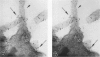
Abstract
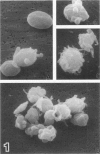
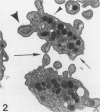
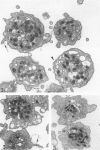
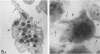
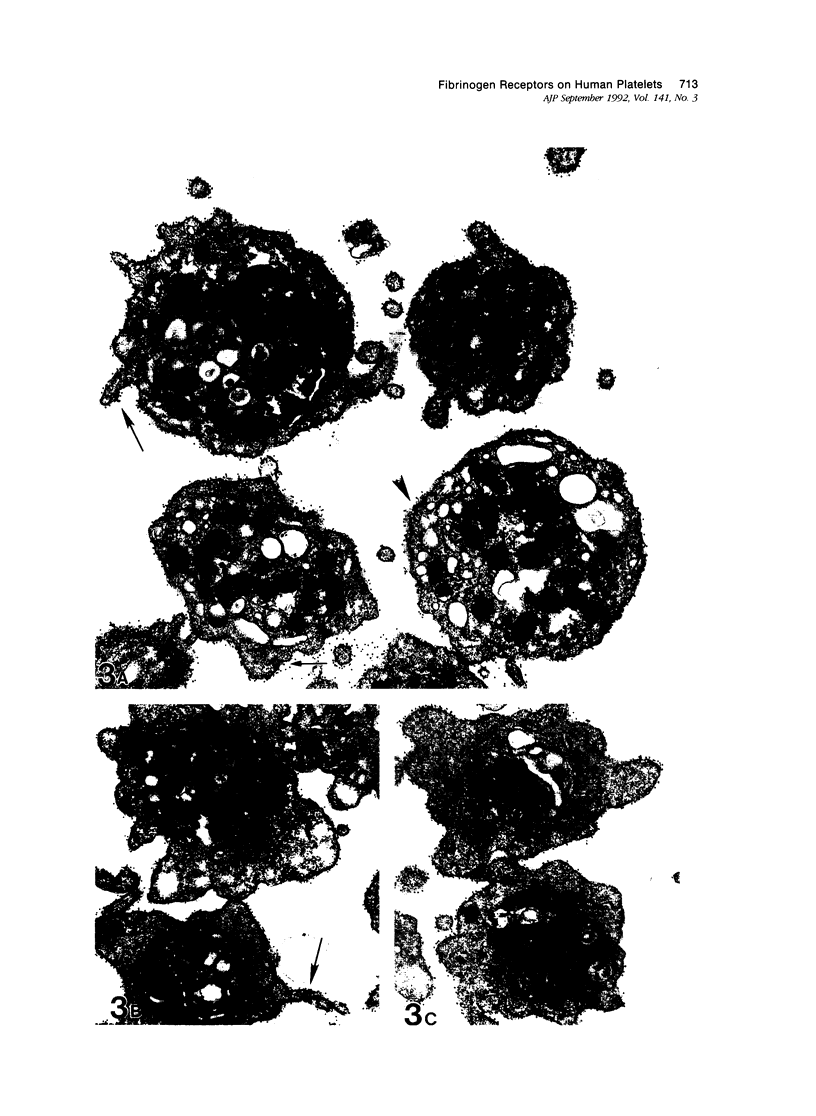
Platelet exposure to agonists results in rapid morphologic changes paralleled by fibrinogen binding and platelet aggregation. The current study used standardized stereology in conjunction with immunogold electron microscopy to correlate the initial morphologic changes with fibrinogen receptor localization on the surfaces of ADP-activated human platelets. A 45% increase in platelet circumference was observed after 3 seconds of activation (P = 0.001). Virtually all of this increase was due to a 13-fold increase in projection membrane, and the projections observed by stereo microscopy at this time were mostly blunt. Both blunt and long projections also accounted for the increase in platelet-platelet contacts at 10 seconds of activation. Immunogold electron microscopy using the monoclonal antibodies P2 and AP-2 against the fibrinogen receptor, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GP IIb/IIIa), showed relatively equivalent immunogold densities on projections compared with cell body during 30 seconds of activation. The activation-dependent anti-GP IIb/IIIa monoclonal antibody, 7E3, showed an immunogold density 37% greater on projections compared with cell body (P = 0.0001). Colocalization studies using 7E3 with a polyclonal antifibrinogen antibody showed bound fibrinogen in close proximity to the GP IIb/IIIa localized by 7E3 on projections. These studies support an important role for platelet projections during the earliest stages of fibrinogen binding and ADP-induced aggregation.
Full text
PDF


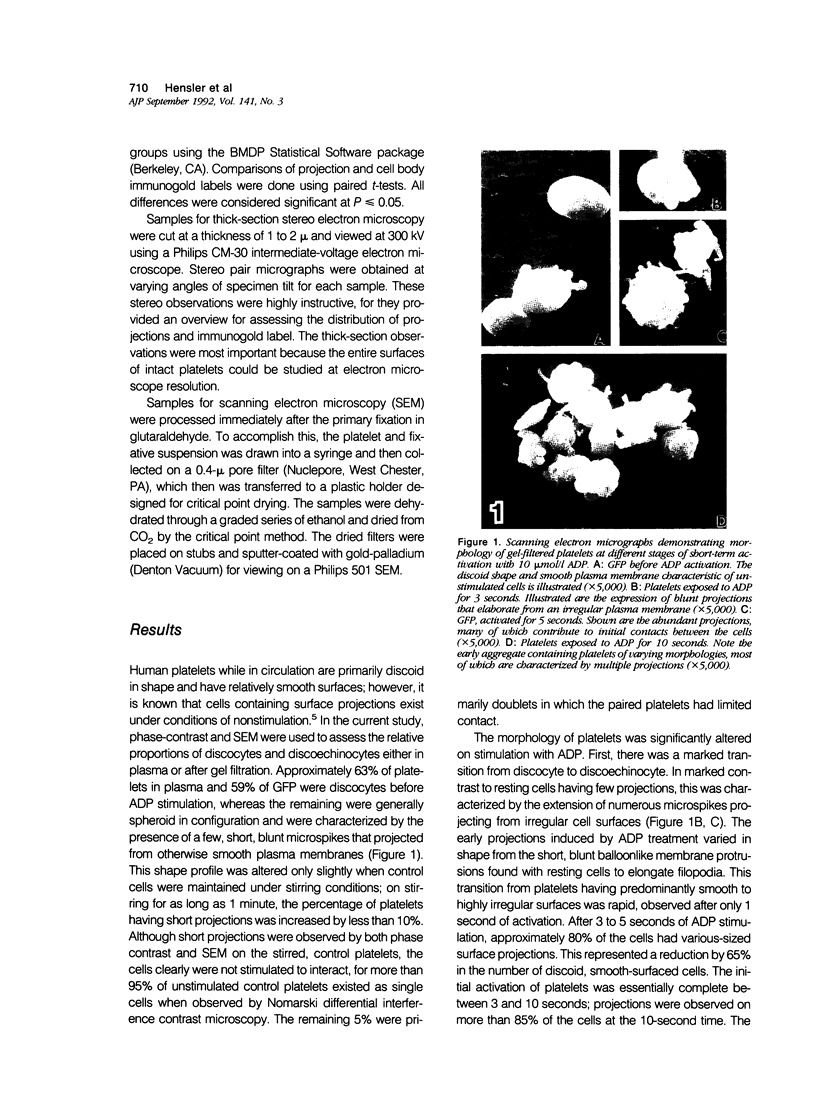




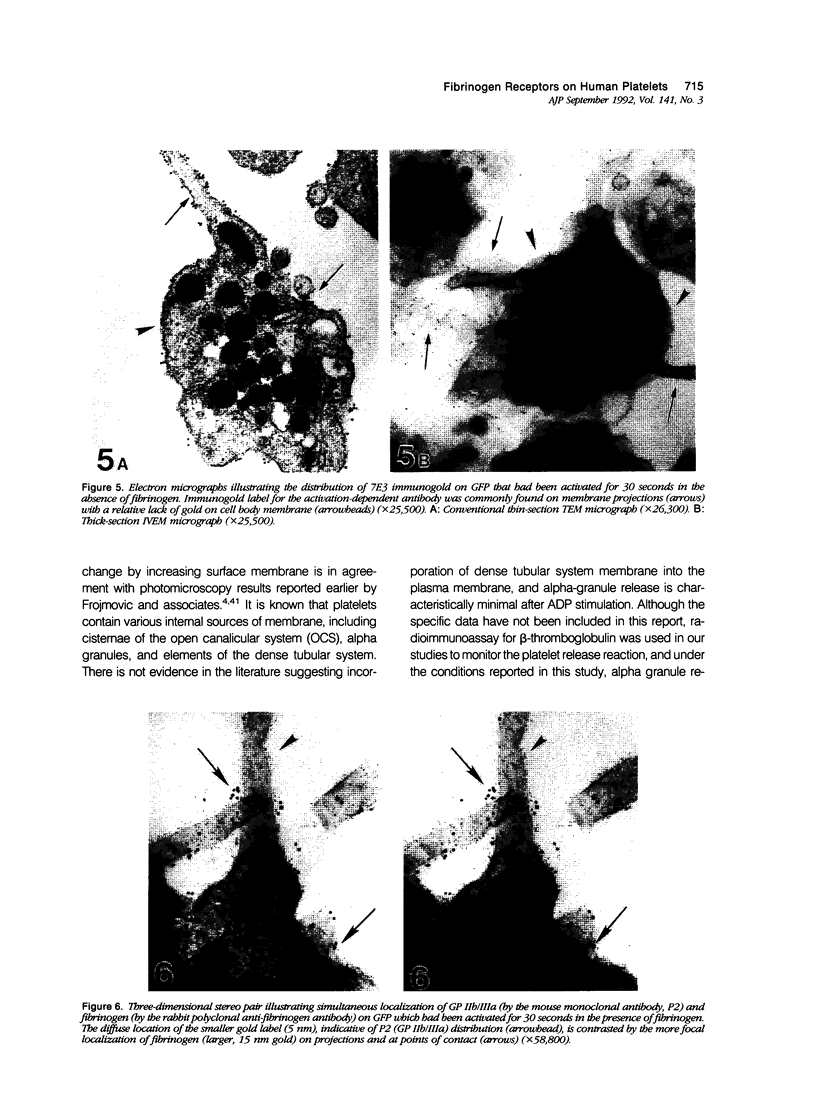




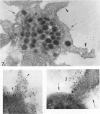
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Zacharski L. R., Widirstky S. T., Rosenstein R., Zaitlin L. M., Burgess D. R. Transformation and motility of human platelets: details of the shape change and release reaction observed by optical and electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):126–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asch A. S., Leung L. L., Polley M. J., Nachman R. L. Platelet membrane topography: colocalization of thrombospondin and fibrinogen with the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):926–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart M. I., Walsh R. T., Robinson J. A. A three-dimensional view of platelet responses to chemical stimuli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Oct 27;201:360–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI109597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P. F., Leung C. S., Shuman M. A. Human platelets and megakaryocytes contain alternately spliced glycoprotein IIb mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton-Gorius J., Lewis J. C., Guichard J., Kieffer N., Vainchenker W. Monoclonal antibodies specific for human platelet membrane glycoproteins bind to monocytes by focal absorption of platelet membrane fragments: an ultrastructural immunogold study. Leukemia. 1987 Feb;1(2):131–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Gerrard J. M., White J. G. Ultrastructure of clots during isometric contraction. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):775–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. Activation affects access to the platelet receptor for adhesive glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):451–456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., Leistikow E., White J. G. The fate of the open canalicular system in surface and suspension-activated platelets. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1983–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Milton J. G., Duchastel A. Microscopic measurements of platelet aggregation reveal a low ADP-dependent process distinct from turbidometrically measured aggregation. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jun;101(6):964–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Milton J. G. Human platelet size, shape, and related functions in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):185–261. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Milton J. G. Physical, chemical and functional changes following platelet activation in normal and "giant" platelets. Blood Cells. 1983;9(2):359–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M., Longmire K., van de Ven T. G. Long-range interactions in mammalian platelet aggregation. II. The role of platelet pseudopod number and length. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82378-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear A. R. Rapid reactions of platelets studied by a quenched-flow approach: aggregation kinetics. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Dec;100(6):866–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Nurden A. T., Phillips D. R. Molecular defects in interactions of platelets with the vessel wall. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 25;311(17):1084–1098. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410253111705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grouse L. H., Rao G. H., Weiss D. J., Perman V., White J. G. Surface-activated bovine platelets do not spread, they unfold. Am J Pathol. 1990 Feb;136(2):399–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R. A study of the kinetics of ADP-triggered platelet shape change. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):896–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourdille P., Benabdallah S., Belloc F., Nurden A. T. Distribution of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complexes in the surface membranes of human platelets and megakaryocytes. Br J Haematol. 1985 Jan;59(1):171–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg W. M., McEver R. P., Phillips D. R., Shuman M. A., Bainton D. F. The platelet fibrinogen receptor: an immunogold-surface replica study of agonist-induced ligand binding and receptor clustering. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1655–1663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. W., Jennings L. K. Heterogeneity of fibrinogen receptor expression on platelets activated in normal plasma with ADP: analysis by flow cytometry. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jul;72(3):407–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Pidard D., Rosa J. P., Nurden A. T. The formation of Ca++-dependent complexes of platelet membrane glycoproteins IIb and IIIa in solution as determined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Hantgan R. R., Stevenson S. C., Thornburg T., Kieffer N., Guichard J., Breton-Gorius J. Fibrinogen and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa localization during platelet adhesion. Localization to the granulomere and at sites of platelet interaction. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):239–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Johnson C., Ramsamooj P., Hantgan R. R. Orientation and specificity of fibrin protofibril binding to ADP-stimulated platelets. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1992–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., White M. S., Prater T., Taylor R. G., Davis K. S. Ultrastructural analysis of platelets in nonhuman primates. III. Stereo microscopy of microtubules during platelet adhesion and the release reaction. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Dec;37(3):370–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Albrecht R. M. Redistribution of the fibrinogen receptor of human platelets after surface activation. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):822–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5357–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh S. A., Jones G. E. Microspike function in cell aggregation. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;28(2):278–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. L., McGregor L., Bauer A. S., Catimel B., Brochier J., Dechavanne M., Clemetson K. J. Identification of two distinct regions within the binding sites for fibrinogen and fibronectin on the IIb-IIIa human platelet membrane glycoprotein complex by monoclonal antibodies P2 and P4. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton J. G., Frojmovic M. M. Adrenaline and adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation require shape change. Importance of pseudopods. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Nov;104(5):805–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton J. G., Frojmovic M. M. Turbidometric evaluations of platelet activation: relative contributions of measured shape change, volume, and early aggregation. J Pharmacol Methods. 1983 Apr;9(2):101–115. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(83)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niiya K., Hodson E., Bader R., Byers-Ward V., Koziol J. A., Plow E. F., Ruggeri Z. M. Increased surface expression of the membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex induced by platelet activation. Relationship to the binding of fibrinogen and platelet aggregation. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):475–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. A., Albrecht R. M. Colloidal gold labelling of fibrinogen receptors in epinephrine- and ADP-activated platelet suspensions. Scanning Microsc. 1987 Jun;1(2):745–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parise L. V., Phillips D. R. Reconstitution of the purified platelet fibrinogen receptor. Fibrinogen binding properties of the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10698–10707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Zucker M. B. Fibrinogen receptor exposure and aggregation of human blood platelets produced by ADP and chilling. Blood. 1981 Apr;57(4):663–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., Egan J. J., Johnson M. M. Correlation between fibrinogen binding to human platelets and platelet aggregability. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidard D., Montgomery R. R., Bennett J. S., Kunicki T. J. Interaction of AP-2, a monoclonal antibody specific for the human platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex, with intact platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12582–12586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G. A. Induction of the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by epinephrine and the combination of epinephrine and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10971–10977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley M. J., Leung L. L., Clark F. Y., Nachman R. L. Thrombin-induced platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb and IIIa complex formation. An electron microscope study. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1058–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoso S., Zimmermann U., Neppert J., Mueller-Eckhardt C. Receptor patching and capping of platelet membranes induced by monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):343–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Hoxie J. A., Cunningham M., Brass L. F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11107–11114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A., Flaherty L., Brass L. F. Expression of fibrinogen receptors during activation and subsequent desensitization of human platelets by epinephrine. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1224–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wencel-Drake J. D., Plow E. F., Kunicki T. J., Woods V. L., Keller D. M., Ginsberg M. H. Localization of internal pools of membrane glycoproteins involved in platelet adhesive responses. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):324–334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Krumwiede M. Further studies of the secretory pathway in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1196–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods V. L., Jr, Wolff L. E., Keller D. M. Resting platelets contain a substantial centrally located pool of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex which may be accessible to some but not other extracellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15242–15251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]