Abstract
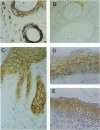
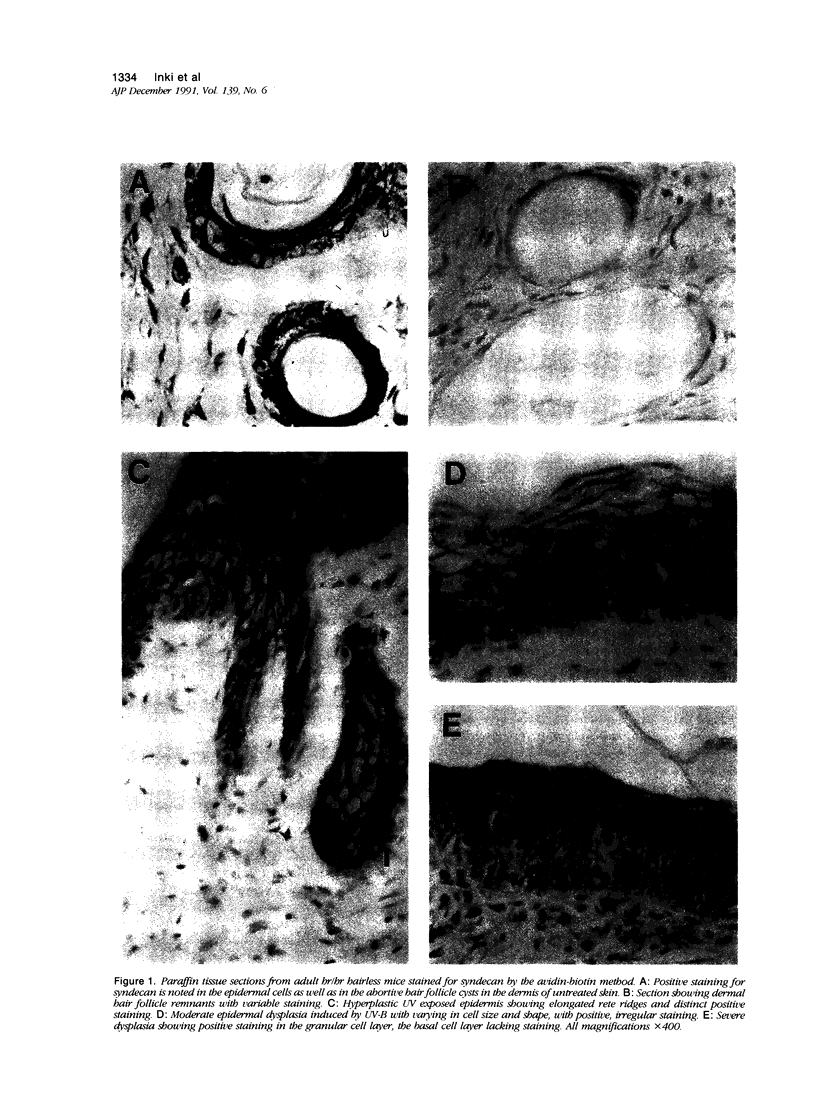
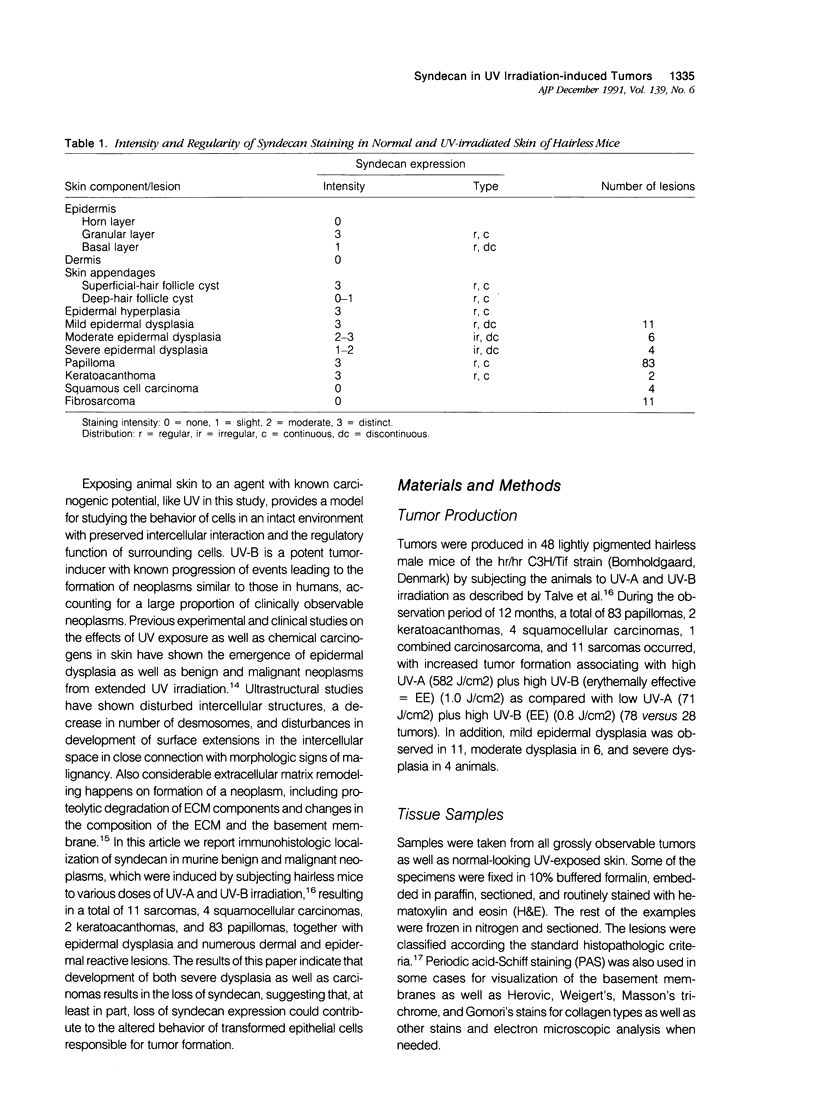
Immunoreactivity for syndecan, a cell surface proteoglycan, which binds extracellular matrix molecules and growth factors, was studied in hairless (hr/hr) mice exposed to UV-A and UV-B irradiation. Positive staining was observed at the surface of normal epidermal cells as well as in the dermal abortive hair follicle cysts characteristic to this mouse strain. Early reaction to UV-irradiation showing hyperplastic epidermis with slight cellular atypia showed also positive, although reduced, staining of epidermal cell surfaces. Specimens with severe dysplasia showed weak staining in the granular cell layer, whereas the basal cell layer was negative. In papillomas and keratoacanthomas, immunoreactivity for syndecan was observed in the benign hyperplastic epidermal cells as well as in the proliferating epidermal cells of the horn cysts. Malignant transformation of epithelium, expressed as the formation of early invasive and anaplastic squamous cell carcinomas, was uniformly associated with loss of syndecan staining. These results are consistent with the previous findings of reduced expression of syndecan associated with malignant transformation of cultured epithelial cells, but also suggest an important role for syndecan in the maintenance of normal tissue architecture and differentiation pattern of the skin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Smith J. W., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A novel vitronectin receptor integrin (alpha v beta x) is responsible for distinct adhesive properties of carcinoma cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Salmivirta M., Inki P., Mali M., Jalkanen M. Binding of human syndecan to extracellular matrix proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17837–17843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Vainio S., Laato M., Salmivirta M., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Induced expression of syndecan in healing wounds. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):585–595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Hayashi M., Jalkanen M., Firestone J. H., Trelstad R. L., Bernfield M. Immunocytochemistry of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan in mouse tissues. A light and electron microscopic study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Oct;35(10):1079–1088. doi: 10.1177/35.10.2957423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Nguyen H., Rapraeger A., Kurn N., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells: localization on the cell surface with a monoclonal antibody. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):976–984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Mouse mammary epithelial cells produce basement membrane and cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans containing distinct core proteins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):953–962. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Stephans J. C., Crawford K., Okino K., Barr P. J. Ligand-affinity cloning and structure of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan that binds basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppä S., Härkönen P., Jalkanen M. Steroid-induced epithelial-fibroblastic conversion associated with syndecan suppression in S115 mouse mammary tumor cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Jan;2(1):1–11. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mali M., Jaakkola P., Arvilommi A. M., Jalkanen M. Sequence of human syndecan indicates a novel gene family of integral membrane proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6884–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantefaber L. C., Hynes R. O. Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90902-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. C., Krufka A., Olwin B. B. Requirement of heparan sulfate for bFGF-mediated fibroblast growth and myoblast differentiation. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1705–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.1646484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan associates with the cytoskeleton at the basolateral cell surface of mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2683–2696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Giancotti F. G. Integrins and tumor cell dissemination. Cancer Cells. 1989 Dec;1(4):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Yamaguchi Y. Proteoglycans as modulators of growth factor activities. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):867–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90308-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Jalkanen M., O'Farrell S., Bernfield M. Molecular cloning of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1547–1556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solursh M., Reiter R. S., Jensen K. L., Kato M., Bernfield M. Transient expression of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan (syndecan) during limb development. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90055-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenbäck F. Life history and histopathology of ultraviolet light-induced skin tumors. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1978 Dec;(50):57–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenbäck F., Wasenius V. M., Kallioinen M. Basement membranes in experimentally induced skin tumors. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Aug;87(2):185–189. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12695326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talve L., Stenbäck F., Jansén C. T. UVA irradiation increases the incidence of epithelial tumors in UVB-irradiated hairless mice. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1990 Jun;7(3):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Jalkanen M., Vainio S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan expression correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Lehtonen E., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M., Saxén L. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions regulate the stage-specific expression of a cell surface proteoglycan, syndecan, in the developing kidney. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]