Abstract
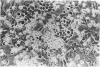
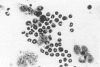
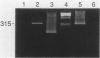
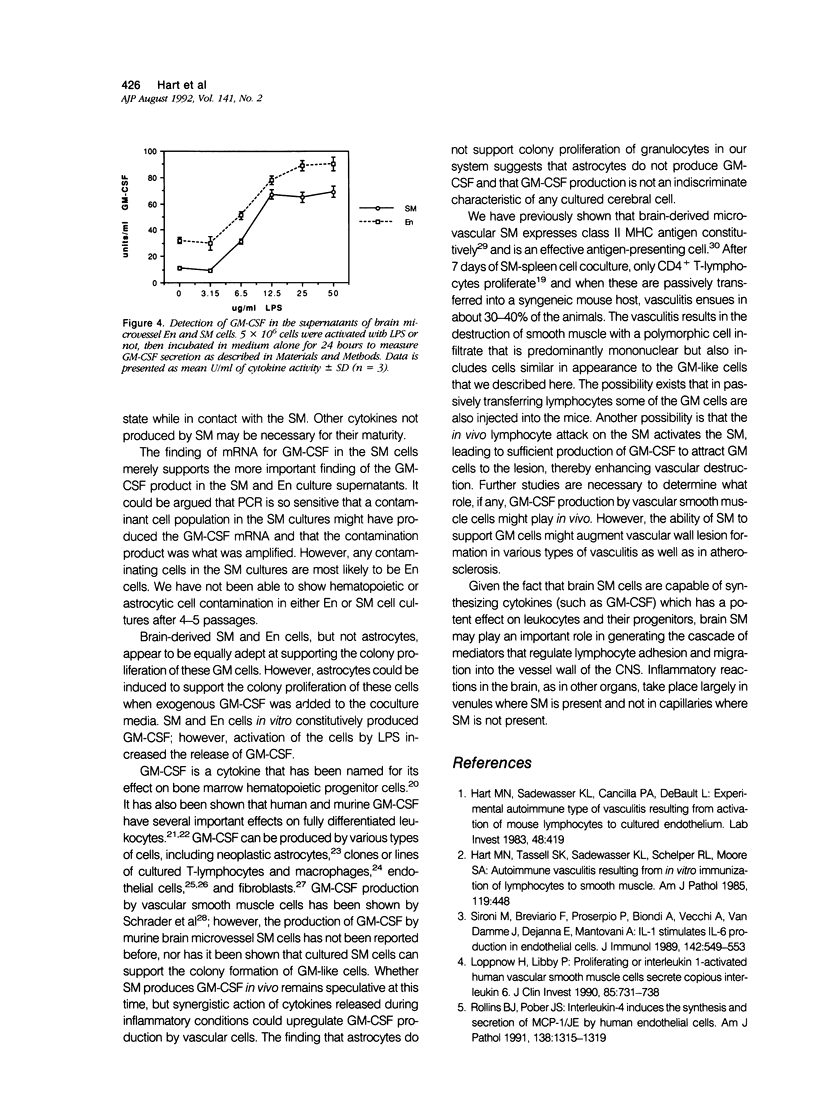
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is a potent stimulator of macrophages and neutrophils and plays a role in inflammatory diseases. In this article, we report that mouse brain-derived microvascular smooth muscle cells (SM) and endothelial cells (En) in coculture with splenocytes support the colony proliferation of immature granulocyte-macrophage-like (GM) cells. Unstimulated SM and En cells release GM-CSF as shown by ELISA assay and SM expresses mRNA for GM-CSF by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Stimulation of SM and En by a nonspecific activator (lipopolysaccharide) results in upregulation of GM-CSF production. GM colonies cannot be grown on cultured astrocytes or on extracellular matrix alone prepared from smooth muscle or endothelium. However, colonies form on the extracellular matrix and on astrocytes, either in the presence of SM- or En-conditioned medium or after the addition of recombinant GM-CSF. The GM cells are positive for nonspecific esterase, peroxidase, and MAC-1 markers but are negative for FC gamma receptors and for Thy 1.2, CD8, CD4, MHC class II, and Asialo GM1 markers. These observations emphasize the possibility for active participation of brain microvasculature SM and En in acute inflammatory reactions of the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broudy V. C., Kaushansky K., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Interleukin 1 stimulates human endothelial cells to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):464–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBault L. E., Henriquez E., Hart M. N., Cancilla P. A. Cerebral microvessels and derived cells in tissue culture: II. Establishment, identification, and preliminary characterization of an endothelial cell line. In Vitro. 1981 Jun;17(6):480–494. doi: 10.1007/BF02633509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry Z., Waldschmidt M. M., Moore S. A., Hart M. N. Antigen presentation by brain microvessel smooth muscle and endothelium. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Jun;28(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90041-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry Z., Waldschmidt M. M., Van Dyk L., Moore S. A., Hart M. N. Activation of CD4+ lymphocytes by syngeneic brain microvascular smooth muscle cells. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1099–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Delgado D., Vlodavsky I. Permissive effect of the extracellular matrix on cell proliferation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Metcalf D., Gough J., Grail D., Dunn A. R. Structure and expression of the mRNA for murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):645–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. N., Sadewasser K. L., Cancilla P. A., DeBault L. E. Experimental autoimmune type of vasculitis resulting from activation of mouse lymphocytes to cultured endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. N., Tassell S. K., Sadewasser K. L., Schelper R. L., Moore S. A. Autoimmune vasculitis resulting from in vitro immunization of lymphocytes to smooth muscle. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):448–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. N., Waldschmidt M. M., Hanley-Hyde J. M., Moore S. A., Kemp J. D., Schelper R. L. Brain microvascular smooth muscle expresses class II antigens. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2960–2963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Metcalf D., Battye F. L., Sewell W. A., Vadas M. Activation of granulocyte cytotoxic function by purified mouse colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2983–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Libby P. Proliferating or interleukin 1-activated human vascular smooth muscle cells secrete copious interleukin 6. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):731–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI114498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. A., Strauch A. R., Yoder E. J., Rubenstein P. A., Hart M. N. Cerebral microvascular smooth muscle in tissue culture. In Vitro. 1984 Jun;20(6):512–520. doi: 10.1007/BF02619625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesenberry P. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Vascular endothelium as a regulator of granulopoiesis: production of colony-stimulating activity by cultured human endothelial cells. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1060–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Pober J. S. Interleukin-4 induces the synthesis and secretion of MCP-1/JE by human endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1315–1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahagun G., Moore S. A., Fabry Z., Schelper R. L., Hart M. N. Purification of murine endothelial cell cultures by flow cytometry using fluorescein-labeled griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1227–1232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Kan M., McKeehan W. L. Opposite effects of monokines (interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor) on proliferation and heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor binding to human aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990 Feb;26(2):213–216. doi: 10.1007/BF02624115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Moyer C., Ziltener H. J., Reinisch C. L. Release of the cytokines colony-stimulating factor-1, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and IL-6 by cloned murine vascular smooth muscle cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3799–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sironi M., Breviario F., Proserpio P., Biondi A., Vecchi A., Van Damme J., Dejana E., Mantovani A. IL-1 stimulates IL-6 production in endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):549–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Gans P. J., McCarroll L. A. The synthesis and secretion of granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating activity (CSA) by isolated human monocytes: kinetics of the response to bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweardy D. J., Mott P. L., Glazer E. W. Monokine modulation of human astroglial cell production of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. I. Effects of IL-1 alpha and IL-beta. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2233–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucali J. R., Dinarello C. A., Oblon D. J., Gross M. A., Anderson L., Weiner R. S. Interleukin 1 stimulates fibroblasts to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating activity and prostaglandin E2. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1857–1863. doi: 10.1172/JCI112512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]