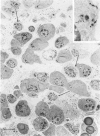
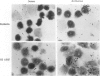
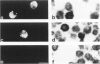
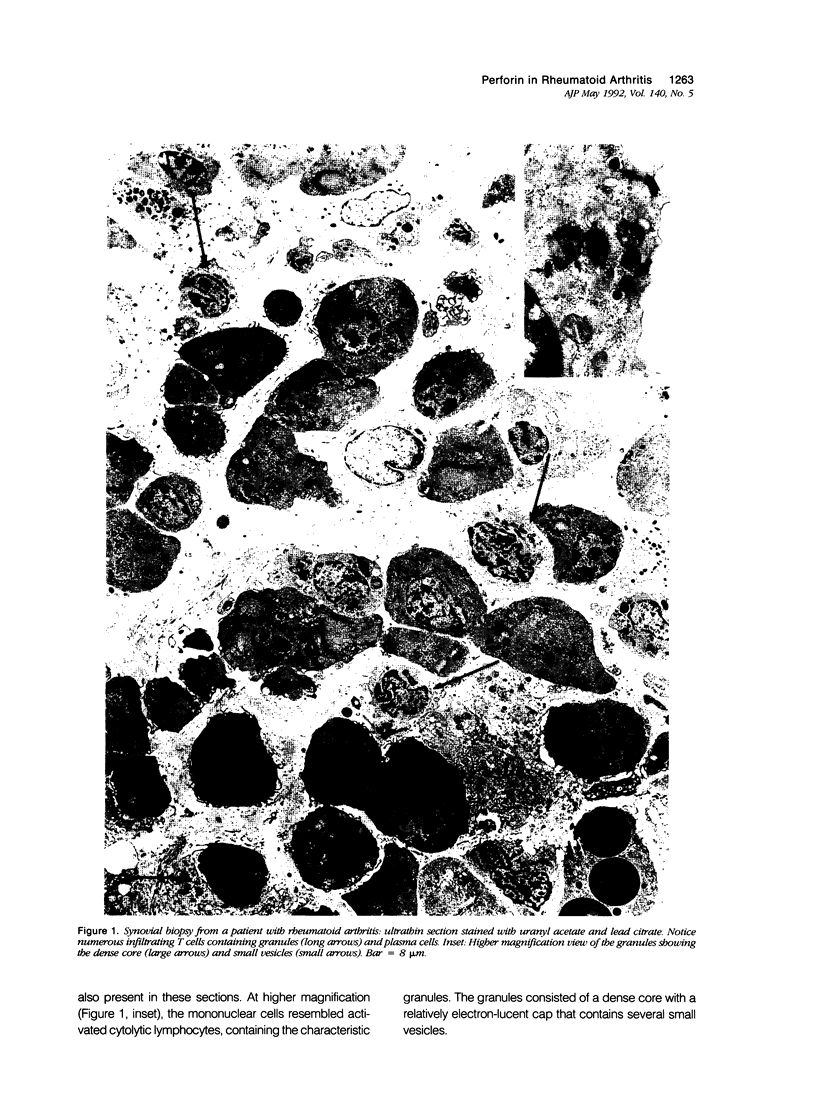
Abstract
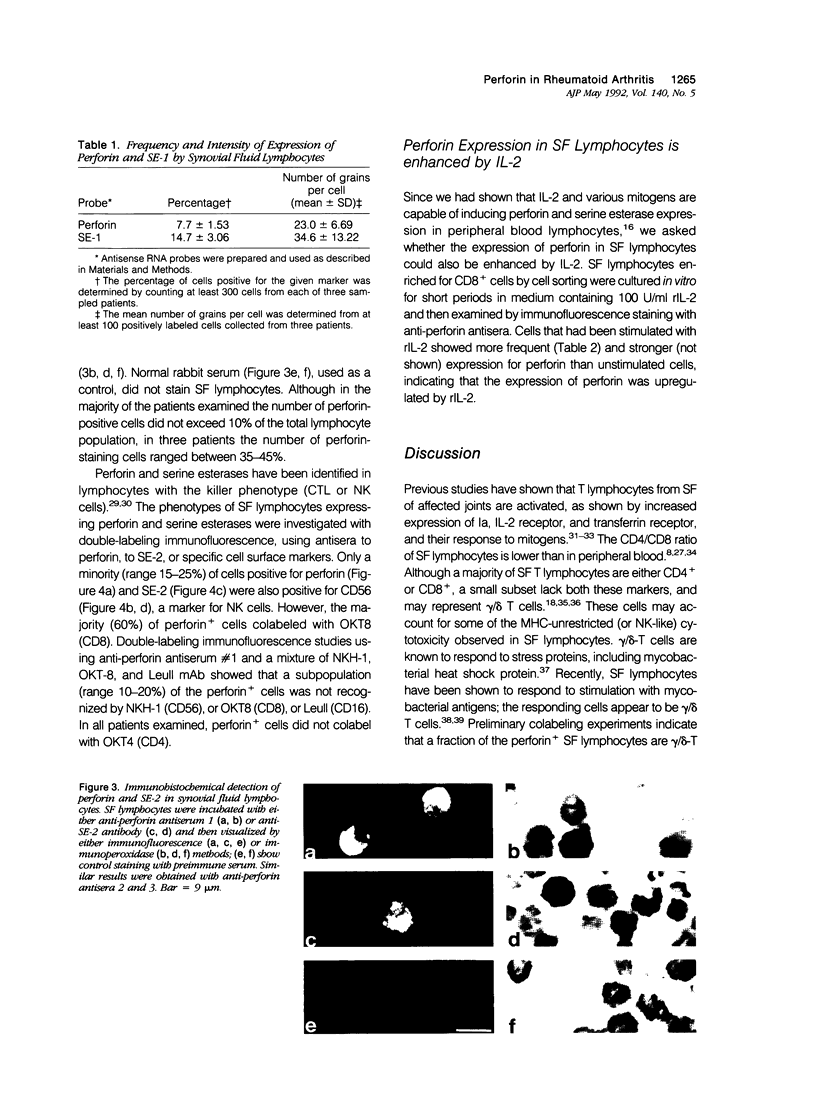
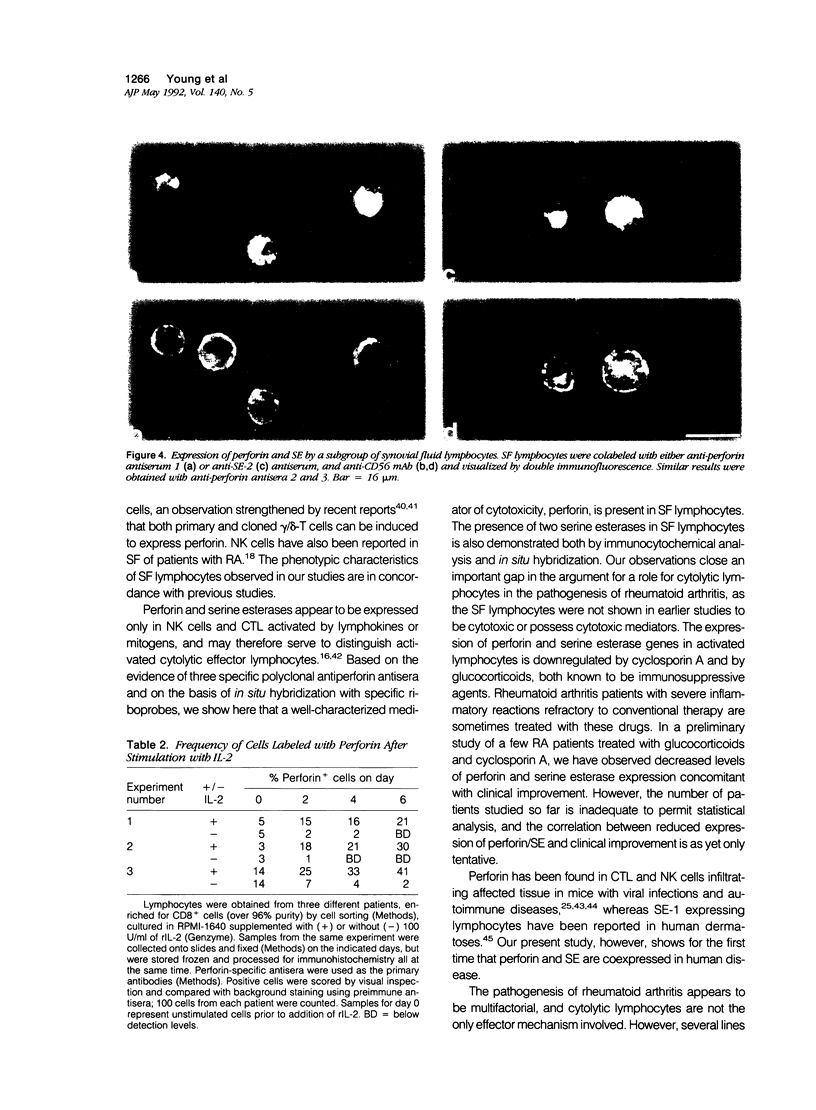
To understand the role of cytolytic lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, we investigated the expression of lymphocyte cytotoxicity mediators, perforin, and serine esterases, in lymphocytes derived from the synovial fluid of 15 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Previous work has shown that CD8+ lymphocytes that possess markers of activation appear to be present in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). By means of in situ hybridization techniques and immunohistochemical analysis, the authors show that perforin and two serine esterases (serine esterase 1/Hanukah factor/granzyme A, and serine esterase 2/granzyme B) are expressed by subpopulations of CD8+ and CD56+ lymphocytes obtained from synovial fluid. The presence of these cytotoxic mediators suggests a possible mechanism for tissue damage, and provides evidence implicating cytolytic lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of RA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleackley R. C., Lobe C. G., Duggan B., Ehrman N., Fregeau C., Meier M., Letellier M., Havele C., Shaw J., Paetkau V. The isolation and characterization of a family of serine protease genes expressed in activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:5–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Yu D. T., Irani A. M., Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J. Ia+ T cells in synovial fluid and tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Nov;24(11):1370–1376. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maria A., Malnati M., Moretta A., Pende D., Bottino C., Casorati G., Cottafava F., Melioli G., Mingari M. C., Migone N. CD3+4-8-WT31-(T cell receptor gamma+) cells and other unusual phenotypes are frequently detected among spontaneously interleukin 2-responsive T lymphocytes present in the joint fluid in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. A clonal analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1815–1819. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke O., Panayi G. S., Janossy G., Poulter L. W., Tidman N. Analysis of T cell subsets in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis by means of monoclonal antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42(4):357–361. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Fong S., Sabharwal N., Carstens S. A., Kung P. C., Vaughan J. H. Synovial fluid lymphocytes differ from peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):351–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Bailey L. C., Bacon P. A. In vitro responses to a 65-kilodalton mycobacterial protein by synovial T cells from inflammatory arthritis patients. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2494–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Hershberger R. J., Shows T. B., Weissman I. L. Cloning and chromosomal assignment of a human cDNA encoding a T cell- and natural killer cell-specific trypsin-like serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Miyamoto T., Nishioka K., Uchida S. T cytotoxic and helper cells are markedly increased, and T suppressor and inducer cells are markedly decreased, in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):737–743. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Zvaifler N. J. Characterization of the natural killer-like lymphocytes in rheumatoid synovial fluid. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1483–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A. In situ hybridization for interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor mRNA in T cells activated in the presence or absence of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1649–1658. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercend T., Griffin J. D., Bensussan A., Schmidt R. E., Edson M. A., Brennan A., Murray C., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Ritz J. Generation of monoclonal antibodies to a human natural killer clone. Characterization of two natural killer-associated antigens, NKH1A and NKH2, expressed on subsets of large granular lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):932–943. doi: 10.1172/JCI111794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovdenes J., Gaudernack G., Kvien T. K., Egeland T. Expression of activation markers on CD4+ and CD8+ cells from synovial fluid, synovial tissue, and peripheral blood of patients with inflammatory arthritides. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(6):631–639. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Granzymes, a family of serine proteases released from granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes upon T cell receptor stimulation. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:53–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Granzymes: a family of serine proteases in granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;140:33–47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-73911-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley G., Pitzalis C., Panayi G. S. Immunogenetic and cellular immune mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis: relevance to new therapeutic strategies. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Feb;29(1):58–64. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi H., Liu C. C., Zheng L. M., Joag S. V., Bayne N. K., Holoshitz J., Young J. D. Expression of perforin and serine esterases by human gamma/delta T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):499–502. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y., Bergroth V., Nykänen P. Lymphocyte activation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid in vivo. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Nov;22(5):503–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. A., Shore A. A review of current concepts on the pathogenesis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1990 Mar;21:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Rafii S., Granelli-Piperno A., Trapani J. A., Young J. D. Perforin and serine esterase gene expression in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2105–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K. What do anti-collagen antibodies mean? Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Jan;49(1):62–65. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The molecular basis of target cell killing by human lymphocytes and of killer cell self-protection. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:87–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C., Kägi D., Aebischer T., Odermatt B., Held W., Podack E. R., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Detection of perforin and granzyme A mRNA in infiltrating cells during infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1253–1259. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata M., Smyth M. J., Norihisa Y., Kawasaki A., Shinkai Y., Okumura K., Yagita H. Constitutive expression of pore-forming protein in peripheral blood gamma/delta T cells: implication for their cytotoxic role in vivo. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1877–1880. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson E., Biberfeld G. T lymphocyte subpopulations defined by monoclonal antibodies in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic disease. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Nov;9(2):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormandy C. J., Clarke C. L., Sutherland R. L. Solubilization and characterization of a lactogenic receptor from human placental chorion membranes. J Cell Biochem. 1990 May;43(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240430102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini P. M., Young J. D. The primary structure of the lymphocyte pore-forming protein perforin: partial amino acid sequencing and determination of isoelectric point. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):740–745. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Murphy J., Panayi G. Abnormal distribution of the helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer T-lymphocyte subsets in the rheumatoid joint. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Nov;45(2):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Redelman D., Zvaifler N. J., Naides S. Studies of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. I. Evidence for activated natural killer- (NK) like cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1758–1763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapani J. A., Klein J. L., White P. C., Dupont B. Molecular cloning of an inducible serine esterase gene from human cytotoxic lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Jongeneel C. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated cytolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2641–2646. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veys E. M., Hermanns P., Verbruggen G., Schindler J., Goldstein G. Evaluation of T cell subsets with monoclonal antibodies in synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1982 Nov-Dec;9(6):821–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L. Rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(4):613–618. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(90)90020-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Mueller C., Warnke R. A., Weissman I. L. In situ localization of HuHF serine protease mRNA and cytotoxic cell-associated antigens in human dermatoses. A novel method for the detection of cytotoxic cells in human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):218–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Liu C. C., Persechini P. M., Cohn Z. A. Perforin-dependent and -independent pathways of cytotoxicity mediated by lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:161–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Joag S. V., Zheng L. M., Lee C. P., Lee Y. S., Young J. D. Perforin-mediated myocardial damage in acute myocarditis. Lancet. 1990 Oct 27;336(8722):1019–1021. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Klavinskis L. S., Oldstone M. B., Young J. D. In vivo expression of perforin by CD8+ lymphocytes during an acute viral infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2159–2171. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Liu C. C., Joag S., Rafii S., Young J. D. How lymphocytes kill. Annu Rev Med. 1990;41:45–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.41.020190.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Peterson L. B., Wicker L. S., Persechini P. M., Young J. D. In vivo expression of perforin by CD8+ lymphocytes in autoimmune disease. Studies on spontaneous and adoptively transferred diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3994–3999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff M. Rheumatoid arthritis--its present and future. J Rheumatol. 1990 Feb;17(2):127–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]