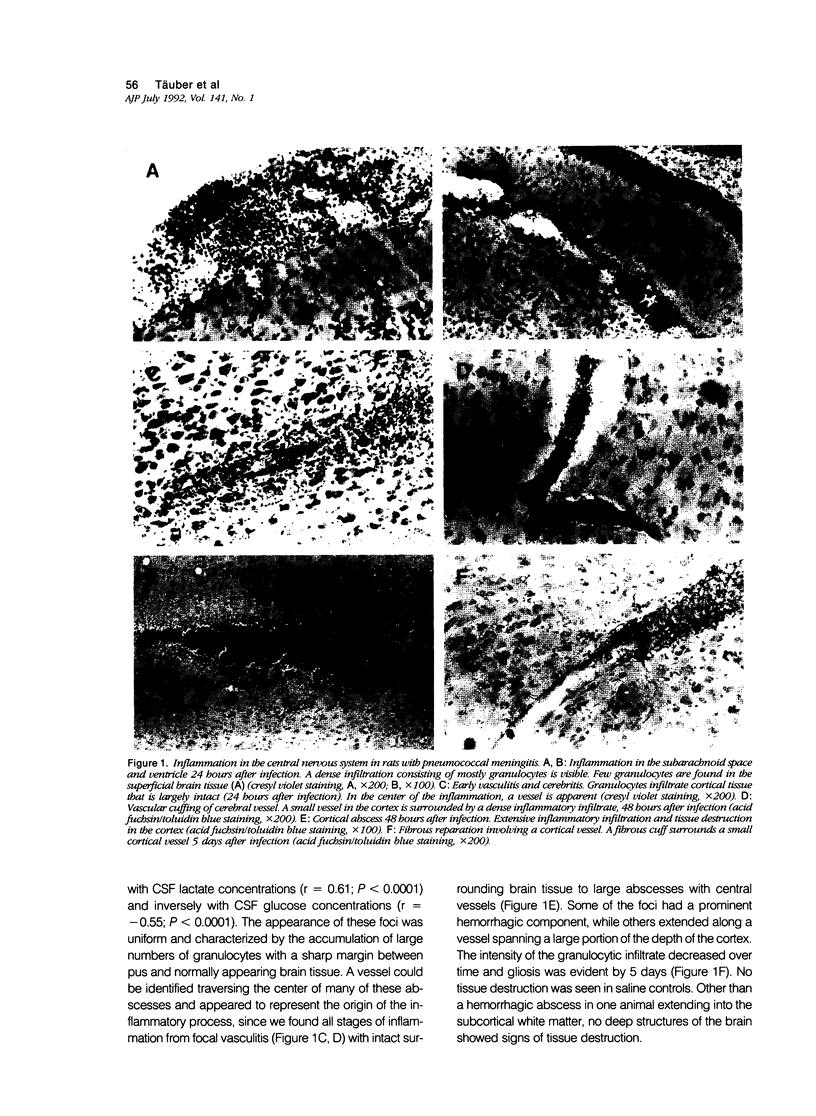
Abstract
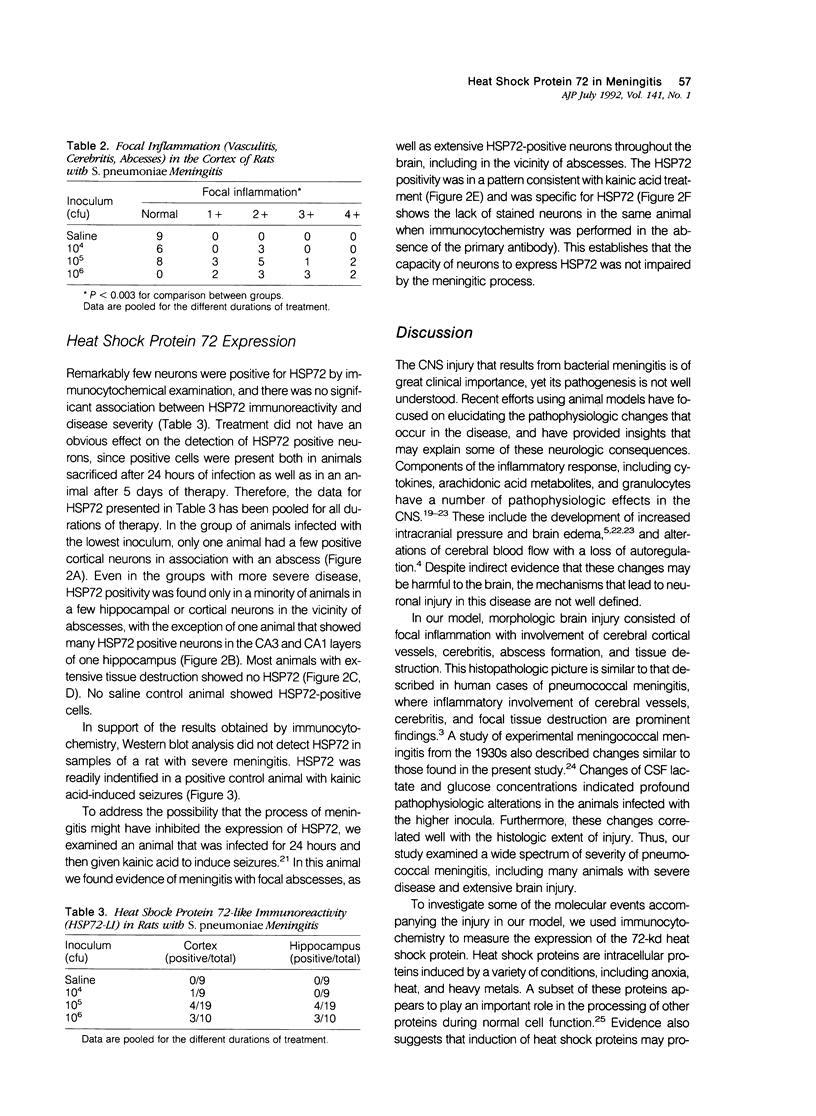
We examined whether experimental pneumococcal meningitis induced the 72-kd heat shock protein (HSP72), a sensitive marker of neuronal stress in other models of central nervous system (CNS) injury. Brain injury was characterized by vasculitis, cerebritis, and abscess formation in the cortex of infected animals. The extent of these changes correlated with the size of the inoculum (P less than 0.003) and with pathophysiologic parameters of disease severity, i.e., cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lactate (r = 0.61, P less than 0.0001) and CSF glucose concentrations (r = -0.55, P less than 0.0001). Despite the presence of numerous cortical regions having morphologic evidence of injury, HSP72 was not detected in most animals. When present, only rare neurons were HSP72 positive. Western blot analysis of brain samples confirmed the paucity of HSP72 induction. The lack of neuronal HSP72 expression in this model suggests that at least some of the events leading to neuronal injury in meningitis are unique, when compared with CNS diseases associated with HSP72 induction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird D. R., Whittle H. C., Greenwood B. M. Mortality from pneumococcal meningitis. Lancet. 1976 Dec 18;2(7999):1344–1346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91985-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbe M. F., Tytell M., Gower D. J., Welch W. J. Hyperthermia protects against light damage in the rat retina. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1817–1820. doi: 10.1126/science.3175623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V., Paulson O. B., Rasmussen N. Pneumococcal meningitis. Late neurologic sequelae and features of prognostic impact. Arch Neurol. 1984 Oct;41(10):1045–1049. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050210043012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. R., Rush S., Ivy G. O. Induction of a heat shock gene at the site of tissue injury in the rat brain. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1559–1564. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. S., Palmer E., Welch W. J., Sheppard D. The response of guinea pig airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages to environmental stress. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Aug;5(2):133–143. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer B. E., Nishimura R. N., Brown I. R. Synthesis of the major inducible heat shock protein in rat hippocampus after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Exp Neurol. 1989 Apr;104(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferriero D. M., Soberano H. Q., Simon R. P., Sharp F. R. Hypoxia-ischemia induces heat shock protein-like (HSP72) immunoreactivity in neonatal rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Apr 1;53(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90136-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez M. F., Shiraishi K., Hisanaga K., Sagar S. M., Mandabach M., Sharp F. R. Heat shock proteins as markers of neural injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Jul;6(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges G. R., Perkins R. L. Acute bacterial meningitis: an analysis of factors influencing prognosis. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Nov-Dec;270(3):427–440. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197511000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein D. H., Chan P. H., Miles M. F. The stress protein response in cultured neurons: characterization and evidence for a protective role in excitotoxicity. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):1053–1060. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein D. H., Simon R. P., Sharp F. R. The pattern of 72-kDa heat shock protein-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain following flurothyl-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 29;531(1-2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90771-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamin J. B., Volpe J. J. Bacterial meningitis in infancy: effects on intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow velocity. Neurology. 1984 Apr;34(4):500–504. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.4.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Characterization of the thermotolerant cell. I. Effects on protein synthesis activity and the regulation of heat-shock protein 70 expression. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1105–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa M. M., Ramilo O., Olsen K. D., Franklin P. S., Hansen E. J., Beutler B., McCracken G. H., Jr Tumor necrosis factor in mediating experimental Haemophilus influenzae type B meningitis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1253–1259. doi: 10.1172/JCI114292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson O. B., Brodersen P., Hansen E. L., Kristensen H. S. Regional cerebral blood flow, cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen, and cerebrospinal fluid acid-base variables in patients with acute meningitis and with acute encephalitis. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Sep;196(3):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb00994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for NOVEMBER 4, 1932. Public Health Rep. 1932 Nov 4;47(45):2137–2158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarello V. J., Long W. J., Scheld W. M. Morphologic alterations of the blood-brain barrier with experimental meningitis in the rat. Temporal sequence and role of encapsulation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1084–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI112407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Heat shock is lethal to fibroblasts microinjected with antibodies against hsp70. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):433–436. doi: 10.1126/science.3175665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Sande S., Cioffe C., Wolpe S., Sherry B., Cerami A., Tuomanen E. The role of cytokines in the generation of inflammation and tissue damage in experimental gram-positive meningitis. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):439–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Dacey R. G., Winn H. R., Welsh J. E., Jane J. A., Sande M. A. Cerebrospinal fluid outflow resistance in rabbits with experimental meningitis. Alterations with penicillin and methylprednisolone. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):243–253. doi: 10.1172/JCI109850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Ward J. I., Band J. D., Hightower A., Fraser D. W., Broome C. V. Bacterial meningitis in the United States, 1978 through 1981. The National Bacterial Meningitis Surveillance Study. JAMA. 1985 Mar 22;253(12):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. H., Webb W. W., Pate J. E., Doyne E. O. Psychological sequelae to bacterial meningitis: two controlled studies. Pediatrics. 1972 Feb;49(2):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. P., Cho H., Gwinn R., Lowenstein D. H. The temporal profile of 72-kDa heat-shock protein expression following global ischemia. J Neurosci. 1991 Mar;11(3):881–889. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-03-00881.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E. I., Saukkonen K., Sande S., Cioffe C., Wright S. D. Reduction of inflammation, tissue damage, and mortality in bacterial meningitis in rabbits treated with monoclonal antibodies against adhesion-promoting receptors of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):959–969. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tureen J. H., Dworkin R. J., Kennedy S. L., Sachdeva M., Sande M. A. Loss of cerebrovascular autoregulation in experimental meningitis in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):577–581. doi: 10.1172/JCI114475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tureen J. H., Täuber M. G., Sande M. A. Effect of indomethacin on the pathophysiology of experimental meningitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):647–649. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Borschberg U., Sande M. A. Influence of granulocytes on brain edema, intracranial pressure, and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of lactate and protein in experimental meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):456–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Burroughs M., Niemöller U. M., Kuster H., Borschberg U., Tuomanen E. Differences of pathophysiology in experimental meningitis caused by three strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):806–811. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Khayam-Bashi H., Sande M. A. Effects of ampicillin and corticosteroids on brain water content, cerebrospinal fluid pressure, and cerebrospinal fluid lactate levels in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):528–534. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Shibl A. M., Hackbarth C. J., Larrick J. W., Sande M. A. Antibiotic therapy, endotoxin concentration in cerebrospinal fluid, and brain edema in experimental Escherichia coli meningitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):456–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vass K., Berger M. L., Nowak T. S., Jr, Welch W. J., Lassmann H. Induction of stress protein HSP70 in nerve cells after status epilepticus in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90695-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]