Abstract
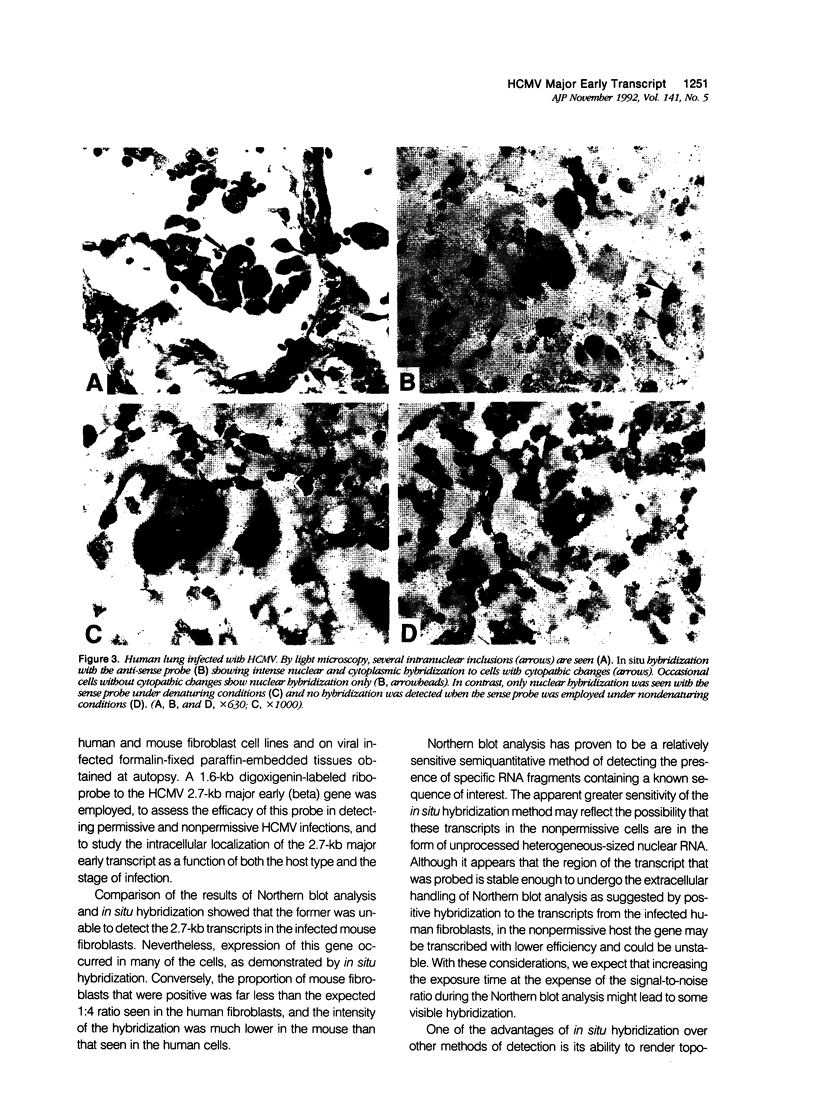
During the early phase of a human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection, the 2.7-kb early gene is by far the most abundantly transcribed RNA. Using strand-specific 32P or digoxigenin-labeled riboprobes derived from a subgenomic fragment of the HCMV Towne 2.7-kb early gene, we have performed Northern blot analysis and RNA in situ hybridization on human and mouse fibroblasts infected with HCMV and on 23 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of tissue obtained at autopsy. By Northern blot analysis, expression of the 2.7 kb early gene was found only in permissive infections. In contrast, specific hybridization was detected in both permissive and nonpermissive cells by RNA in situ hybridization. In nonpermissive cells, hybridization was weak and predominantly nuclear. In permissive cells, strong nuclear and cytoplasmic hybridization was noted. Specific hybridization to cells with and without cytopathic changes was detected with the anti-sense probe in CMV infected tissue obtained at autopsy. When the sense riboprobe was employed, no specific hybridization was found under nondenaturing conditions. These results suggest that in situ hybridization with a probe directed at the 2.7-kb early gene is an effective method of detecting both permissive and nonpermissive HCMV infections in different stages of infection and in localizing the expression of the major early gene in various cell types.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder R. F., Newman C., Hayward G. S., Biggar R., Melbye M., Kestens L., Van Marck E., Piot P., Gigase P., Wright P. B. Lack of association of cytomegalovirus with endemic African Kaposi's sarcoma. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):193–197. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler S. H., McDougall J. K. Comparison of restriction site polymorphisms among clinical isolates and laboratory strains of human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2179–2192. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehab F. F., Xiao X., Kan Y. W., Yen T. S. Detection of cytomegalovirus infection in paraffin-embedded tissue specimens with the polymerase chain reaction. Mod Pathol. 1989 Mar;2(2):75–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M., Blankenship M. L., Brown G. D., Kaplan A. S. Size and complexity of human cytomegalovirus DNA. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Correlation between stimulation of host cell DNA synthesis by human cytomegalovirus and lack of expression of a subset of early virus genes. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):274–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Nature of the block in the expression of some early virus genes in cells abortively infected with human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Post-transcriptional control of human cytomegalovirus gene expression. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling A., Keil G. M., Knust E., Koszinowski U. H. Molecular cloning and physical mapping of murine cytomegalovirus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):421–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.421-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fioretti A., Furukawa T., Santoli D., Plotkin S. A. Nonproductive infection of guinea pig cells with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.998-1003.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao M., Isom H. C. Characterization of the guinea pig cytomegalovirus genome by molecular cloning and physical mapping. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):436–447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.436-447.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. A cis-acting element within the 5' leader of a cytomegalovirus beta transcript determines kinetic class. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway P. J., Oram J. D., Downing R. G., Patel K. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: BamHI, EcoRI and PstI restriction endonuclease cleavage maps. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Raap A. K., van de Rijke F. M., Mulder A., Weening J. J., Zwaan F. E., The T. H., van der Ploeg M. Detection of cytomegalovirus antigens and DNA in tissues fixed in formaldehyde. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jul;42(7):749–754. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.7.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. A., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Analysis of cytomegalovirus genomes with restriction endonucleases Hin D III and EcoR-1. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1095–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1095-1105.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. Replicative forms of human cytomegalovirus DNA with joined termini are found in permissively infected human cells but not in non-permissive Balb/c-3T3 mouse cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):373–389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafemina R. L., Hayward G. S. Differences in cell-type-specific blocks to immediate early gene expression and DNA replication of human, simian and murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):355–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafemina R. L., Pizzorno M. C., Mosca J. D., Hayward G. S. Expression of the acidic nuclear immediate-early protein (IE1) of human cytomegalovirus in stable cell lines and its preferential association with metaphase chromosomes. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):584–600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. Analysis of the major transcripts encoded by the long repeat of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):711–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.711-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Hock L. J., Spector D. H. Construction of a cloned library of the EcoRI fragments from the human cytomegalovirus genome (strain AD169). J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):547–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.547-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Cloning of the human cytomegalovirus genome as endonuclease XbaI fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolber R. A., Lloyd R. V. Cytomegalovirus detection by nonisotopic in situ DNA hybridization and viral antigen immunostaining using a two-color technique. Hum Pathol. 1988 Jun;19(6):736–741. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Mann R. B., Epstein J. I., MacMahon E., Lee W. A., Charache P., Hayward S. D., Kurman R. J., Hayward G. S., Ambinder R. F. Abundant expression of EBER1 small nuclear RNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A morphologically distinctive target for detection of Epstein-Barr virus in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded carcinoma specimens. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1461–1469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]