enhanced by 50% formic acid, whereas beta-protein in senile plaques is best enhanced at higher formic acid concentrations. After treatment with 50% formic acid, beta-protein was found in all E-NFT. Interestingly, after treatment with 10% formic acid, half of intraneuronal-NFT (I-NFT) also contained beta-protein immunoreactivity. The finding that beta-protein immunoreactivity in senile plaques, E-NFT and I-NFT is increased at different formic acid concentrations suggests that beta-protein in each location is in a different conformation. In contrast, no beta-protein immunoreactivity could be found in E-NFT of the brain stem, an area in which dystrophic neurites do not infiltrate E-NFT. These findings indicate a correlation between neuritic infiltration and presence of beta-protein in E-NFT and suggests the two are linked in Alzheimer's disease for E-NFT as well as senile plaques.
Full text
PDF
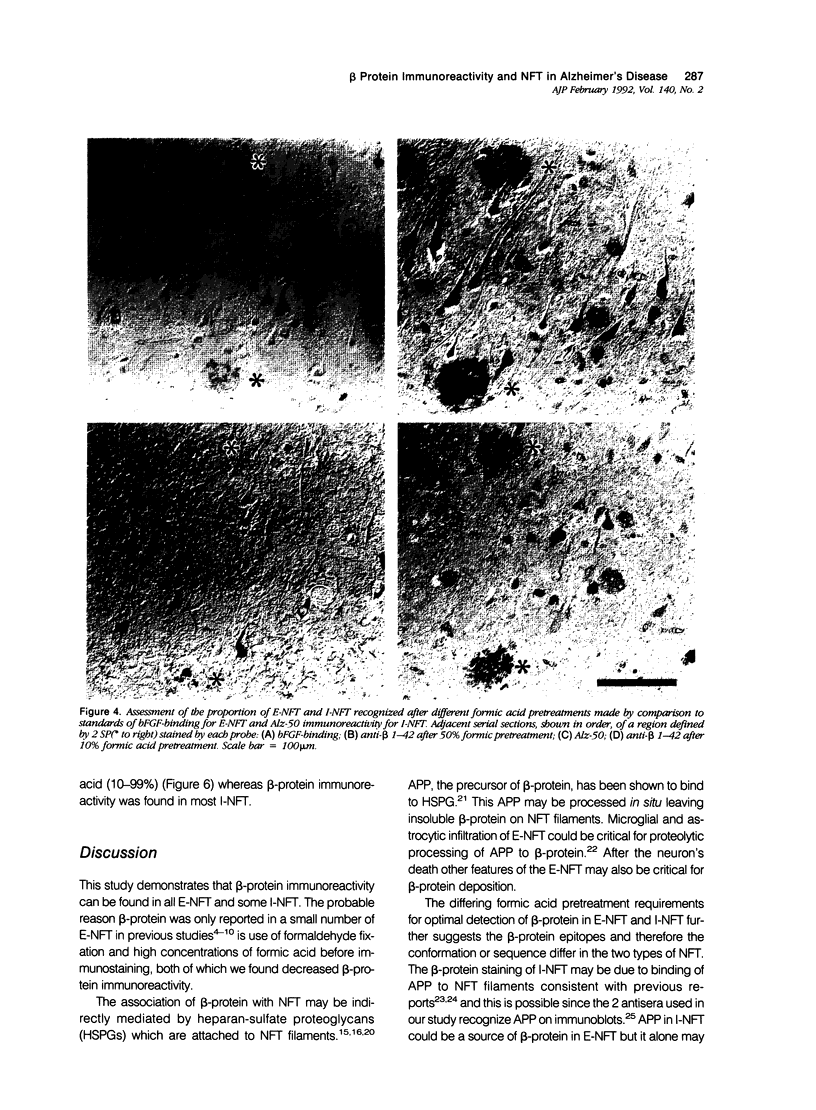
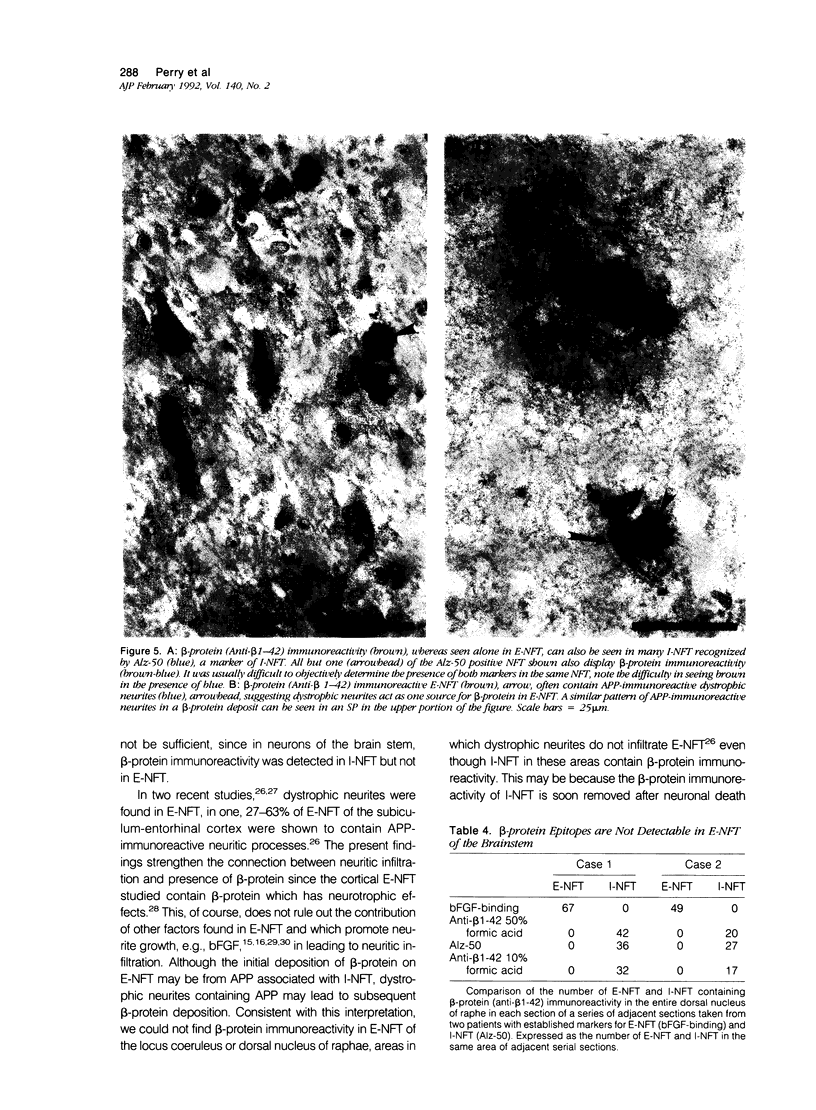


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsop D., Haga S., Bruton C., Ishii T., Roberts G. W. Neurofibrillary tangles in some cases of dementia pugilistica share antigens with amyloid beta-protein of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Feb;136(2):255–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondareff W., Wischik C. M., Novak M., Amos W. B., Klug A., Roth M. Molecular analysis of neurofibrillary degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. An immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):711–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Gorevic P. D., Migheli A., Frangione B. In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from two synthetic peptides of different lengths homologous to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):782–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cras P., Kawai M., Siedlak S., Mulvihill P., Gambetti P., Lowery D., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Greenberg B., Perry G. Neuronal and microglial involvement in beta-amyloid protein deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):241–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cras P., Kawai M., Siedlak S., Perry G. Microglia are associated with the extracellular neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. 1991 Sep 6;558(2):312–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90783-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L., Wolska B., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Martins R., Simms G., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 amyloid protein deposition and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: prevalence in aged brains determined by immunocytochemistry compared with conventional neuropathologic techniques. Neurology. 1988 Nov;38(11):1688–1693. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Pinilla F., Cummings B. J., Cotman C. W. Induction of basic fibroblast growth factor in Alzheimer's disease pathology. Neuroreport. 1990 Nov-Dec;1(3-4):211–214. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199011000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 amyloid protein immunoreactivity is present in Alzheimer's disease neurofibrillary tangles. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 3;101(3):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Kalaria R. N., Harik S. I., Perry G. The relationship of amyloid plaques to cerebral capillaries in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1435–1446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Siedlak S. L., Podlisny M. B., Greenberg B., Shelton E. R., Chan H. W., Usiak M., Selkoe D. J., Perry G., Younkin S. G. Soluble derivatives of the beta amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease are labeled by antisera to the beta amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Siedlak S. L., Richey P., Kawai M., Cras P., Kalaria R. N., Galloway P. G., Scardina J. M., Cordell B., Greenberg B. D. Association of heparan sulfate proteoglycan with the neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3679–3683. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03679.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Schroeder R., LaCorbiere M., Saitoh T., Cole G. Amyloid beta protein precursor is possibly a heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2968652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siedlak S. L., Cras P., Kawai M., Richey P., Perry G. Basic fibroblast growth factor binding is a marker for extracellular neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Jul;39(7):899–904. doi: 10.1177/39.7.1865106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Mar H., Nochlin D., Sekiguchi R. T., Kimata K., Koike Y., Wight T. N. Early accumulation of heparan sulfate in neurons and in the beta-amyloid protein-containing lesions of Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1253–1270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini M. G., Goedert M., Jakes R., Klug A. Different configurational states of beta-amyloid and their distributions relative to plaques and tangles in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3947–3951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini M. G., Goedert M., Jakes R., Klug A. Topographical relationship between beta-amyloid and tau protein epitopes in tangle-bearing cells in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopa E. G., Gonzalez A. M., Chorsky R., Corona R. J., Alvarez J., Bird E. D., Baird A. Basic fibroblast growth factor in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):690–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaton M., Cammarata S., Mancardi G., Manetto V., Autilio-Gambetti L., Perry G., Gambetti P. Ultrastructural localization of beta-amyloid, tau, and ubiquitin epitopes in extracellular neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Weghe J., Cras P., Kawai M., Siedlak S. L., Tabaton M., Greenberg B., Perry G. Dystrophic neurites infiltrate extracellular neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. 1991 Sep 27;560(1-2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitson J. S., Selkoe D. J., Cotman C. W. Amyloid beta protein enhances the survival of hippocampal neurons in vitro. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1488–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2928783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Ishiguro K., Shoji M., Yamazaki T., Nakazato Y., Ihara Y., Hirai S. Amyloid beta/A4 protein precursor is bound to neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer-type dementia. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 24;537(1-2):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90377-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Nakazato Y., Kawarabayashi T., Ishiguro K., Ihara Y., Morimatsu M., Hirai S. Extracellular neurofibrillary tangles associated with degenerating neurites and neuropil threads in Alzheimer-type dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(6):603–609. doi: 10.1007/BF00296369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Nakazato Y., Shoji M., Okamoto K., Ihara Y., Morimatsu M., Hirai S. Secondary deposition of beta amyloid within extracellular neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer-type dementia. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):699–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]