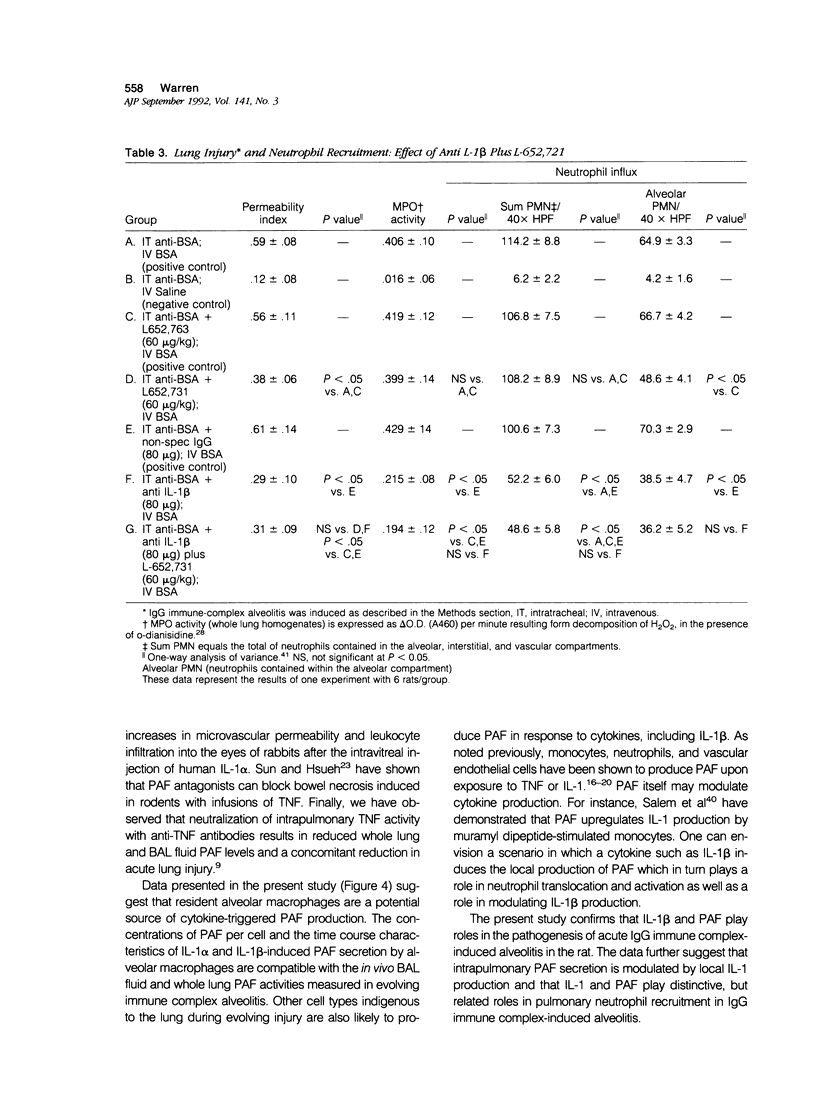
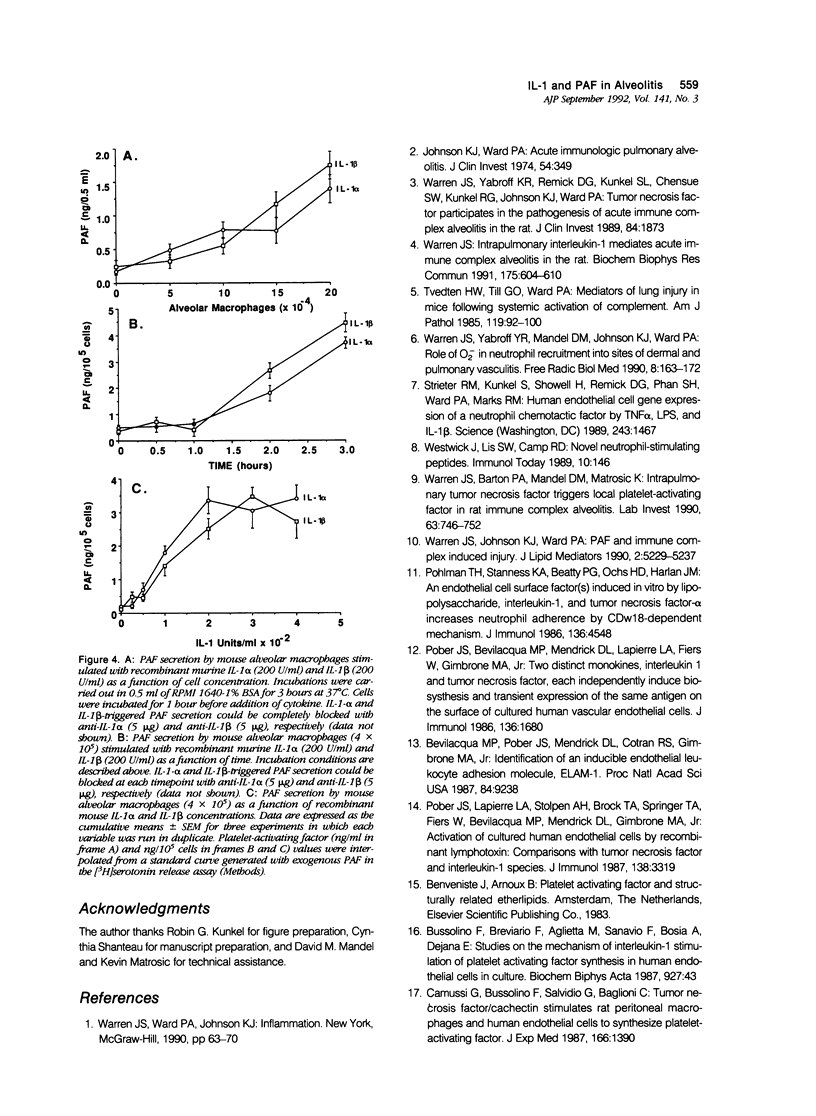
Abstract
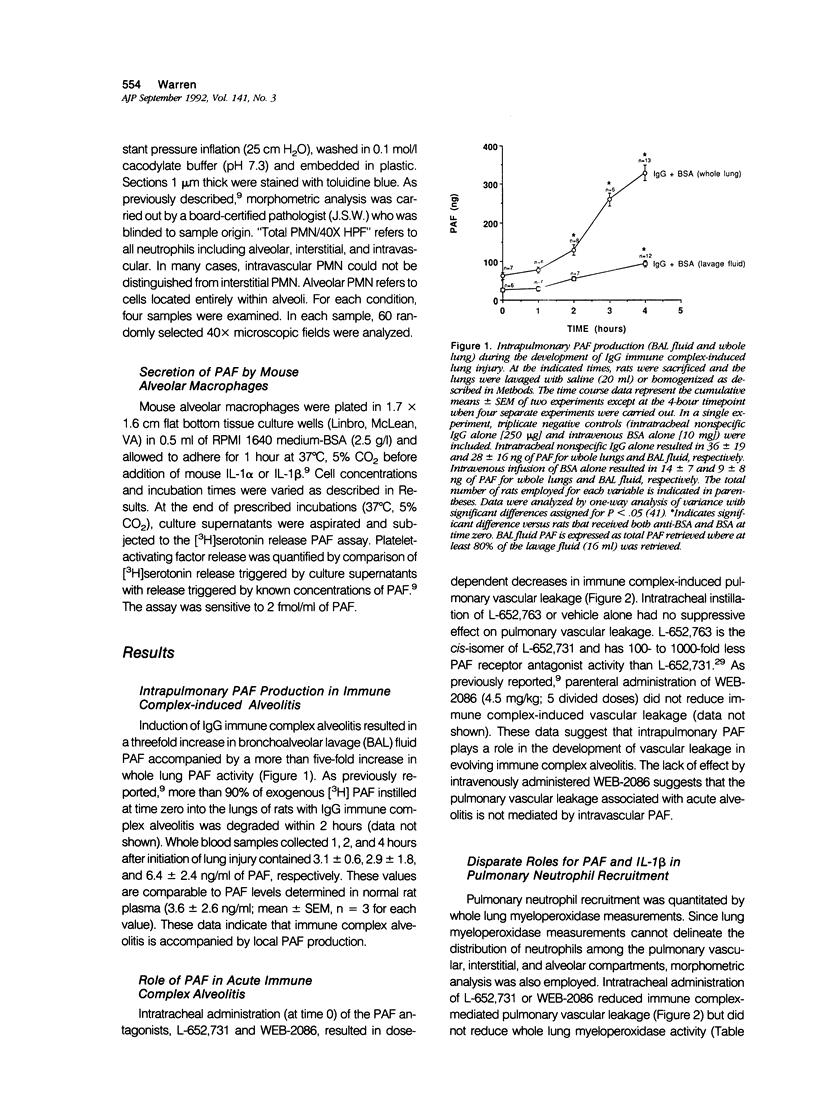
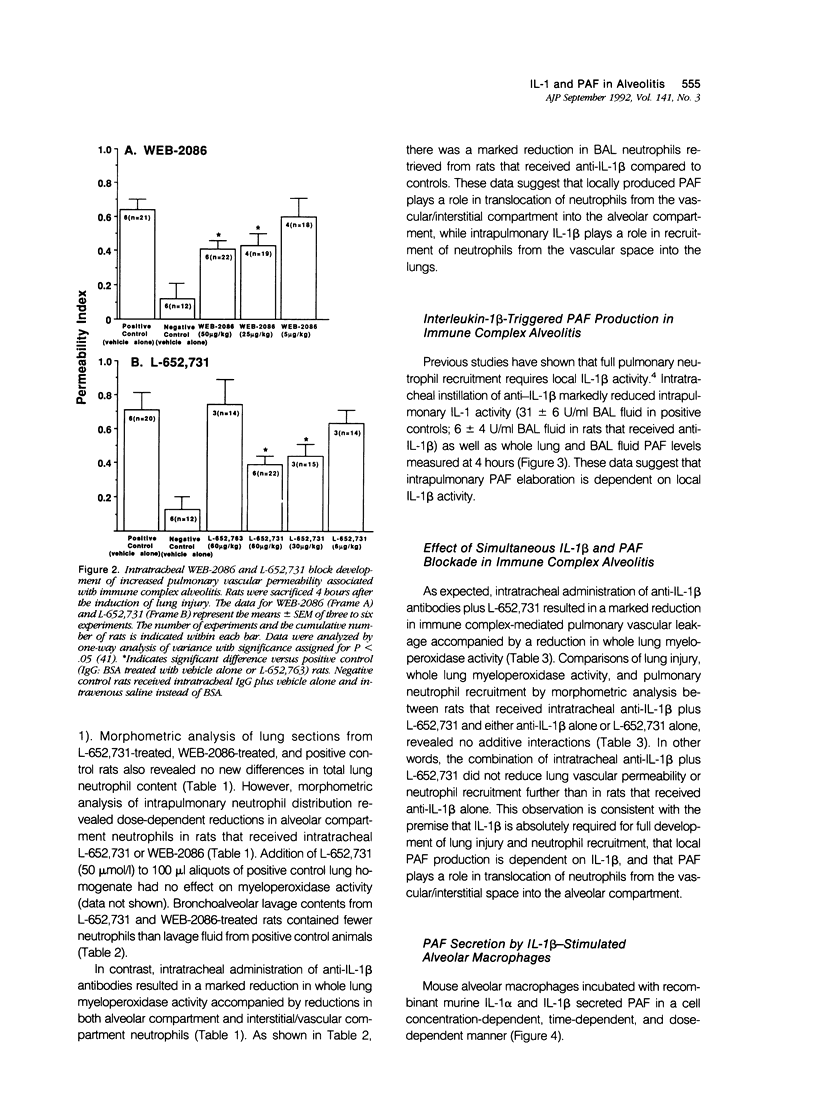
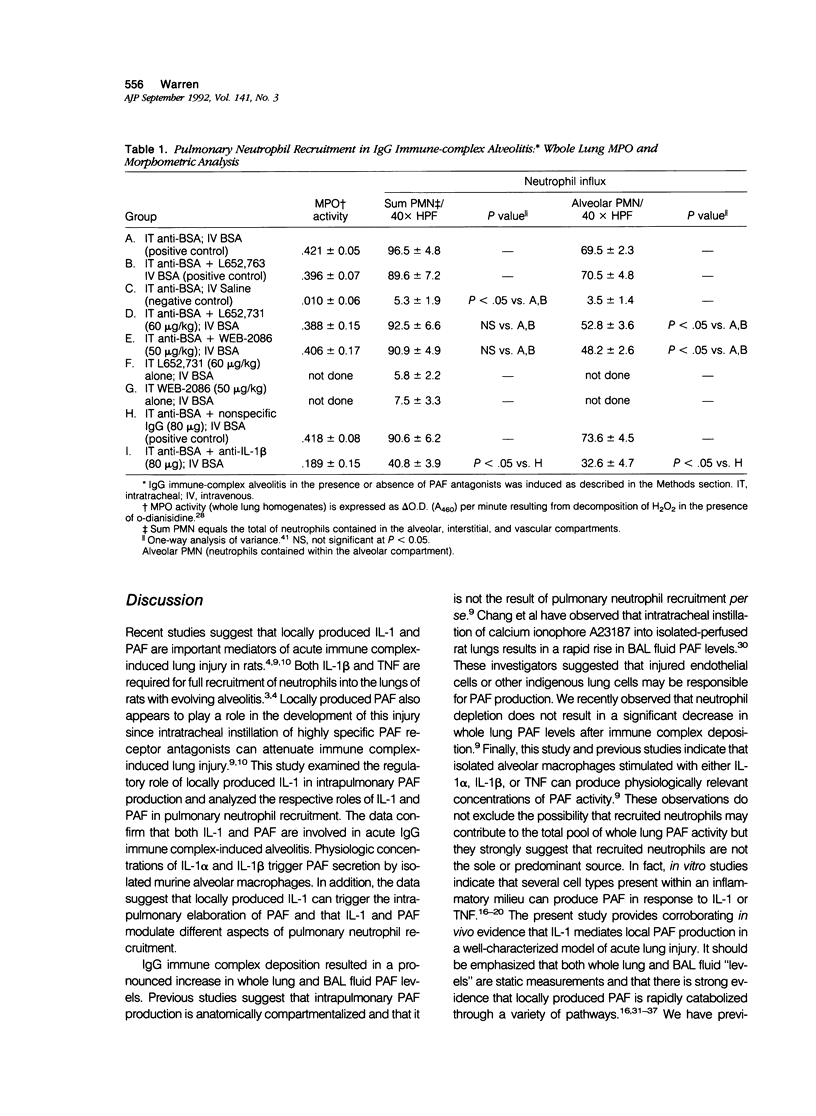
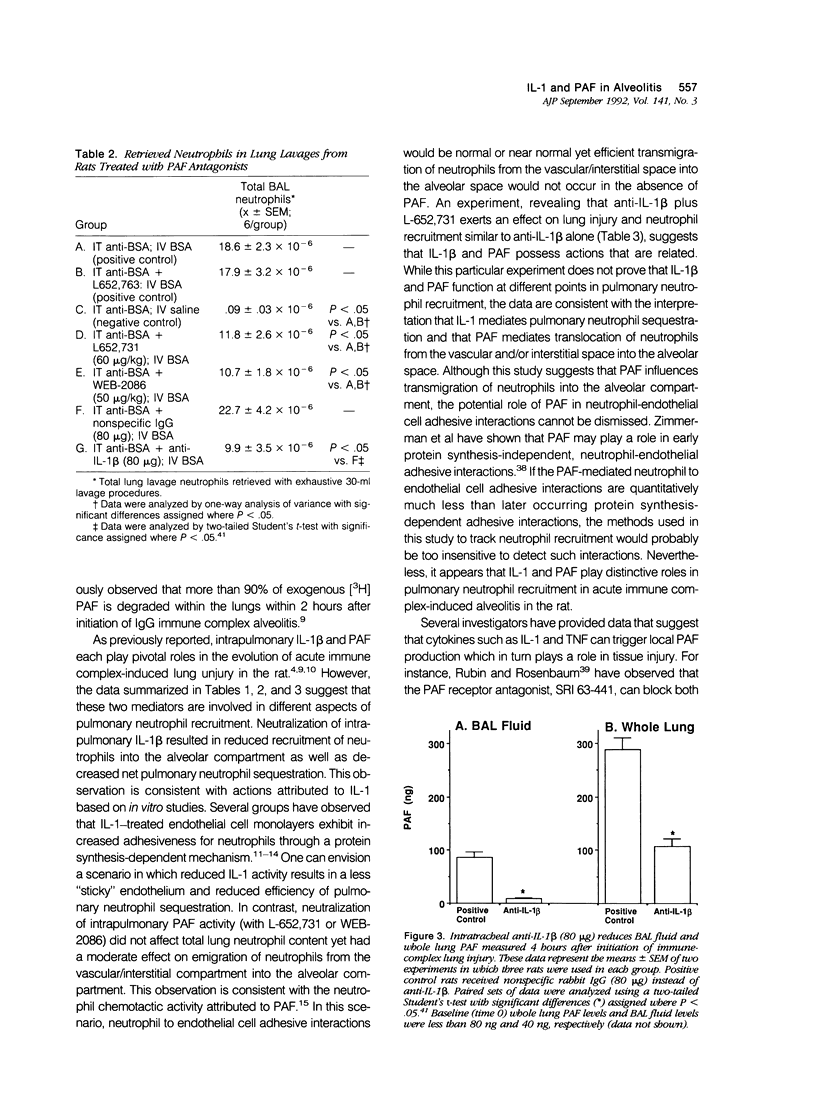
Intrapulmonary interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) participates in the pathogenesis of acute IgG immune-complex alveolitis through a mechanism involving neutrophil recruitment. We have examined the relationship between intrapulmonary IL-1 beta and locally produced platelet-activating factor (PAF) in the development of acute alveolitis. Instillation of IgG anti-bovine albumin into the lungs of rats, followed immediately by intravenous infusion of bovine serum albumin (BSA), resulted in acute neutrophil-mediated lung injury. Development of IgG immune-complex lung injury was accompanied by three- and five-fold increases in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid and whole lung PAF levels, respectively. Intratracheal administration of the PAF antagonists, WEB-2086 (Boehringer) or L-652,731 (Merck, Sharpe, and Dohme, Rahway, NJ), reduced pulmonary vascular leakage. Neutralization of intrapulmonary IL-1 activity with anti-IL-1 beta antibodies reduced pulmonary vascular permeability and whole lung PAF levels. Morphometric analysis and whole lung myeloperoxidase measurements revealed a differential effect between the PAF antagonists and anti-IL-1 beta with respect to pulmonary neutrophil recruitment. Intratracheal instillation of anti-IL-1 beta retarded net pulmonary neutrophil recruitment while the PAF antagonists retarded migration of neutrophils from the interstitial/vascular compartments into the alveolar compartment. Intratracheal instillation of anti-IL-1 beta plus L-652,731 resulted in reduction in lung vascular permeability and retarded net pulmonary neutrophil recruitment. No additive effect was observed. Stimulation of isolated mouse alveolar macrophages with recombinant murine IL-1 beta or IL-1 alpha resulted in rapid, dose-dependent, and cell concentration-dependent increases in PAF secretion. These data suggest that intrapulmonary IL-1 beta amplifies local PAF production and that IL-1 beta and PAF modulate different aspects of pulmonary neutrophil recruitment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Mendrick D. L., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Spector A. A., Kaduce T. L., Lee T. C., Snyder F. Metabolism of platelet activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) and 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol by human endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 21;876(3):373–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Breviario F., Aglietta M., Sanavio F., Bosia A., Dejana E. Studies on the mechanism of interleukin 1 stimulation of platelet activating factor synthesis in human endothelial cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 19;927(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Camussi G., Baglioni C. Synthesis and release of platelet-activating factor by human vascular endothelial cells treated with tumor necrosis factor or interleukin 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11856–11861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Bussolino F., Salvidio G., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin stimulates peritoneal macrophages, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, and vascular endothelial cells to synthesize and release platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1390–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., O'Flaherty J. T., Ellis J. M., Swendsen C. L., Wykle R. L. Metabolic fate of platelet-activating factor in neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6357–6361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., O'Flaherty J. T., Ellis J. M., Swendsen C. L., Wykle R. L. Selective acylation of lyso platelet activating factor by arachidonate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7268–7271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel M., Undem B. J., Chilton F. H. Release of platelet-activating factor and the metabolism of leukotriene B4 by the human neutrophil when studied in a cell superfusion model. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3659–3665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Breviario F., Erroi A., Bussolino F., Mussoni L., Gramse M., Pintucci G., Casali B., Dinarello C. A., Van Damme J. Modulation of endothelial cell functions by different molecular species of interleukin 1. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):695–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandel K. E., Farr R. S., Wanderer A. A., Eisenstadt T. C., Wasserman S. I. Association of platelet-activating factor with primary acquired cold urticaria. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 15;313(7):405–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508153130702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haroldsen P. E., Voelkel N. F., Henson J. E., Henson P. M., Murphy R. C. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor in isolated perfused rat lung. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1860–1867. doi: 10.1172/JCI113028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Activation and desensitization of platelets by platelet-activating factor (PAF) derived from IgE-sensitized basophils. I. Characteristics of the secretory response. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):937–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Zanolari B., Schwartzman N. A., Hong S. R. Intracellular control of human neutrophil secretion. I. C5a-induced stimulus-specific desensitization and the effects of cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Patton G. M., Pritzker C. R., Deykin D. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor in human platelets. Transacylase-mediated synthesis of 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13316–13320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. M., Lotner G. Z., Betz S. J., Henson P. M. The release of a platelet-activating factor by stimulated rabbit neutrophils. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1219–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Two distinct monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, each independently induce biosynthesis and transient expression of the same antigen on the surface of cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1680–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Lapierre L. A., Stolpen A. H., Brock T. A., Springer T. A., Fiers W., Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Activation of cultured human endothelial cells by recombinant lymphotoxin: comparison with tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 species. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3319–3324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Stanness K. A., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. An endothelial cell surface factor(s) induced in vitro by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases neutrophil adherence by a CDw18-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4548–4553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Snyder F. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor by rat alveolar macrophages: lyso-PAF as an obligatory intermediate in the formation of alkylarachidonoyl glycerophosphocholine species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 23;837(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. M., Rosenbaum J. T. A platelet-activating factor antagonist inhibits interleukin 1-induced inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90704-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem P., Deryckx S., Dulioust A., Vivier E., Denizot Y., Damais C., Dinarello C. A., Thomas Y. Immunoregulatory functions of paf-acether. IV. Enhancement of IL-1 production by muramyl dipeptide-stimulated monocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1338–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Bowel necrosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in rats is mediated by platelet-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1328–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI113459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tvedten H. W., Till G. O., Ward P. A. Mediators of lung injury in mice following systemic activation of complement. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):92–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Epstein L. B. Biphasic platelet-activating factor synthesis by human monocytes stimulated with IL-1-beta, tumor necrosis factor, or IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3945–3950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S., Barton P. A., Mandel D. M., Matrosic K. Intrapulmonary tumor necrosis factor triggers local platelet-activating factor production in rat immune complex alveolitis. Lab Invest. 1990 Dec;63(6):746–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S. Intrapulmonary interleukin 1 mediates acute immune complex alveolitis in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):604–610. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91608-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S., Yabroff K. R., Mandel D. M., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Role of O2- in neutrophil recruitment into sites of dermal and pulmonary vasculitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;8(2):163–172. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S., Yabroff K. R., Remick D. G., Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Kunkel R. G., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Tumor necrosis factor participates in the pathogenesis of acute immune complex alveolitis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1873–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI114374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwick J., Li S. W., Camp R. D. Novel neutrophil-stimulating peptides. Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):146–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M. Thrombin stimulates the adherence of neutrophils to human endothelial cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2235–2246. doi: 10.1172/JCI112232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


