Abstract
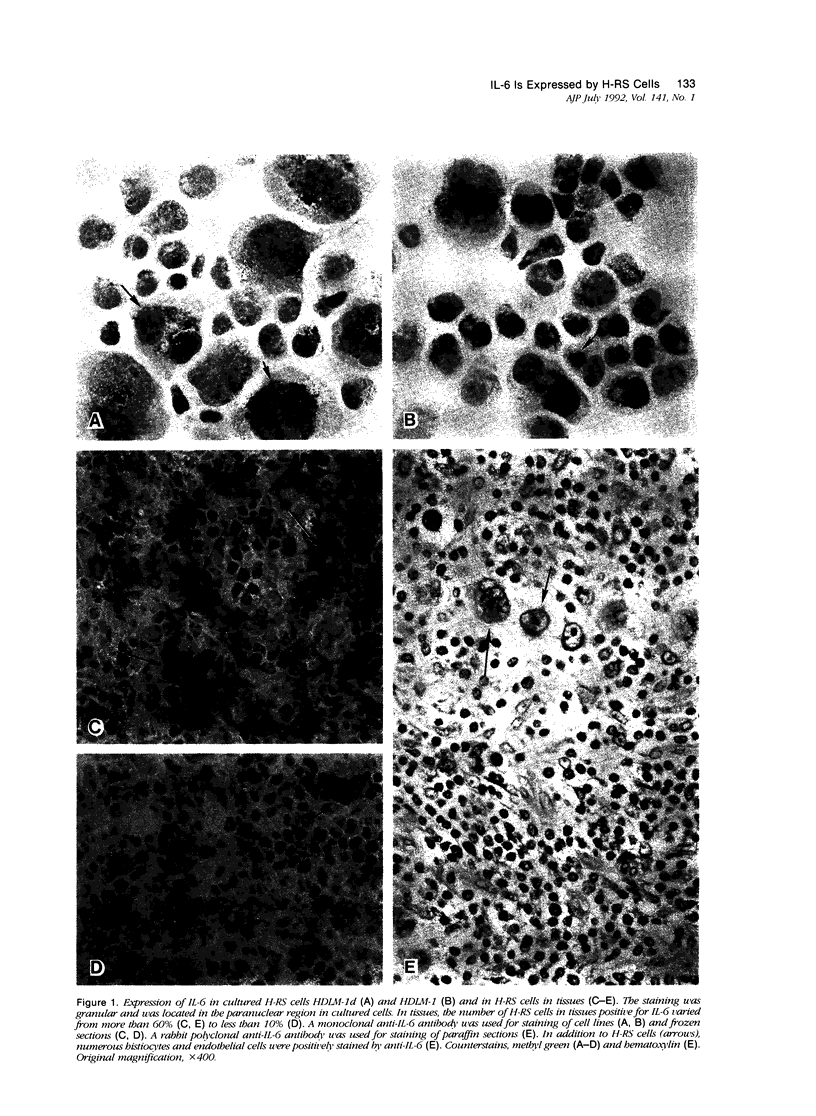
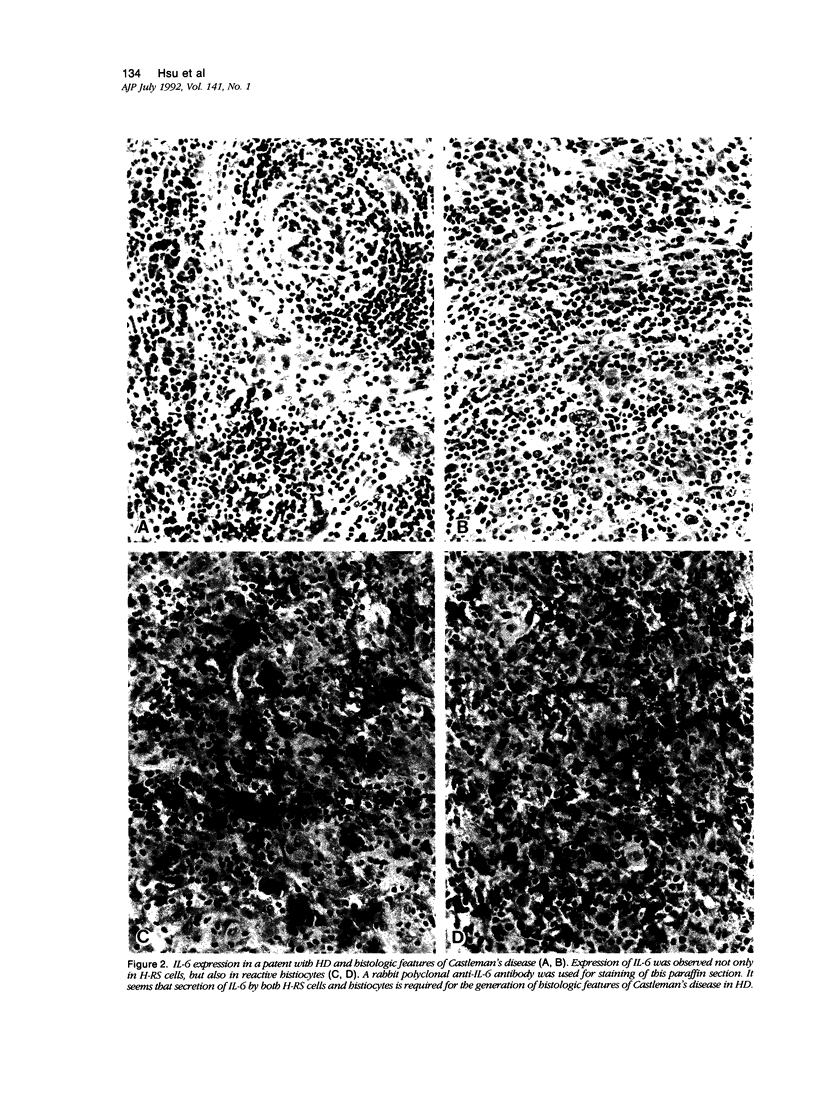
Hodgkin's disease (HD) is a neoplastic disease that is characterized by unbalanced and/or unregulated cytokine production. Information accumulated in our own and other laboratories indicates that the cytokines interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-5, IL-9, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), macrophage CSF (M-CSF), and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) are secreted by Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) cells. These and perhaps additional cytokines are likely to be responsible for the unique histopathologic and clinical alterations seen in patients with HD. In this study, we confirmed that IL-6 is produced by cultured H-RS cells as well as by H-RS cells in tissues. By using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we found that approximately 2 to 10 ng/ml of IL-6 was secreted by cultured H-RS cells (10(6) cells/ml). In tissues, we were able to immunolocalize IL-6 in the cytoplasm in 10 to 30% of H-RS cells by using rabbit polyclonal and mouse monoclonal anti-IL-6 antibodies. There was no correlation among the IL-6 staining intensity, number of H-RS cells stained, and the degree of plasma cell infiltration. However, in 3 of 17 cases studied, a large number (60%) of H-RS cells were positive for IL-6, and in these patients, abundant plasma cells were present. In one patient, the involved lymph node also showed histologic features similar to those of Castleman's disease. In this patient, we noted abundant IL-6 expression not only in H-RS cells, but also in most reactive histiocytes. The cultured H-RS cells did not express functional receptors for IL-6, and exogenously added IL-6 did not induce proliferation of these cells. We also conducted studies with specific anti-IL-4 antibodies, which did not show IL-4 production by H-RS cells in both cultures and tissues. In tissues, only rare IL-4 positive lymphoid cells or dendritic cells were identified. Thus, the study demonstrated that adequate amounts of IL-6 are required for an abundant plasma cell reaction, and that an additional source of IL-6 from histiocytes is essential for the formation of Castleman's disease-like changes in lymph nodes involved by HD. Furthermore, IL-4 is not likely to be responsible for the T-lymphocyte reaction in tissues, by a mechanism distinct from that in T-cell-rich B-cell lymphomas.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson U., Andersson J., Lindfors A., Wagner K., Möller G., Heusser C. H. Simultaneous production of interleukin 2, interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma by activated human blood lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jul;20(7):1591–1596. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Ganter U., Geiger T., Jacobshagen U., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Kishimoto T., Andus T., Acs G., Gerok W. Regulation of interleukin-6 expression in cultured human blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1134–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini J. N., Benson E. M. The role of human interleukin-6 in B-cell isotype regulation and differentiation. Cell Immunol. 1990 Jan;125(1):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosseloir A., Hooghe-Peters E. L., Heinen E., Cormann N., Kinet-Denoël C., Vanhaelst L., Simar L. Localization of interleukin 6 mRNA in human tonsils by in situ hybridization. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2379–2381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Bodine D. M., Dunbar C. E., Nienhuis A. W. Dysregulated interleukin 6 expression produces a syndrome resembling Castleman's disease in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):592–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI114749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrichter H., Heit W., Schaadt M., Kirchner H., Diehl V. Production of colony-stimulating factors by Hodgkin cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1983 Mar 15;31(3):269–274. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne P. V., Heit W. F., March C. J. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor purified from a Hodgkin's tumor cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 12;874(3):266–273. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Andus T., Geiger T., Trullenque R., Fabra R., Heinrich P. C. Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicco N. A., Lindemann A., Content J., Vandenbussche P., Lübbert M., Gauss J., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Inducible production of interleukin-6 by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):2049–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H. G., Gaedicke G., Lok M. S., Diehl V., Minowada J. Hodgkin's disease derived cell lines HDLM-2 and L-428: comparison of morphology, immunological and isoenzyme profiles. Leuk Res. 1986;10(5):487–500. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(86)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Lentz V. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor synergistically stimulate fibroblast IL-6 production and stabilize IL-6 messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Waage A., Faxvaag A., Shalaby M. R. Regulation of interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 production from T-cells: involvement of interleukin-1 beta and transforming growth factor-beta. Cell Immunol. 1990 Mar;126(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R. Soluble cytokine receptors: their role in immunoregulation. FASEB J. 1991 Aug;5(11):2567–2574. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.11.1868981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. I., Bostick-Bruton F., Sauder D. N., Scala G., Diehl V. Neoplastic cells obtained from Hodgkin's disease are potent stimulators of human primary mixed lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2666–2670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Freedman A. S., Rabinowe S. N., Segil J. M., Horowitz J., Rosen K., Whitman J. F., Nadler L. M. Interleukin 6 gene expression in normal and neoplastic B cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1512–1518. doi: 10.1172/JCI114046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Brock M., Taylor C. R., Lyons B. IL-4 regulates differentiation and proliferation of human precursor B cells. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Coulie P. G., Olive D., Van Snick J. Synergistic activation of human T cells by interleukin 1 and interleukin 6. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):653–656. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Hsu S. M. Identification of an Mr 70,000 antigen associated with Reed-Sternberg cells and interdigitating reticulum cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Jan 15;50(2):350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Hsu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin by cells of Hodgkin's neoplastic cell lines HDLM-1 and KM-H2. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):735–745. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Lin Y. C., Hsu S. M. Expression of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) in two Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) cell lines, HDLM-1 and KM-H2, and in H-RS cells in tissues. Int J Hematol. 1991 Aug;54(4):315–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Aberrant expression of T cell and B cell markers in myelocyte/monocyte/histiocyte-derived lymphoma and leukemia cells. Is the infrequent expression of T/B cell markers sufficient to establish a lymphoid origin for Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg cells? Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):203–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Lack of effect of colony-stimulating factors, interleukins, interferons, and tumor necrosis factor on the growth and differentiation of cultured Reed-Sternberg cells. Comparison with effects of phorbol ester and retinoic acid. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):181–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Phenotypes and phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human histiocytic lymphoma cell lines (U-937 and SU-DHL-1) and Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):223–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Krupen K., Lachman L. B. Heterogeneity of interleukin 1 production in cultured Reed-Sternberg cell lines HDLM-1, HDLM-1d, and KM-H2. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):33–38. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Pescovitz M. D., Hsu P. L. Monoclonal antibodies against SU-DHL-1 cells stain the neoplastic cells in true histiocytic lymphoma, malignant histiocytosis, and Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Xie S. S., Hsu P. L. Cultured Reed-Sternberg cells HDLM-1 and KM-H2 can be induced to become histiocytelike cells. H-RS cells are not derived from lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):353–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhao X., Chakraborty S., Liu Y. F., Whang-Peng J., Lok M. S., Fukuhara S. Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's cell lines HDLM, L-428, and KM-H2 are not actively replicating: lack of bromodeoxyuridine uptake by multinuclear cells in culture. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhao X. Expression of interleukin-1 in Reed-Sternberg cells and neoplastic cells from true histiocytic malignancies. Am J Pathol. 1986 Nov;125(2):221–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M. M., Markowitz A. B., Gutterman J. U., Knowles R. D., Snyder J. S., Kleinerman E. S. Effect of recombinant human interleukin 4 on human monocyte activity. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3154–3158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jücker M., Abts H., Li W., Schindler R., Merz H., Günther A., von Kalle C., Schaadt M., Diamantstein T., Feller A. C. Expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-6 receptor in Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1991 Jun 1;77(11):2413–2418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamesaki H., Fukuhara S., Tatsumi E., Uchino H., Yamabe H., Miwa H., Shirakawa S., Hatanaka M., Honjo T. Cytochemical, immunologic, chromosomal, and molecular genetic analysis of a novel cell line derived from Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Kuramoto A., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cytokines as autocrine growth factors in malignancies. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(4):905–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Zhang X. G., Jourdan M., Content J., Houssiau F., Aarden L., Piechaczyk M., Bataille R. Paracrine rather than autocrine regulation of myeloma-cell growth and differentiation by interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J. M., Vilcek J. Interleukin 6: a multifunctional cytokine regulating immune reactions and the acute phase protein response. Lab Invest. 1989 Dec;61(6):588–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran P. R., Ramsay A. D., Norton A. J., Roche W. R. Hodgkin's disease presenting with the histological features of Castleman's disease. Histopathology. 1991 Mar;18(3):249–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz H., Houssiau F. A., Orscheschek K., Renauld J. C., Fliedner A., Herin M., Noel H., Kadin M., Mueller-Hermelink H. K., Van Snick J. Interleukin-9 expression in human malignant lymphomas: unique association with Hodgkin's disease and large cell anaplastic lymphoma. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1311–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. A., Rezai A. R., Salazar-González J. F., Vander Meyden M., Stevens R. H., Logan D. M., Mitsuyasu R. T., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. AIDS Kaposi sarcoma-derived cells produce and respond to interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motro B., Itin A., Sachs L., Keshet E. Pattern of interleukin 6 gene expression in vivo suggests a role for this cytokine in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., Kadin M. E., Ansari A. A. Production of transforming growth factor-beta activity by Ki-1 positive lymphoma cells and analysis of its role in the regulation of Ki-1 positive lymphoma growth. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jun;131(3):569–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Braciak T. A., Hattori M., Lee F., Fey G. H. Structure of the rat interleukin 6 gene and its expression in macrophage-derived cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16072–16082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paietta E., Racevskis J., Stanley E. R., Andreeff M., Papenhausen P., Wiernik P. H. Expression of the macrophage growth factor, CSF-1 and its receptor c-fms by a Hodgkin's disease-derived cell line and its variants. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 1;50(7):2049–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M., Nansen L. Detection of interleukin-5 messenger RNA in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease with eosinophilia. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Waage A., Espevik T. Cytokine regulation of interleukin 6 production by human endothelial cells. Cell Immunol. 1989 Jul;121(2):372–382. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabibzadeh S. S., Poubouridis D., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Interleukin-6 immunoreactivity in human tumors. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):427–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Tanner J., Jones K. D., Revel M., Pike S. E. Identification of interleukin-6 as an autocrine growth factor for Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3033–3041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3033-3041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Wauters P., Van Snick J. Accessory factors involved in murine T cell activation. Distinct roles of interleukin 6, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolvekamp M. C., Marquet R. L. Interleukin-6: historical background, genetics and biological significance. Immunol Lett. 1990 Mar-Apr;24(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90028-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Nakanishi K., Matsui K., Hirose S., Hiroishi K., Tanaka T., Hada T., Hamaoka T., Higashino K. IL-5 up-regulates but IL-4 down-regulates IL-2R expression on a cloned B lymphoma line. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki K., Matsuda T., Nishimoto N., Kuritani T., Taeho L., Aozasa K., Nakahata T., Kawai H., Tagoh H., Komori T. Pathogenic significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2) in Castleman's disease. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1360–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]