Abstract
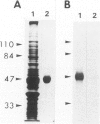
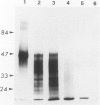
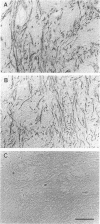
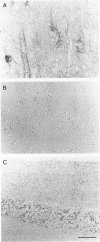
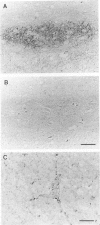
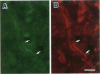
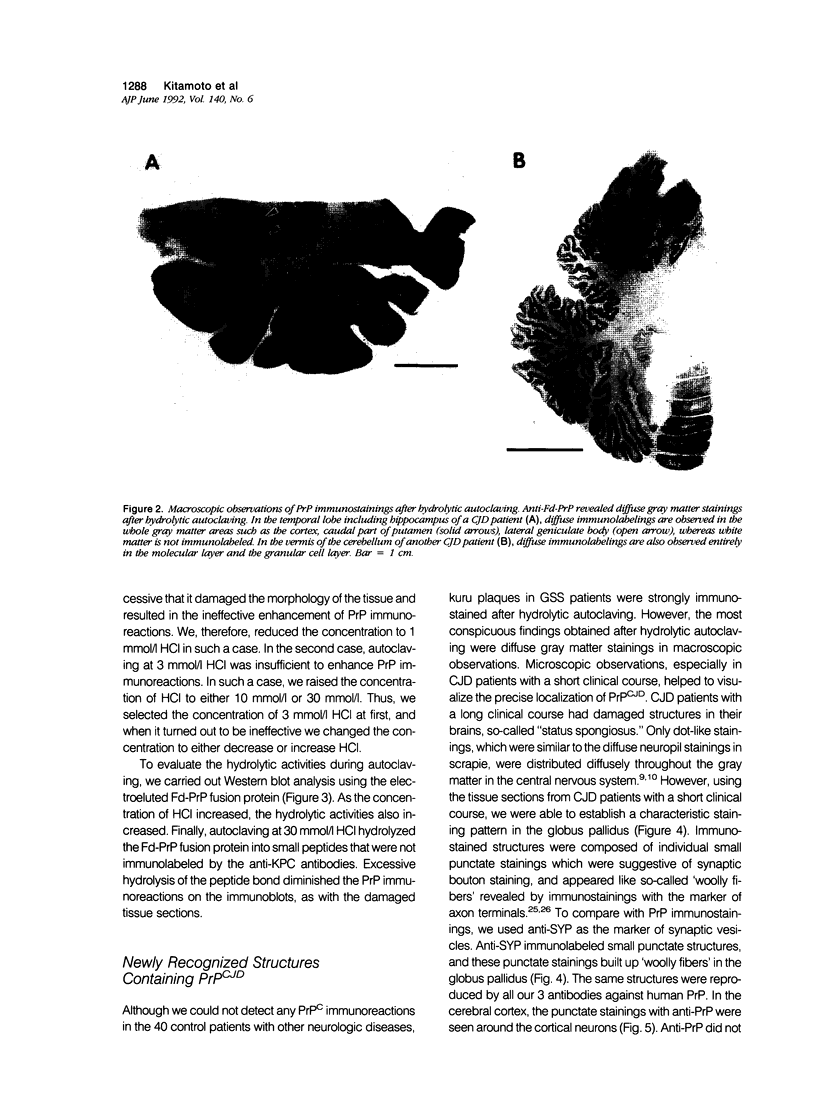
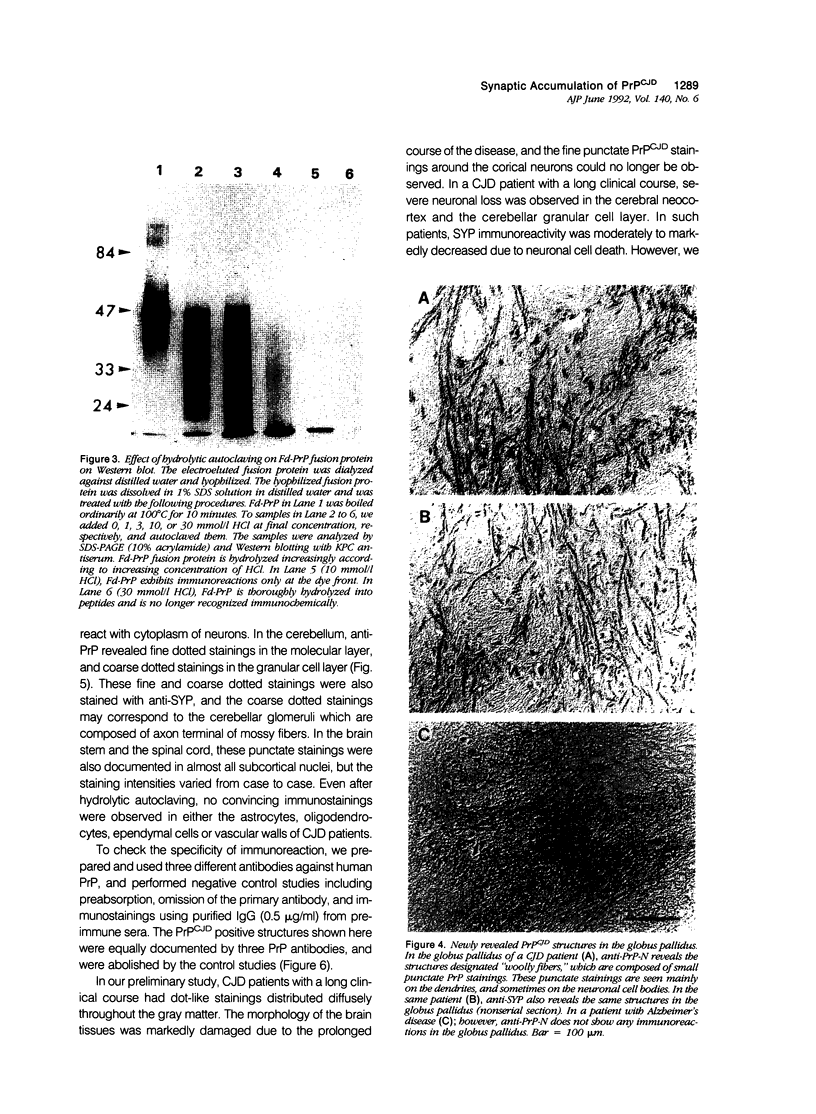
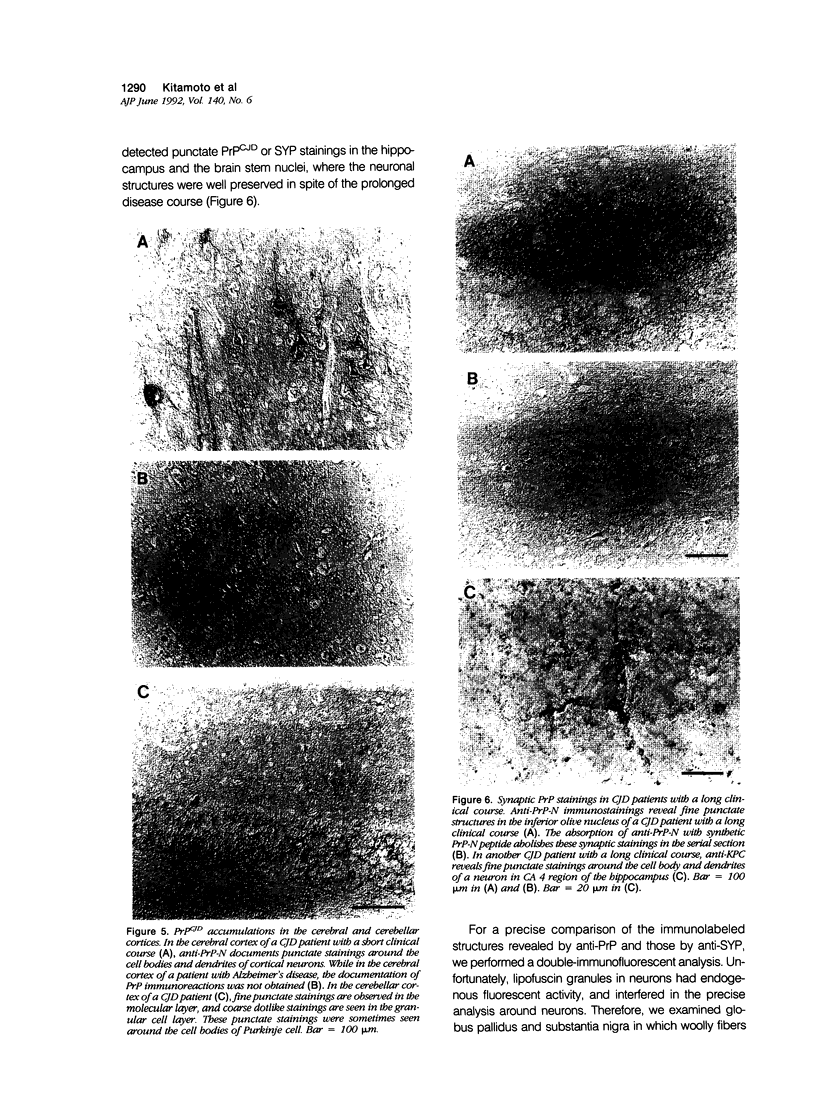
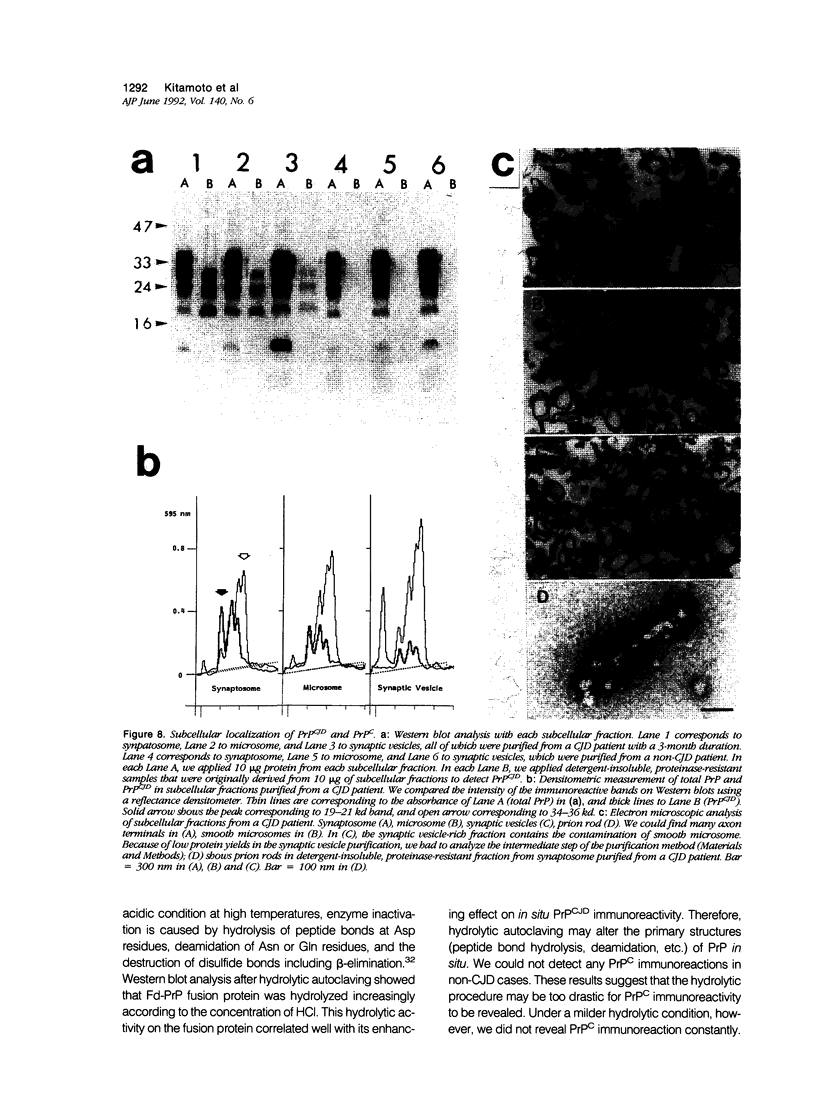
A new method, which enabled the first immunohistochemical documentation of abnormal prion protein (PrP) in all patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), was established. This method designated as "hydrolytic autoclaving" revealed punctate PrPCJD stainings around the neuronal cell bodies and dendrites in CJD brains. These punctate stainings were almost identical with that of synaptophysin, suggesting PrPCJD accumulations in the synaptic structures. Subcellular fractionation revealed that prion protein in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (PrPCJD) was most concentrated in the synaptosomal fraction. In CJD patients with a long clinical course, synaptophysin immunoreactivity decreased, and synaptic PrPCJD accumulated with a wider distribution. These results suggest that synaptic PrPCJD accumulations might be responsible for the neuronal dysfunction and degeneration in CJD.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahern T. J., Klibanov A. M. The mechanisms of irreversible enzyme inactivation at 100C. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1280–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.4001942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Oesch B., Scott M., Westaway D., Wälchli M., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B., Weissmann C. Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90662-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Kingsbury D. T., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Prusiner S. B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins in human brains. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Coker-Vann M., Pomeroy K., Franko M., Asher D. M., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease by Western blot identification of marker protein in human brain tissue. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 27;314(9):547–551. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602273140904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. E., McBride P. A., Farquhar C. F. Precise targeting of the pathology of the sialoglycoprotein, PrP, and vacuolar degeneration in mouse scrapie. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 17;102(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doh-ura K., Tateishi J., Sasaki H., Kitamoto T., Sakaki Y. Pro----leu change at position 102 of prion protein is the most common but not the sole mutation related to Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):974–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi-Yi R., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J. Immunoreactivity of cerebral amyloidosis is enhanced by protein denaturation treatments. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):260–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00308810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H., Dickinson A. G. Targeting of scrapie lesions and spread of agent via the retino-tectal projection. Brain Res. 1985 Oct 28;346(1):32–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H. Neuronal spread of scrapie agent and targeting of lesions within the retino-tectal pathway. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):149–150. doi: 10.1038/295149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S., Hirano A. Synaptophysin expression in the striatum in Huntington's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(1):88–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00294227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber S. N., Nauta W. J. Ramifications of the globus pallidus in the rat as indicated by patterns of immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience. 1983 Jun;9(2):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Tonna-DeMasi M., Fersko R., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Mouse polyclonal and monoclonal antibody to scrapie-associated fibril proteins. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3688–3693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3688-3693.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Hikita K., Tashima T., Tateishi J., Sato Y. Scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) purification method yields amyloid proteins from systemic and cerebral amyloidosis. Biosci Rep. 1986 May;6(5):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF01116137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Mohri S., Tateishi J. Organ distribution of proteinase-resistant prion protein in humans and mice with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3371–3379. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Muramoto T., Hilbich C., Beyreuther K., Tateishi J. N-terminal sequence of prion protein is also integrated into kuru plaques in patients with Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Brain Res. 1991 Apr 5;545(1-2):319–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91306-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Muramoto T., Mohri S., Doh-Ura K., Tateishi J. Abnormal isoform of prion protein accumulates in follicular dendritic cells in mice with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6292–6295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6292-6295.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J. Immunohistochemical confirmation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with a long clinical course with amyloid plaque core antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jun;131(3):435–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Yi R., Mohri S., Tateishi J. Cerebral amyloid in mice with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is influenced by the strain of the infectious agent. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 29;508(1):165–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91132-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberski P. P., Yanagihara R., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Spread of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus along visual pathways after intraocular inoculation. Arch Virol. 1990;111(1-2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01310512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccardo P., Safar J., Ceroni M., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Immunohistochemical localization of prion protein in spongiform encephalopathies and normal brain tissue. Neurology. 1990 Mar;40(3 Pt 1):518–522. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.3_part_1.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safar J., Ceroni M., Piccardo P., Liberski P. P., Miyazaki M., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Subcellular distribution and physicochemical properties of scrapie-associated precursor protein and relationship with scrapie agent. Neurology. 1990 Mar;40(3 Pt 1):503–508. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.3_part_1.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serban D., Taraboulos A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Rapid detection of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie prion proteins. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):110–117. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin R. W., Iwaki T., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J. Hydrated autoclave pretreatment enhances tau immunoreactivity in formalin-fixed normal and Alzheimer's disease brain tissues. Lab Invest. 1991 May;64(5):693–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion proteins accumulate in the cytoplasm of persistently infected cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2117–2132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]