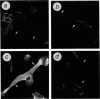
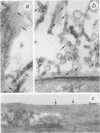
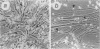
Abstract
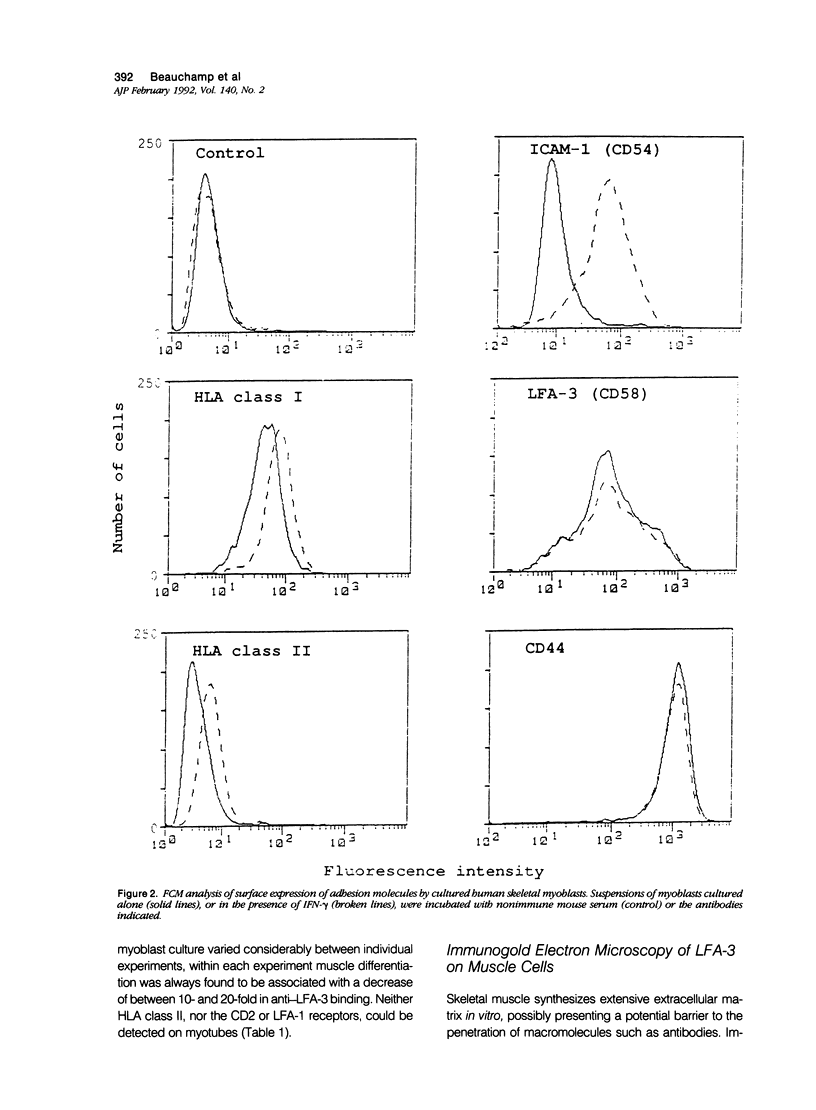
The infiltration of skeletal muscle by leukocytes occurs in a variety of myopathies and frequently accompanies muscle degeneration and regeneration. The latter involves development of new myofibers from precursor myoblasts, and so infiltrating cells may interact with muscle at all stages of differentiation. The authors have investigated the surface expression of ligands for T-cell adhesion during the differentiation of human skeletal muscle in vitro. Myoblasts expressed low levels of ICAM-1 (CD54), which remained constant during muscle cell differentiation and could be induced by cytokines such as gamma-interferon. It is therefore likely that ICAM-1 is involved in the invasive accumulation of lymphocytes during skeletal muscle inflammation. In contrast, LFA-3 (CD58) was expressed at higher levels than ICAM-1 on myoblasts, decreased significantly during myogenesis, and was unaffected by immune mediators. Both ICAM-1 and LFA-3 were able to mediate T cell binding to myoblasts, whereas adhesion to myotubes was independent of the LFA-3 ligand. Although expressed throughout myogenesis, human leukocyte antigen class I and CD44 did not appear to mediate T cell binding. The expression of ligands that facilitate interaction of myogenic cells with lymphocytes may have important implications for myoblast transplantation.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham D. J., Bou-Gharios G., Beauchamp J. R., Plater-Zyberk C., Maini R. N., Olsen I. Function and regulation of the murine lymphocyte CD2 receptor. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Apr;49(4):329–341. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.4.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham D., Bokth S., Bou-Gharios G., Beauchamp J., Olsen I. Interactions between lymphocytes and dermal fibroblasts: an in vitro model of cutaneous lymphocyte trafficking. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Sep;190(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90152-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. H., Hubscher S. G., Shaw J., Rothlein R., Neuberger J. M. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on liver allografts during rejection. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1122–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albelda S. M., Buck C. A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2868–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard S. T., Dunn M. J., Dubowitz V., Rose M. L. Increased expression of HLA ABC class I antigens by muscle fibres in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, inflammatory myopathy, and other neuromuscular disorders. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):361–363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arahata K., Engel A. G. Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. I: Quantitation of subsets according to diagnosis and sites of accumulation and demonstration and counts of muscle fibers invaded by T cells. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan W. M., Behan P. O., Durward W. F., McQueen A. The inflammatory process in polymyositis: monoclonal antibody analysis of muscle and peripheral blood immunoregulatory lymphocytes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Nov;50(11):1468–1474. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.11.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belitsos P. C., Hildreth J. E., August J. T. Homotypic cell aggregation induced by anti-CD44(Pgp-1) monoclonal antibodies and related to CD44(Pgp-1) expression. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1661–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Sleckman B. P., Ratnofsky S. E., Burakoff S. J. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:579–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Hall B. M. Expression of leucocyte and lymphocyte adhesion molecules in the human kidney. Kidney Int. 1989 Dec;36(6):1078–1085. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Webster C. Isolation and characterization of human muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bou-Gharios G., Moss J., Olsen I., Partridge T. Ultrastructural localization of a lysosomal enzyme in resin-embedded lymphocytes. Histochemistry. 1988;89(1):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00496587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brod S. A., Purvee M., Benjamin D., Hafler D. A. T-T cell interactions are mediated by adhesion molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2259–2268. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson B. M., Faulkner J. A. The regeneration of skeletal muscle fibers following injury: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(3):187–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton G. R., Morgan J. E., Partridge T. A., Sloper J. C. The mdx mouse skeletal muscle myopathy: I. A histological, morphometric and biochemical investigation. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1988 Jan-Feb;14(1):53–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1988.tb00866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuomo L., Trivedi P., Wang F., Winberg G., Klein G., Masucci M. G. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded membrane antigen (LMP) increases the stimulatory capacity of EBV-negative B lymphoma lines in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte cultures. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2293–2299. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of HLA-A, B, C antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):287–292. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakas M. C. Morphologic changes in the muscles of patients with postpoliomyelitis neuromuscular symptoms. Neurology. 1988 Jan;38(1):99–104. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Staunton D. E., de Fougerolles A. R., Stacker S. A., Garcia-Aguilar J., Hibbs M. L., Springer T. A. ICAM-1 (CD54): a counter-receptor for Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3129–3139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Interaction between CD4 and class II MHC molecules mediates cell adhesion. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):256–259. doi: 10.1038/330256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dransfield I., Buckle A. M., Hogg N. Early events of the immune response mediated by leukocyte integrins. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:29–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Sanders M. E., Shaw S., Springer T. A. Purified lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 binds to CD2 and mediates T lymphocyte adhesion. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):677–692. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Singer K. H., Tuck D. T., Springer T. A. Adhesion of T lymphoblasts to epidermal keratinocytes is regulated by interferon gamma and is mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1323–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figarella-Branger D., Pellissier J. F., Bianco N., Devictor B., Toga M. Inflammatory and non-inflammatory inclusion body myositis. Characterization of the mononuclear cells and expression of the immunoreactive class I major histocompatibility complex product. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;79(5):528–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00296113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Wayner E. A., Hoffman P. A., St John T., Butcher E. C., Carter W. G. Structural homology between lymphocyte receptors for high endothelium and class III extracellular matrix receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4654–4658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower H. J., Moore S. E., Dickson G., Elsom V. L., Nayak R., Walsh F. S. Cloning and characterization of a myoblast cell surface antigen defined by 24.1D5 monoclonal antibody. Development. 1989 Apr;105(4):723–731. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.4.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Telen M. J., Hale L. P., Denning S. M. CD44--a molecule involved in leukocyte adherence and T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1989 Dec;10(12):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Engel A. G. Induction of HLA-DR expression on human myoblasts with interferon-gamma. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):503–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Engel A. G. Lysis of myotubes by alloreactive cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells. Relevance to myoblast transplantation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):370–374. doi: 10.1172/JCI114711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Rowe D., Shearer M., Novick D., Beverley P. C. Localization of interferons and interleukin 2 in polymyositis and muscular dystrophy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Feb;63(2):450–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Pouliot Y., Carpenter S. Expression of immunoreactive major histocompatibility complex products in human skeletal muscles. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jan;23(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Pouliot Y., Zubrzycka-Gaarn E., Carpenter S., Ray P. N., Worton R. G., Holland P. Dystrophin is expressed in mdx skeletal muscle fibers after normal myoblast implantation. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):27–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. J., Foster R. F., Haye K. R., Faiman L. E. Expression of a developmentally regulated antigen on the surface of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1977–1987. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. J., Foster R. F. Remodeling of the myoblast membrane accompanies development. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. D., Batchelor A. H., Lawlor P., Katz D. R. The role of CD44, CD45, CD45RO, CD46 and CD55 as potential anti-adhesion molecules involved in the binding of human tonsillar T cells to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-differentiated U-937 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):363–368. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Sanchez-Madrid F., Robbins E., Nagy J. A., Springer T. A., Burakoff S. J. The functional significance, distribution, and structure of LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3: cell surface antigens associated with CTL-target interactions. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lough J., Keay S., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. Inhibition of chicken myogenesis in vitro by partially purified interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. C., Ito H., Blau H. M., Torti F. M. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits human myogenesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2295–2301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moingeon P., Chang H. C., Sayre P. H., Clayton L. K., Alcover A., Gardner P., Reinherz E. L. The structural biology of CD2. Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:111–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moingeon P., Chang H. C., Wallner B. P., Stebbins C., Frey A. Z., Reinherz E. L. CD2-mediated adhesion facilitates T lymphocyte antigen recognition function. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):312–314. doi: 10.1038/339312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norment A. M., Salter R. D., Parham P., Engelhard V. H., Littman D. R. Cell-cell adhesion mediated by CD8 and MHC class I molecules. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):79–81. doi: 10.1038/336079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge T. A., Morgan J. E., Coulton G. R., Hoffman E. P., Kunkel L. M. Conversion of mdx myofibres from dystrophin-negative to -positive by injection of normal myoblasts. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):176–179. doi: 10.1038/337176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Nakache M., Butcher E. C. Monoclonal antibodies to human lymphocyte homing receptors define a novel class of adhesion molecules on diverse cell types. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):927–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Munro J. M., Bevilacqua M. P. Inducible cell adhesion molecule 110 (INCAM-110) is an endothelial receptor for lymphocytes. A CD11/CD18-independent adhesion mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1369–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Kihlström M. Lysosomal changes in mouse skeletal muscle during the repair of exercise injuries. Muscle Nerve. 1985 May;8(4):269–279. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert W., Kontozis L., Sticker G., Schwan H., Haraldsen G., Jerusalem F. Immunofluorescent evidence for presence of interleukin-1 in normal and diseased human skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1988 Aug;11(8):890–892. doi: 10.1002/mus.880110814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz E., Jaryszak D. L. Effects of skeletal muscle regeneration on the proliferation potential of satellite cells. Mech Ageing Dev. 1985 Apr;30(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(85)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz Z., Dgani R., Lancet M., Kessler I. Uterine sarcoma in Israel: a study of 104 cases. Gynecol Oncol. 1985 Mar;20(3):354–363. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(85)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiohara T., Nickoloff B. J., Sagawa Y., Gomi T., Nagashima M. Fixed drug eruption. Expression of epidermal keratinocyte intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Arch Dermatol. 1989 Oct;125(10):1371–1376. doi: 10.1001/archderm.125.10.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. M., Bender A. N. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated myopathy: analysis of 11 patients. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jul;24(1):79–84. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H. Interactions between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes: role of adhesion molecules. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Oct;48(4):367–374. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoskiewicz M. J., Colvin R. B., Schneeberger E. E., Russell P. S. Widespread and selective induction of major histocompatibility complex-determined antigens in vivo by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1645–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Seventer G. A., Shimizu Y., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. The LFA-1 ligand ICAM-1 provides an important costimulatory signal for T cell receptor-mediated activation of resting T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4579–4586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Ritter M. A. Surface antigen differentiation during human myogenesis in culture. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):60–64. doi: 10.1038/289060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawryk S. O., Novotny J. R., Wicks I. P., Wilkinson D., Maher D., Salvaris E., Welch K., Fecondo J., Boyd A. W. The role of the LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction in human leukocyte homing and adhesion. Immunol Rev. 1989 Apr;108:135–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Cohen S., Gatter K. C., Fells P., Shine B. Immunohistochemical analysis of the retrobulbar tissues in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Feb;75(2):222–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Cohen S., Makgoba M. W., Borysiewicz L. K. Expression of an intercellular adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, by human thyroid cells. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):185–191. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Freeman M., Borysiewicz L. K., Makgoba M. W. Functional analysis of intercellular adhesion molecule-1-expressing human thyroid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):271–275. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner C. D., Gundel R. H., Reilly P., Haynes N., Letts L. G., Rothlein R. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.1967851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuk J. A., Fletcher A. Skeletal muscle expression of class II histocompatibility antigens (HLA-DR) in polymyositis and other muscle disorders with an inflammatory infiltrate. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Apr;41(4):410–414. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.4.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]