Abstract
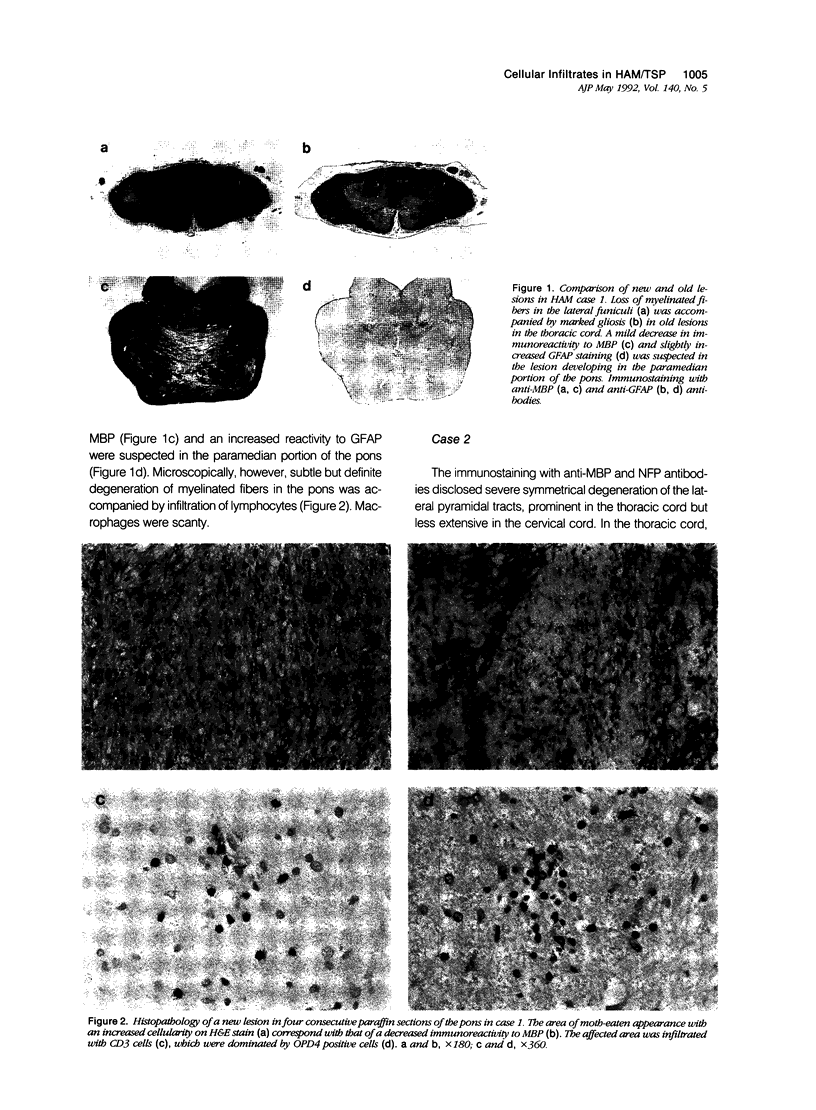
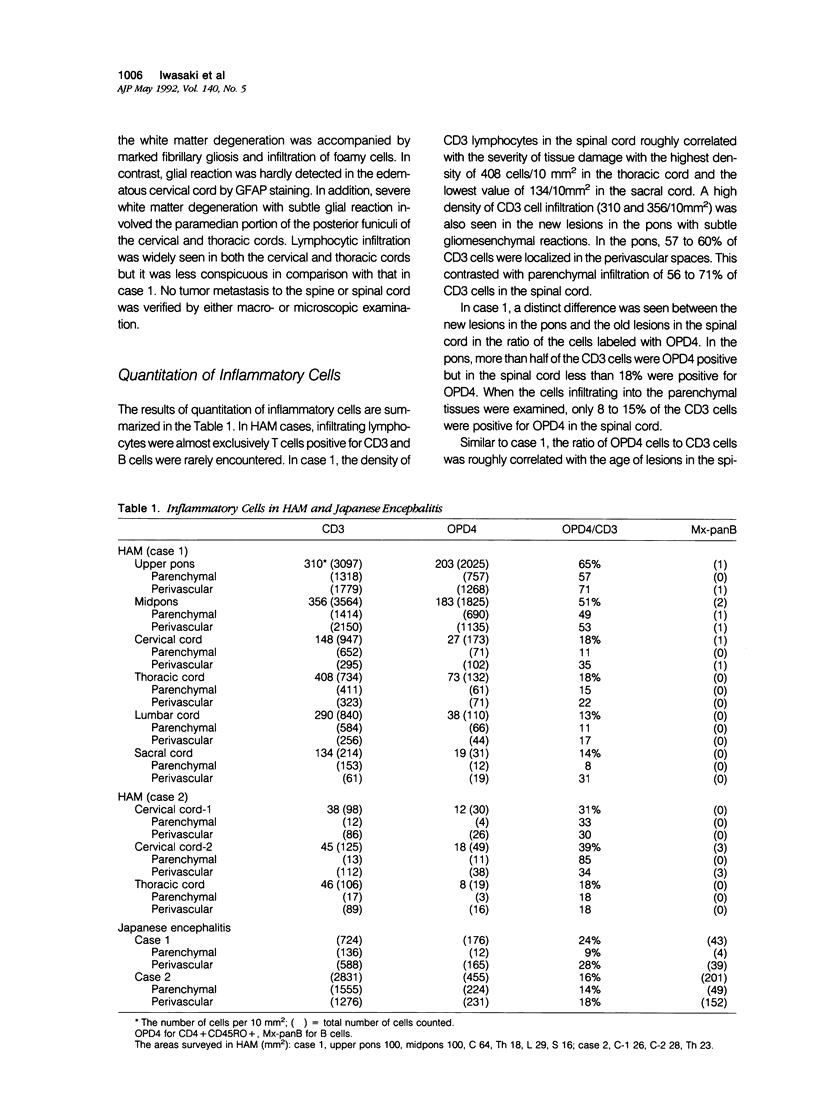
Cellular infiltrates in new and old lesions in two cases of human T-cell leukemia virus associated myelopathy (HAM) were analyzed with anti-CD3 antibody and OPD4 antibody recognizing CD4 + CD45RO + T lymphocytes. A subset of CD4 lymphocytes with helper/inducer function and labeled with OPD4 constitutes up to 65% of CD3 cells in new lesions in the pons and the cervical cord. In contrast, nonhelper cells and macrophages were dominant in long-standing spinal cord lesions of these HAM cases and inflammatory lesions in two cases of Japanese encephalitis. Thus, unlike in viral infections, the central nervous system (CNS) tissue damage associated with human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-1) infection appeared to be heralded by the infiltration of helper/inducer T cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akizuki S., Nakazato O., Higuchi Y., Tanabe K., Setoguchi M., Yoshida S., Miyazaki Y., Yamamoto S., Sudou S., Sannomiya K. Necropsy findings in HTLV-I associated myelopathy. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):156–157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91984-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chofflon M., Weiner H. L., Morimoto C., Hafler D. A. Loss of functional suppression is linked to decreases in circulating suppressor inducer (CD4+ 2H4+) T cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1988 Aug;24(2):185–191. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank J. K., Rudge P., Dalgleish A. G., Newton M., McLean B. N., Barnard R. O., Kendall B. E., Miller D. H. Tropical spastic paraparesis and human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 in the United Kingdom. Brain. 1989 Aug;112(Pt 4):1057–1090. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.4.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Uemura Y., Fujishita M., Kitagawa T., Yamashita M., Imamura J., Ohtsuki Y., Taguchi H., Miyoshi I. Isolation of HTLV-I from cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with myelopathy. Lancet. 1986 Aug 16;2(8503):397–398. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii Y., Takami T., Yuasa H., Takei T., Kikuchi K. Two distinct antigen systems in human B lymphocytes: identification of cell surface and intracellular antigens using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):183–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Kira J., Fujii N., Goto I., Yamamoto N. Increases in helper inducer T cells and activated T cells in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 1989 Aug;26(2):257–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y. Pathology of chronic myelopathy associated with HTLV-I infection (HAM/TSP). J Neurol Sci. 1990 Apr;96(1):103–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90060-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Zhao J. X., Yamamoto T., Konno H. Immunohistochemical demonstration of viral antigens in Japanese encephalitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;70(1):79–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00689518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Raine C. S., Mingioli E. S., McFarlin D. E. Isolation of an HTLV-1-like retrovirus from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):540–543. doi: 10.1038/331540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kira J., Minato S., Itoyama Y., Goto I., Kato M., Hasuo K. Leukoencephalopathy in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: MRI and EEG data. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Nov;87(2-3):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda Y., Fujiyama F., Nagumo F. Analysis of factors of relevance to rapid clinical progression in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Sep;105(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90119-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Cordell J., Brown M., Pallesen G., Ralfkiaer E., Rothbard J., Crumpton M., Gatter K. C. Detection of T cells in paraffin wax embedded tissue using antibodies against a peptide sequence from the CD3 antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Nov;42(11):1194–1200. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.11.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Traugott U., Scheinberg L. C., Raine C. S. Tropical spastic paraparesis: a model of virus-induced, cytotoxic T-cell-mediated demyelination? Ann Neurol. 1989 Oct;26(4):523–530. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M., Cruickshank K., Miller D., Dalgleish A., Rudge P., Clayden S., Moseley I. Antibody to human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 in West-Indian-born UK residents with spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1987 Feb 21;1(8530):415–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Janssen R., Kubota H., Nishitani H., Igata A., Nagataki S., Mori M., Goto I., Shimabukuro H., Khabbaz R. Nationwide survey of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy in Japan: association with blood transfusion. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):50–56. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Usuku K., Izumo S., Ijichi N., Amitani H., Igata A., Matsumoto M., Tara M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986 May 3;1(8488):1031–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccardo P., Ceroni M., Rodgers-Johnson P., Mora C., Asher D. M., Char G., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Pathological and immunological observations on tropical spastic paraparesis in patients from Jamaica. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S156–S160. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Lai R., Visser L. Monoclonal antibody OPD4 is reactive with CD45RO, but differs from UCHL1 by the absence of monocyte reactivity. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):725–729. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. H., Edwards A. J., Cruickshank J. K., Rudge P., Dalgleish A. G. In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5682–5687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5682-5687.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose L. M., Ginsberg A. H., Rothstein T. L., Ledbetter J. A., Clark E. A. Fluctuations of CD4+ T-cell subsets in remitting-relapsing multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1988 Aug;24(2):192–199. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Hafler D. A., Castro E. E., Morimoto C., Weiner H. L. The 2H4 (CD45R) antigen is selectively decreased in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2210–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Franz H., Yamamoto T., Iwasaki Y., Konno H. Identification of the normal microglial population in human and rodent nervous tissue using lectin-histochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1988 May-Jun;14(3):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1988.tb00883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Reinherz E. L., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis. Distribution of T cells, T cell subsets and Ia-positive macrophages in lesions of different ages. J Neuroimmunol. 1983 Jun;4(3):201–221. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(83)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernant J. C., Roman G. C. Les paraplégies associées au virus HTLV-I. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1989;145(4):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino T., Mukuzono H., Aoki H., Takahashi K., Takeuchi T., Kubonishi I., Ohtsuki Y., Motoi M., Akagi T. A novel monoclonal antibody (OPD4) recognizing a helper/inducer T cell subset. Its application to paraffin-embedded tissues. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1339–1346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]